2002 Pacific hurricane season
| 2002 Pacific hurricane season | |
|---|---|
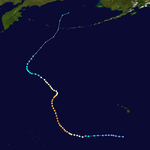
 Season summary map | |
| Seasonal boundaries | |
| First system formed | May 24, 2002 |
| Last system dissipated | November 16, 2002 |
| Strongest storm | |
| Name | Kenna |
| • Maximum winds | 165 mph (270 km/h) (1-minute sustained) |
| • Lowest pressure | 913 mbar (hPa; 26.96 inHg) |
| Seasonal statistics | |
| Total depressions | 19 |
| Total storms | 15 |
| Hurricanes | 8 |
| Major hurricanes (Cat. 3+) | 6 |
| Total fatalities | 7 total |
| Total damage | $101.02 million (2002 USD) |
| Related articles | |
The 2002 Pacific hurricane season was a near–average season which produced fifteen named storms. Eight hurricanes formed, including a record-equaling three Category 5 hurricanes, a record it shares with the 1994 and 2018 seasons. It was also a near-average season in terms of accumulated cyclone energy (ACE), having an ACE of 125. The season officially began on May 15, 2002 in the East Pacific Ocean, and on June 1, 2002 in the Central Pacific; both ended on November 30. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclone formation occurs in these regions of the Pacific. The first system of the 2002 season, Hurricane Alma, formed on May 24, and the last, Tropical Depression Sixteen-E, dissipated on November 16.
The strongest hurricane of the season, Kenna, formed on October 22 and peaked as a Category 5 hurricane two days later. Land impact was relatively significant. Kenna made landfall near Puerto Vallarta, located in the Mexican state of Jalisco on October 25, killing four people. Kenna was, at the time, the second-most powerful hurricane to ever strike the western coast of Mexico, hitting with winds of 140 mph (220 km/h), as well as the strongest landfall in terms of windspeed until Hurricane Patricia in 2015. Elsewhere, Tropical Storm Julio made landfall in Mexico, and Tropical Storm Boris dumped torrential rain along the Mexican coast, despite remaining offshore. Hurricanes Elida and Hernan also reached Category 5 intensity, but neither caused any damage. Damage across the basin reached $101.23 million (2002 USD), while 7 people were killed by Julio and Kenna.
Seasonal summary

The season officially began on May 15 in Eastern Pacific and on June 1 in Central Pacific; both ended on November 30.[1] In the eastern Pacific, the season saw below average activity in terms of the number of total storms and hurricanes, but about average activity in terms of major hurricanes.[2][3] There were 16 tropical storms in the eastern Pacific Ocean in the season. Of those, eight became hurricanes, of which six became major hurricanes by reaching Category 3 or higher on the Saffir–Simpson scale. Three reached Category 5 intensity,[4] equaling the record set in 1994, and later equaled in 2018.[4][5] Additionally, four tropical depressions formed and dissipated before reaching the intensity of a tropical storm.[6] Three tropical storms formed in the Central Pacific Hurricane Center's area of responsibility, where overall activity was near normal. Two of the storms strengthened into hurricanes, with one of them intensifying into a major hurricane. Two additional systems tracked into the area from the eastern Pacific.[7]
Activity commenced on May 24, with the formation of the first tropical depression, which became Hurricane Alma, and intensified into a rare May major hurricane. June was extremely quiet with only one named storm developing, Tropical Storm Boris. Though it remained offshore, Boris was able to dump torrential rain along the coast of southwestern Mexico.[8] There were two hurricanes and one tropical storm in July. Among them, Hurricane Elida underwent one of the fastest rates of rapid intensification on record for an eastern Pacific hurricane. It went from a 30 mph (45 km/h) depression to an 80 mph (130 km/h) hurricane in 30 hours, then proceed to intensify into a 160 mph (260 km/h) Category 5 hurricane during the 24 hours that followed.[9]
August was active with five systems developing, of which three became hurricanes. Fausto peaked as a strong Category 4 hurricane in the eastern Pacific, before crossing into the central Pacific as a depression. Then, after degenerating into a remnant low well northeast of Hawaii Fausto regenerated into a weak tropical storm at an unusually high latitude. Late that month, Ele became the first of two central Pacific hurricanes to cross the International Date Line into the western Pacific where they became typhoons; the other was Huko in late October.[7] Hernan closed out the month; forming on August 30, it peaked at Category 5 strength two days later, far from land. Activity decreased appreciably in September and October as most of the storms remained weak and were short-lived. The exception was Kenna, which formed on October 22 and peaked as a Category 5 hurricane two days later; it was the strongest hurricane of the season, Kenna was one of two landfalling systems this season, the other being Tropical Storm Julio in September. All casualties and most of the damage incurred during the season was caused by Kenna.[2] No named storms formed during the final few weeks of the season, which effectively came to a close on November 16 when Tropical Depression Sixteen-E, dissipated.
