Jasmonic acid
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
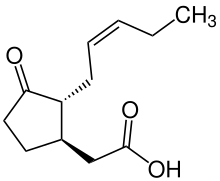
| IUPAC name
(1R,2R)-3-Oxo-2-(2Z)-2-pentenyl-cyclopentaneacetic acid
| |
| Other names
Jasmonic acid
(-)-Jasmonic acid JA | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| Properties | |
| C12H18O3 | |
| Molar mass | 210.27 g/mol |
| Density | ? g/cm3 |
| Boiling point | 160 °C at 0.7 mmHg |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Jasmonic acid (JA) is derived from the fatty acid linolenic acid. It is a member of the jasmonate class of plant hormones. It is biosynthesized from linolenic acid by the octadecanoid pathway.
The major function of JA in regulating plant growth include growth inhibition, senescence, and leaf abscission. It is also responsible for tuber formation in potatoes, yams, and onions. It has an important role in response to wounding of plants and systemic acquired resistance. When plants are attacked by insects, they respond by releasing JA, which inhibits the insects' ability to digest protein.
Jasmonic acid is also converted to a variety of derivatives including esters such as methyl jasmonate; it may also be conjugated to amino acids.
The chemical may have a role in pest control, according to an October 2008 BBC News report [1]
References
This article has an unclear citation style. (September 2007) |
- Comprehensive Natural Products Chemistry : Polyketides and Other Secondary Metabolites Including Fatty Acids and Their Derivatives by Ushio Sankawa (Editor), Derek H. R. Barton (Editor), Koji Nakanishi (Editor) and Otto Meth-Cohn (Editor). ISBN 0-08-043153-4
