Amphipoda
| Amphipoda | |
|---|---|

| |
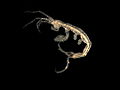
| A hyperiid amphipod (Hyperia macrocephala) | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Subphylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | Amphipoda Latreille, 1816
|
| Sub-orders | |
Amphipoda (amphipods) is an order of animals that includes over 7000 described species of small, shrimp-like crustaceans.
Most amphipods are marine; although a small number of species are limnic or terrestrial. Marine amphipods may be pelagic (living in the water column) or benthic (living on the ocean bottom). Pelagic amphipods are eaten by seabirds, fish, and marine mammals. Terrestrial amphipods such as sand fleas can often be seen amongst sand and pebbles or on beaches.
Distribution and life
Many species of pelagic amphipods are mutualistic or (usually) parasitic, living in association with jellyfish and salps. Phronima is a relatively common genus of pelagic amphipod that kills and cleans out the barrel-shaped body of a salp to live inside and raise its young.

Of the relatively few species of free-living, planktonic amphipods, the most abundant of all is Themisto gaudichaudii. Living in the Southern Ocean, this amphipod congregates in dense swarms, where it is a voracious predator of copepods and other small members of the zooplankton.
After copepods, krill and salps, which are mostly herbivorous, the carnivorous Themisto is the most abundant member of the mesozooplankton in the Southern Ocean.
In cold seas, benthic amphipods are enormously diverse and abundant. In the Southern Ocean, amphipods are the most abundant benthic crustaceans. Some are grazers, many are omnivorous, some even act as piranha-like scavengers, quickly cleaning the carcasses of dead tissue. Amphipods are one of the few animal groups frequently seen when submarines venture to the deepest parts of the oceans. Other benthic amphipods are the primary food of Gray Whales.
A ship hull fouling species of amphipod common to Atlantic and estuarine waters is Jassa falcata.
External links
- Amphipoda page at www.crustacea.net includes a list of families
- The Amphipod Home Page
- A database of amphipod literature
-
A gammarid amphipod
-
A hyperiid amphipod
-
A corophiid amphipod