A moderately strong El Niño, ongoing during the season, may have contributed to the disproportionate number of major hurricanes,[10] as well as reduced activity in the Atlantic.[11] Also of note was an unusual gap in storm formation during the first three weeks of August in this season,[4] historically a prime period for tropical cyclone formation.[12]
Systems
Hurricane Alma
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | May 24 – June 1 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 115 mph (185 km/h) (1-min); 960 mbar (hPa) |
A complex formation involving a tropical wave and a gale over the Gulf of Tehuantepec formed Tropical Depression One-E on May 24. It slowly strengthened into the first tropical storm of the season two days later. Alma then turned north, moving near the edge of a subtropical ridge over Mexico. Its rate of intensification picked up, and Alma became a hurricane on May 28. Alma reached Category 3 intensity on May 30. The hurricane began to weaken almost immediately thereafter under the influence of wind shear and cool water. Alma rapidly fell apart, and degenerated into a weak low-pressure area by June 1.[13]
Alma did not impact land.[13]
Tropical Storm Boris
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 8 – June 11 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 60 mph (95 km/h) (1-min); 997 mbar (hPa) |
On June 8, an area of disturbed weather that had absorbed a tropical wave spawned Tropical Depression Two-E. It became a tropical storm the next day. After peaking on June 9, with a pressure of 997 mb, steering currents collapsed and Boris stalled out in the ocean between two ridges of high pressure. Shear increased, and the cyclone weakened to a depression on June 10. The next day, Boris degenerated into a remnant low. The remnant drifted east and then southeast before dissipating on June 12.[14]
Boris dumped heavy rains on sections of the Mexican coast. The maximum amount was 10.60 inches (269 mm) at San Felipe Usila.[8] These rains damaged several homes at an unspecified location. In addition, rainfall damaged several homes in Tequila, Jalisco, but the National Hurricane Center believes that Boris likely did not cause the rain. No deaths were attributed to this storm.[14]
Tropical Depression Three-E
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | June 27 – June 29 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min); 1006 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave that crossed Central America organized and developed into a tropical depression on June 27.[15] Contrary to forecasts,[16] the depression did not strengthen further because of strong wind shear. By June 29, the depression had become a remnant low, which was observed as a swirl of clouds for a few more days before dissipating.[15]
Tropical Storm Cristina
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 9 – July 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 mph (100 km/h) (1-min); 994 mbar (hPa) |
An area of disturbed weather near Panama drifted to a location south of Puerto Ángel, Oaxaca, and organized into Tropical Depression Four-E on July 9. It moved westward through a hostile environment of strong shear. The wind shear disrupted the cyclone's convection and weakened its circulation. Despite the shear, the depression strengthened into a tropical storm early on July 12 and was named Cristina. This broke down the steering ridge, and Cristina turned to the north and peaked on July 14. Then, the wind shear won out and Cristina quickly weakened. Cristina dissipated into a swirl of clouds on July 16, without ever threatening land. No impact was reported.[17]
Hurricane Douglas
| Category 2 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 20 – July 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 105 mph (165 km/h) (1-min); 970 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave exited the west coast of Africa on July 8 and crossed the Atlantic without much development. In the Caribbean, showers increased, but wind shear prevented development. The wave crossed into the eastern Pacific on July 16, and wind shear decreased to allow the convection to organize. Tropical Depression Five-E developed on July 20 about 395 miles (636 km) south of Manzanillo, Mexico.[18] At that time, gradual strengthening was anticipated.[19] The depression quickly intensified into Tropical Storm Douglas.[18] Around that time, most of the deep convection was situated south of the atmospheric circulation.[20] Initially expected to become a hurricane only briefly,[21] late on July 21, the NHC reported that Douglas had become a hurricane.[22] Upon becoming a hurricane, Douglas was situated in low wind shear environment; however, Hurricane Douglas was expected to reach cold waters in 36 hours, and thus was not predicted to become a major hurricane.[23] Douglas became a Category 2 hurricane on July 22, reaching peak winds of 105 miles per hour (170 km/h).[24] Douglas held this intensity for 18 hours as it traveled westward.[18] When Douglas weakened from its peak intensity, it had an organized cloud pattern, but the thunderstorm activity was weakening, typical of most Pacific hurricanes that reach cooler waters.[25] The weakening briefly stopped after Douglas went through an eyewall replacement cycle,[26] but Douglas was downgraded to a tropical storm late on July 24 as the storm only had a small area of deep convection left.[18] Tropical storm Douglas briefly stopped weakening as convection increased, only to fade away again hours later.[27] The storm was downgraded to a tropical depression early on July 26,[18] and later that day degenerated into a remnant low-pressure area.[28] The remnant low dissipated the next day.[18]
Hurricane Elida
| Category 5 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | July 23 – July 30 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 160 mph (260 km/h) (1-min); 921 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave generated into Tropical Depression Six-E on July 23. It moved westward and reached storm strength 12 hours after it formed. Elida rapidly deepened, developing a pinhole eye, and becoming a hurricane on July 24 and further reaching major hurricane intensity six hours later. Elida's rapid intensification continued, becoming a Category 5 hurricane for six hours on July 25.[9] Despite moving over warm waters, Elida began to weaken when it underwent an eyewall replacement cycle. By the cycle was completed, the system had moved into cooler water and so has unable to re-strengthen. Elida fell to a tropical storm on July 27, then degenerated into a remnant low and turned to the northeast. The remnant dissipated over the open ocean about 535 mi (860 km) west of Los Angeles.[9]
Elida had no direct impact on land. However, it did send heavy waves along the shores of Mexico. No one was killed and no damage was reported.[9]
Tropical Depression Seven-E
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 6 – August 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min); 1008 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave that had reached the Eastern Pacific from Africa was first spotted on July 23. The wave continued westward with little development occurring until August 3, when convection increased. After additional slow organization, the wave was classified as Tropical Depression Seven-E on August 6 near the tip of Baja California. The system did not strengthen much, and development was halted when wind shear destroyed the system on August 8. The depression never came near land and hence no one was killed or injured.[29] Like Tropical Depression Three-E, this cyclone was forecast to reach tropical storm intensity, but it never did.[30]
Hurricane Fausto
| Category 4 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 21 – September 3 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 145 mph (230 km/h) (1-min); 936 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave exited the west coast of Africa on August 11 and moved across the Atlantic without developing, entering the eastern Pacific on August 17. The system developed a broad circulation, eventually organizing into Tropical Depression Eight-E on August 21 to the southwest of Mexico.[31] The system quickly intensified into Tropical Storm Fausto after developing rainbands.[32] Located south of a ridge, Fausto moved west-northwestward through an area of warm waters, and it continued intensifying as its outflow increased.[33][34] On August 22, the storm intensified into a hurricane,[31] as an eye developed in the center of the convection.[35] On August 24, Fausto reached a peak intensity with estimated peak winds of 145 mph (233 km/h) and a minimum barometric pressure of 936 mbar (936 hPa; 27.6 inHg), making it a Category 4 hurricane.[31] Around that time, the hurricane had a large well-defined eye surrounded by a ring of convection.[36]
Around when it reached peak intensity, Fausto encountered an area of cooler water temperatures.[37] The hurricane quickly weakened, degrading to a tropical storm on August 26, by which time the convection had diminished.[38] On the next day, Fausto crossed 140˚W and entered the central Pacific. The CPHC downgraded Fausto to a remnant low on August 28 while the system was located over 800 mi (1,300 km) north of Hilo, Hawaii on August 28 at 1200 UTC. The remnants turned more to the west, toward an area of warmer waters and a tropical upper tropospheric trough. The interaction caused thunderstorms to reform, and Fausto regenerated into a tropical depression on August 30 about 635 mi (1,022 km) north of Oahu. On September 1, Fausto briefly reintensified into a tropical storm as it curved northward, steered by an approaching trough. On September 3, the front absorbed Fausto, and soon after the system moved across the Aleutian Islands of Alaska.[39]
Tropical Storm Alika
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 22 – August 28 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 65 mph (100 km/h) (1-min); 995 mbar (hPa) |
An area of convection acquired a closed circulation and became Tropical Depression One-C on August 22. It stayed disorganized for the next several days. It organized more fully and intensified into a tropical storm on August 25 and was named Alika. After peaking as a moderately strong tropical storm on August 25, wind shear caused by the pre-Ele tropical depression and an upper-level low near Hawaii weakened the storm to a depression on August 27. Alika dissipated the next day, having never threatened land.[39]
Tropical Storm Genevieve
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 26 – September 1 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min); 989 mbar (hPa) |
A tropical wave formed Tropical Depression Nine-E on August 26. It was upgraded to a tropical storm and named Genevieve the next day. It moved westward and nearly strengthened to a hurricane, peaking in intensity on August 28. At that point, the cyclone encountered cooler waters, which caused it to weaken slowly, weakening to a depression on August 30. The depression hung on until it lost convection on the September 2. A swirl of remnant clouds persisted for a few more days. Genevieve had no impact on land, with no reports of casualties or damage being received by the National Hurricane Center.[40]
Hurricane Ele
| Category 3 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 27 – August 30 (Exited Basin) |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 125 mph (205 km/h) (1-min); 945 mbar (hPa) |
An eastern extension of the monsoon trough south of Hawaii organized into Tropical Depression Two-C on August 27 and strengthened into Tropical Storm Ele six hours later. Despite the nearby presence of Alika, Ele developed rapidly and strengthened into a hurricane on August 28. After contributing to the dissipation of Alika, Ele continued intensifying. It reached Category 2 intensity late on August 28 and quickly became a major hurricane six hours later. The hurricane then crossed the International Date Line and became a typhoon in the 2002 Pacific typhoon season. Typhoon Ele turned to the northwest after crossing the dateline and continued to strengthen. It reached Category 4 before turning north and weakening again. After briefly restrengthening back into a Category 4, the typhoon weakened and turned to the northwest. Ele was downgraded to a tropical storm on September 7, a depression on September 9, and then dissipated shortly afterwards. Ele did not affect land.[39]
Hurricane Hernan
| Category 5 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | August 30 – September 6 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 160 mph (260 km/h) (1-min); 921 mbar (hPa) |
A weak wave in the ITCZ organized into Tropical Depression Ten-E on August 30. It headed west-northwest and quickly intensified into a tropical storm and eventually, a hurricane. Hernan then began rapidly deepening, reaching Category 5 intensity on September 1. It maintained that intensity for 12 hours before tracking over cooler waters. The storm weakened steadily, with wind shear contributing to its deterioration. Hernan then degenerated into a remnant low on September 6. The low turned to the southwest and dissipated three days later.[41]
Hernan passed close enough to Socorro Island to bring strong winds to the island.[41] In addition, the hurricane's large and powerful wind field caused waves between 12 foot (3.7 m) and 20 foot (6.1 m) in height and strong rip currents on the southwest coast of California.[42] Other than the aforementioned regions, Hernan had no significant impact on land.[41]
Tropical Depression Eleven-E
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 5 – September 8 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min); 1006 mbar (hPa) |
Of the four tropical depressions this season that did not become named storms, only Eleven-E threatened land. An area of disturbed weather associated with a tropical wave formed into a tropical cyclone on September 5. It tracked northwestward, before turning southwest. It weakened into a remnant low on September 8. The remnant turned north and dissipated on September 10 offshore of the Baja California peninsula. The cyclone was nearly a tropical storm when it peaked on September 6. It was forecast to become a tropical storm and pass close to the peninsula. This prompted a tropical storm warning and a hurricane watch. With the weakening of the cyclone the watch and warning were discontinued. No damage or casualties were reported in association with this tropical cyclone.[43]
Tropical Storm Iselle
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 15 – September 20 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 70 mph (110 km/h) (1-min); 990 mbar (hPa) |
Part of the same tropical wave that formed Tropical Depression Seven in the Atlantic basin organized into Tropical Depression Twelve-E on September 15. It strengthened further into Tropical Storm Iselle the next day. The storm headed northwest and paralleled the coast of Mexico, nearly strengthening into a hurricane late on September 17. While near its peak intensity, a trough abruptly recurved the system to the northeast. Wind shear also increased, and Iselle consequently fell apart on satellite imagery. It weakened to a depression on September 19. Iselle then degenerated into a remnant low the next day and rapidly degenerated, dissipating on September 20. Iselle never made landfall.[44]
Iselle threatened parts of southwestern Mexico and warnings and watches were issued for that area. Heavy rains were reported over parts of the Baja California Peninsula.[44] The highest amount of rainfall was 6.16 inches (156 mm) at Guadeloupe and Mulege, Baja California Sur.[45] There were no reports of damage or casualties.[44]
Tropical Storm Julio
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | September 25 – September 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 45 mph (75 km/h) (1-min); 1000 mbar (hPa) |
The origins of Julio were from a monsoon-like area of convection, possibly related to Hurricane Isidore, that persisted off the west coast of Central America on September 21. Thunderstorms increased, and a circulation developed late on September 23. After further organization, the system developed into Tropical Depression Thirteen-E early on September 25 about 100 mi (160 km) southwest of Acapulco.[46][47][48] Initially, the storm was expected to attain a peak intensity of 60 mph (95 km/h).[48] The depression intensified into Tropical Storm Julio, which attained peak winds of 45 mph (70 km/h) early on September 26. At peak, the storm was centered just west-northwest of Lázaro Cárdenas. Soon after, Julio made landfall along the coast of Southwestern Mexico, and it rapidly deteriorated over the mountainous terrain. At 1200 UTC September 26, the storm was downgraded into a tropical depression.[46] Even though the storm was initially expected to enter the extreme southern Gulf of California and regain tropical storm strength,[49] Julio dissipated near Manzanillo later that day instead.[46]
Upon Julio becoming a tropical cyclone, a tropical storm warning was issued from Zihuatanejo to Punta San Telma while a tropical storm watch was in effect from Punta San Telma to Manzanillo.[50] While the storm was making landfall, Zihuatanejo reported 40 mph (65 km/h) winds, with gusts up to 50 mph (80 km/h) at 2042 UTC September 25.[46] The highest rainfall reported was 16.10 inches (409 mm) at Zihuatanejo and La Unión, Guerrero.[51] Tropical Storm Julio was responsible for heavy rains to Zihuatanejo, where 100 homes were damaged or destroyed.[52] Across the city, numerous roofs were damaged and many trees fell. Many houses and streets were flooded as well.[53] Meanwhile, in Acapulco, heavy rains triggered flash flooding that damaged another 100 houses.[52] Throughout Colima, many rivers overflowed its banks.[54] Furthermore, 2,000 homes were flooded.[55] Roughly 100 families were evacuated to shelters in Michoacán.[56] In addition, many small shacks lost their roof due to the storm's high winds. On the outskirts of the Taxco, situated 95 mi (155 km) inland, a school bus carrying 40 kids flipped over, killing three and injuring 18 others.[57] An estimated 2700 acres (700 ha) of crops were lost because of the storm. Parts of Guerrero were later declared a disaster area.[58] However, the city of Zihuaranejo was quickly cleaned up proceeding the storm.[53]
Hurricane Kenna
| Category 5 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 22 – October 26 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 165 mph (270 km/h) (1-min); 913 mbar (hPa) |
A disturbance possibly associated with a tropical wave organized into Tropical Depression Fourteen-E on October 22. It strengthened into a tropical storm that same day and a hurricane on October 23. The next day, Kenna became the third Category 5 hurricane of the season. A trough over Mexico recurved the hurricane, and it started accelerating towards Mexico. Despite moving over waters that were still warm, wind shear weakened the system to a minimal Category 4 by the time of its landfall over Mexico late on October 25. Mountainous terrain rapidly weakened Kenna, and the system dissipated early on October 26.[59]
Hurricane Kenna was the third-strongest Pacific hurricane to make landfall on record.[59] It was also the second-strongest October hurricane in any season, and the third strongest Pacific hurricane overall.[4] In San Blas, Nayarit, 8,800 people were affected; 1,540 houses were damaged or destroyed,[60] which was 80% to 90% of houses in the town.[59] In Santiago Ixcuintla, 3,770 houses were damaged. Agriculture in the affected area was disrupted. Farmers required aid, and many fruit crops were destroyed. Tourism in Puerto Vallarta was disrupted,[60] with much of the damage to hotels. Insurance companies reported that Kenna's total damage was $96 million (2002 USD).[61]
Kenna killed four people in Mexico and injured over a hundred. The low death toll is likely due to massive evacuations in San Blas, Nayarit, and elsewhere ahead of the hurricane.[59]
Tropical Storm Lowell
| Tropical storm (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 22 – October 31 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 50 mph (85 km/h) (1-min); 1002 mbar (hPa) |
A weak tropical wave located over the open Pacific Ocean organized into Tropical Depression Fifteen-E on October 22. It strengthened into a tropical storm the next day. Shortly afterwards, wind shear increased. Lowell's convection was disrupted, and its center of circulation became exposed. The cyclone crossed into the Central Pacific Hurricane Center's area of responsibility on October 26. The shear relaxed, and the depression restrengthened into a tropical storm. Lowell drifted in slow steering currents until it approached Hurricane Huko. The proximity of Huko caused a gradual weakening in Lowell, and it dissipated on October 31.[62]
Hurricane Huko
| Category 1 hurricane (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | October 24 – November 3 (Exited basin) |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 85 mph (140 km/h) (1-min); 980 mbar (hPa) |
In late October, an active monsoon trough persisted south of Hawaii along 10°N latitude, developing an area of convection on October 24. Later that day, the disturbance was classified as Tropical Depression Three-C about 850 mi (1,370 km) south-southeast of Honolulu. Initially poorly organized, it moved to the north and steadily intensified, becoming Tropical Storm Huko early on October 26 while turning northwestward. Late on October 28, Huko reached hurricane strength, but its close proximity to Tropical Storm Lowell and a brief increase in wind shear weakened it back to a tropical storm on October 30. Shortly after turning to the west, conditions allowed for Huko to re-attain hurricane strength on October 31 while it was passing around 140 mi (225 km) south of Johnston Atoll. On November 2, a ridge caused the hurricane to accelerate, and the next day it crossed the International Date Line into the Western Pacific, becoming a typhoon.[39][63]
While passing near Johnston Atoll, the outer rainbands of the hurricane produced wind gusts up to 30 mph (48 km/h) and locally heavy rainfall.[63] The remnants of Huko later reentered the basin, eventually affecting California. The system was responsible for heavy rains, causing flooding along a small stream in Bakersfield. Total damage was approximately $23,000 (2002 USD).[64]
Tropical Depression Sixteen-E
| Tropical depression (SSHWS) | |
| Duration | November 14 – November 16 |
|---|---|
| Peak intensity | 35 mph (55 km/h) (1-min); 1006 mbar (hPa) |
Tropical Depression Sixteen-E formed from a disturbance in the Intertropical Convergence Zone. Despite being located in a hostile environment, it managed to organize into a tropical depression on November 14.[65] It was briefly forecast to strengthen into a tropical storm.[66] However, wind shear prevented that from occurring. Consequently, the depression degenerated into a remnant low on November 16 and dissipated soon after that.[65]
Other systems
An area of convection persisted near a developing circulation about 575 mi (925 km) west-southwest of Johnston Atoll on July 18. An upper-level low to the northeast provided outflow, and the Joint Typhoon Warning Center issued a Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert early on July 19.[67] Although not classified by the CPHC, the Japan Meteorological Agency (JMA) remarked that a tropical depression had developed by early on July 20, just east of the International Date Line. Soon after, it crossed into the western Pacific and briefly intensified into Tropical Storm Kalmaegi.[68] Also on October 30, the JMA indicated that Tropical Storm Maysak moved into the basin and became extratropical few hours later.[69]
Storm names
The following list of names was used for named storms that formed in the North Pacific east of 140°W during 2002.[70][71] This was the same list used for the 1996 season,[72] as no names were retired from it afterwards.
|
|
For storms that form in the North Pacific between 140°W and the International Date Line, the names come from a series of four rotating lists. Names are used one after the other without regard to year, and when the bottom of one list is reached, the next named storm receives the name at the top of the next list.[70] Three named storms, listed below, formed within the area in 2002. Also, named storms in the table above that crossed into the area during the season are noted (*).[7]
|
|
|
Retirement
In the spring of 2003, the World Meteorological Organization retired the name Kenna from its rotating eastern Pacific name lists due to the deaths and damages it caused. Kenna was replaced with Karina for the 2008 season.[73][74]
Season effects
This is a table of all of the tropical cyclones that formed in the 2002 Pacific hurricane season. It includes their name, duration (within the basin), peak classification and intensities, areas affected, damage, and death totals. Deaths in parentheses are additional and indirect (an example of an indirect death would be a traffic accident), but were still related to that storm. Damage and deaths include totals while the storm was extratropical, a wave, or a low, and all of the damage figures are in 2002 USD.
| Saffir–Simpson scale | ||||||
| TD | TS | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 | C5 |
| Storm name |
Dates active | Storm category at peak intensity |
Max 1-min wind mph (km/h) |
Min. press. (mbar) |
Areas affected | Damage (USD) |
Deaths | Ref(s) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alma | May 24 – June 1 | Category 3 hurricane | 115 (185) | 960 | None | None | None | |||
| Boris | June 8–11 | Tropical storm | 60 (95) | 997 | Southwestern Mexico | Minimal | None | |||
| Three-E | June 27–29 | Tropical depression | 35 (55) | 1006 | None | None | None | |||
| Cristina | July 9–16 | Tropical storm | 65 (100) | 994 | None | None | None | |||
| Douglas | July 20–26 | Category 2 hurricane | 105 (165) | 970 | None | None | None | |||
| Elida | July 23–30 | Category 5 hurricane | 160 (260) | 921 | None | None | None | |||
| Seven-E | August 6–8 | Tropical depression | 35 (55) | 1008 | None | None | None | |||
| Fausto | August 21 – September 3 | Category 4 hurricane | 145 (230) | 936 | Aleutian Islands, British Columbia | None | None | |||
| Alika | August 22–28 | Tropical storm | 65 (100) | 995 | None | None | None | |||
| Genevieve | August 26 – September 1 | Tropical storm | 70 (110) | 989 | None | None | None | |||
| Ele | August 27–30 | Category 3 hurricane | 125 (205) | 945 | Johnston Atoll, Wake Island | None | None | |||
| Hernan | August 30 – September 6 | Category 5 hurricane | 160 (260) | 921 | Southwestern Mexico, Revillagigedo Islands, Socorro Island, Southwestern United States | None | None | |||
| Eleven-E | September 5–8 | Tropical depression | 35 (55) | 1006 | Baja California Peninsula | Minor | None | |||
| Iselle | September 15–20 | Tropical storm | 70 (110) | 990 | Baja California Peninsula | Minimal | None | |||
| Julio | September 25–26 | Tropical storm | 45 (75) | 1000 | Southwestern Mexico | Minimal | (3) | |||
| Kenna | October 22–26 | Category 5 hurricane | 165 (270) | 913 | Southwestern Mexico, Western Mexico, Southern United States, Revillagigedo Islands, Socorro Island, Texas | $101 million | 4 | |||
| Lowell | October 22–31 | Tropical storm | 50 (85) | 1002 | Hawaii | None | None | |||
| Huko | October 24 – November 3 | Category 1 hurricane | 85 (140) | 980 | Johnston Atoll, Southwestern United States | $23,000 | None | |||
| Sixteen-E | November 14–16 | Tropical depression | 35 (55) | 1006 | None | None | None | |||
| Season aggregates | ||||||||||
| 19 systems | May 24 – November 16 | 165 (270) | 913 | $101 million | 4 (3) | |||||
See also
- Tropical cyclones in 2002
- List of Pacific hurricanes
- Pacific hurricane season
- 2002 Atlantic hurricane season
- 2002 Pacific typhoon season
- 2002 North Indian Ocean cyclone season
- South-West Indian Ocean cyclone seasons: 2001–02, 2002–03
- Australian region cyclone seasons: 2001–02, 2002–03
- South Pacific cyclone seasons: 2001–02, 2002–03
References
- ^ Neal Dorst (June 2, 2016). "TCFAQ G1) When is hurricane season?". Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory. Archived from the original on May 6, 2009. Retrieved July 24, 2018.
- ^ a b Franklin, Avila; Beven; Lawrence; Pasch & Stewart (November 30, 2002). "Monthly Tropical Weather Summary". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 16, 2008.
- ^ "Background Information: Eastern Pacific Hurricane Season". Climate Prediction Center. Archived from the original on May 9, 2009. Retrieved September 16, 2008.
- ^ a b c d "Eastern North Pacific Tracks File 1949–2007". National Hurricane Center. March 21, 2008. Archived from the original (Plaintext) on August 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ Neal Dorst. "Subject: G1) When is hurricane season?". FAQ: Hurricanes, Typhoons, and Tropical Cyclones. Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory Hurricane Research Division. Archived from the original on May 6, 2009. Retrieved September 14, 2008.
- ^ "2002 Eastern Pacific Hurricane Season". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 17, 2008. Retrieved September 14, 2008.
- ^ a b c Andy Nash; Hans Rosendal; Brooke Bingaman; Treena Loos; Jeff Fournier (May 2003). 2002 Central North Pacific Tropical Cyclones (PDF) (Report). Honolulu, Hawaii: Central Pacific Hurricane Center. Retrieved January 30, 2024.
- ^ a b David M. Roth. "Tropical Storm Boris — June 5–12, 2002" (GIF). Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Archived from the original on October 19, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ a b c d Jack Beven (December 13, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Hurricane Elida". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ "Figure 19. Tropical Storms, El Niño, and the Southwest". University of Arizona. August 2002. Retrieved September 16, 2008. [dead link]
- ^ Gerald Bell; Eric Blake; Muthuvel Chelliah; Stanley Goldenberg; Chris Landsea; Richard Pasch. "The 2002 North Atlantic Hurricane Season" (PDF). Climate Prediction Center. Archived (PDF) from the original on September 24, 2008. Retrieved September 16, 2008.
- ^ "Tropical Cyclone Climatology". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 15, 2008. Retrieved September 14, 2008.
- ^ a b Stacy Stewart (July 24, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Hurricane Alma". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ a b James Franklin (June 24, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Tropical Storm Boris". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ a b Lixion Avila (July 6, 2002). "Tropical Depression Report Tropical Depression Three-E". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ Lawrence (June 27, 2002). "Tropical Depression Three-E Discussion Number 1". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on October 21, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ Miles Lawrence; Eric Blake (November 30, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Tropical Storm Cristina". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ a b c d e f Richard Pasch (December 13, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Hurricane Douglas". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ Lixion A. Avila (2002). "Hurricane Douglas Discussion 1". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved October 5, 2008.
- ^ Miles B. Lawrence (2002). "Hurricane Douglas Discussion 2". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved October 5, 2008.
- ^ James Franklin (2002). "Hurricane Douglas Discussion 3". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved October 5, 2008.
- ^ Stacy R. Stewart (2002). "Hurricane Douglas Discussion 7". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved October 5, 2008.
- ^ Richard J. Pasch (2002). "Hurricane Douglas Discussion 8". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved October 5, 2008.
- ^ Miles B. Lawrence (2002). "Hurricane Douglas Discussion 9". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved October 5, 2008.
- ^ Lixion A. Avila (2002). "Hurricane Douglas Discussion 13". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved October 5, 2008.
- ^ Jack Beven (2002). "Hurricane Douglas Discussion 15". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved October 5, 2008.
- ^ Jack Beven (2002). "Hurricane Douglas Discussion 19". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved October 5, 2008.
- ^ Lixion A. Avila (2002). "Hurricane Douglas Discussion 25". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved October 5, 2008.
- ^ Jack Beven (November 20, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Tropical Depression Seven-E". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ Franklin (August 6, 2002). "Tropical Depression Seven-E Discussion 1". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on October 21, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ a b c James Franklin (December 6, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Hurricane Fausto". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ Beven, Jack; Cobb, Hugh (August 21, 2002). "Tropical Storm Fausto Discussion #2". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved December 3, 2010.
- ^ Beven, Jack (August 21, 2002). "Tropical Storm Fausto Discussion #5". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved March 15, 2024.
- ^ Avila, Lixion (August 23, 2002). "Hurricane Fausto Discussion #8". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved March 15, 2024.
- ^ Beven, Jack (August 22, 2002). "Hurricane Fausto Discussion #6". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved March 15, 2024.
- ^ Avila, Lixion (August 24, 2002). "Hurricane Fausto Discussion #12". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved March 15, 2024.
- ^ Brown, Daniel; Lawrence, Miles (August 24, 2002). "Hurricane Fausto Discussion #14". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved March 15, 2024.
- ^ Lawrence, Miles (August 26, 2002). "Tropical Storm Fausto Discussion #21". National Hurricane Center. Retrieved March 15, 2024.
- ^ a b c d Nash, Andy / Rosendal, Hans / Bingaman, Brooke / Loos, Treena / Fournier, Jeff. "2002 Central North Pacific Tropical Cyclones" (PDF). Central Pacific Hurricane Center. Retrieved March 15, 2024.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Lixion Avila (October 12, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Tropical Storm Genevieve". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ a b c Miles Lawrence (December 10, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Hurricane Hernan". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ "Event Record Details". National Climatic Data Center. Archived from the original on May 20, 2011. Retrieved September 14, 2002.
- ^ Richard Pasch (January 21, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Tropical Depression Eleven-E". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 14, 2008.
- ^ a b c Stacy Stewart (November 10, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Tropical Storm Iselle". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ David M. Roth. "Tropical Storm Iselle — September 16–20, 2002" (GIF). Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Archived from the original on October 19, 2008. Retrieved September 14, 2008.
- ^ a b c d Jack Beven (December 11, 2002). Tropical Storm Julio. United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Weather Service (Tropical Cyclone Report). United States National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved May 19, 2013.
- ^ National Hurricane Center; Hurricane Research Division; Central Pacific Hurricane Center (April 26, 2024). "The Northeast and North Central Pacific hurricane database 1949–2023". United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Weather Service. Archived from the original on May 29, 2024. A guide on how to read the database is available here.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b James Franklin (September 25, 2002). Tropical Depression Thirteen-E Discussion 1. United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National Weather Service (Report). United States National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 19, 2013.
- ^ James Franklin; Eric Blake (September 26, 2002). Tropical Storm Julio Discussion 5. United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration's National weather Service (Report). United States National Hurricane Center. Retrieved May 19, 2013.
- ^ "International News". Associated Press Worldstream. September 25, 2002.
- ^ David M. Roth. Tropical Storm Julio — September 23–27, 2002 (GIF). United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (Report). Hydrometeorological Prediction Center. Retrieved May 19, 2013.
- ^ a b Michael Norton (September 25, 2002). "Tropical Storm Lili Heads to Haiti" (International News). Associated Press Online.
- ^ a b "Los efectos de la Tormenta Tropical "Julio" en Zihuatanejo, Gro. el 25 de Septiembre de 2002" (in Spanish). Zinhuatanejo government. Retrieved June 6, 2013.
- ^ "Afecta a Michoacán y Guerrero tormenta tropical Julio". El Universal (in Spanish). September 25, 2002.
- ^ "Reportan en Guerrero 2 mil viviendas inundadas por Julio". El Universal (in Spanish). September 26, 2002.
- ^ "La tormenta tropical "Julio" afectó por lo menos a 100 familias en Michoacán". Chronicle (in Spanish). September 26, 2002. Retrieved June 6, 2013.
- ^ "Tropical Storm Julio weakens into a depression, dumps rain on Mexico coast". Associated Press Mainstream. September 26, 2002.
- ^ "Pedirán que Guerrero declaren zona de desastre por lluvias". El Universal (in Spanish). October 1, 2002.
- ^ a b c d James Franklin (December 26, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Hurricane Kenna". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ a b International Federation of Red Cross And Red Crescent Societies (October 28, 2002). "Mexico: Hurricane Kenna Information Bulletin No. 02/02". ReliefWeb. Retrieved September 14, 2008.
- ^ Guy Carpenter (January 30, 2003). "2002 Tropical Cyclone Review" (PDF). p. ii. Archived from the original (PDF) on February 6, 2012. Retrieved September 14, 2008.
- ^ Lixion Avila (December 27, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Tropical Storm Lowell". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on September 22, 2008. Retrieved September 13, 2008.
- ^ a b "Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Summary October 2002". Gary Padgett. Retrieved June 6, 2008.
- ^ National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (2002). "Storm Data: November 2002" (PDF). National Climatic Data Center. Retrieved June 6, 2008.
- ^ a b Miles Lawrence (December 4, 2002). "Tropical Cyclone Report Tropical Depression Sixteen-E". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on June 28, 2007. Retrieved September 14, 2008.
- ^ Stewart (November 14, 2002). "Tropical Depression Sixteen-E Discussion Number 2". National Hurricane Center. Archived from the original on October 21, 2008. Retrieved September 14, 2008.
- ^ Gary Padgett (2002). "Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Summary July 2002". Retrieved October 14, 2012.
- ^ Annual Report on Activities of the RSMC Tokyo – Typhoon Center 2002 (PDF) (Report). Japan Meteorological Agency. 13. Archived from the original (PDF) on October 14, 2013. Retrieved August 27, 2012.
- ^ "Digital Typhoon: List of weather charts on October 30, 2002 (Wed)".
- ^ a b "World-Wide Tropical Cyclone Names". Archived from the original on October 1, 2002. Retrieved January 30, 2024.
- ^ Padgett, Gary (February 2002). "Monthly Global Tropical Cyclone Summary". Archived from the original on September 27, 2007. Retrieved March 5, 2024.
- ^ National Hurricane Operations Plan (PDF) (Report). Washington, D.C.: NOAA Office of the Federal Coordinator for Meteorological Services and Supporting Research. May 1996. p. 3-8. Retrieved January 30, 2024.
- ^ National Hurricane Operations Plan (PDF) (Report). Washington, D.C.: NOAA Office of the Federal Coordinator for Meteorological Services and Supporting Research. May 2003. p. 3-8. Retrieved January 30, 2024.
- ^ Gary Padgett; Jack Beven; James Lewis Free (December 6, 2006). "Subject: B3) What names have been retired in the Atlantic and East Pacific basin?". FAQ: Hurricanes, Typhoons, and Tropical Cyclones. Atlantic Oceanographic and Meteorological Laboratory Hurricane Research Division. Archived from the original on May 6, 2009. Retrieved September 14, 2008.