Piezoelectric sensor
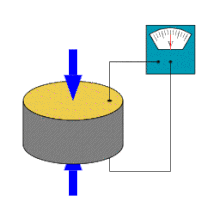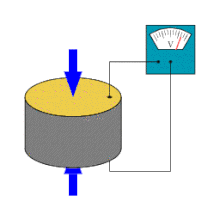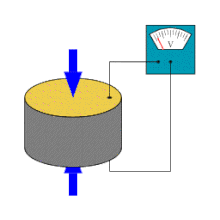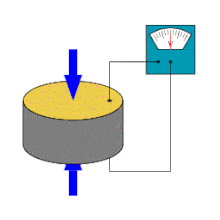
A piezoelectric sensor is a device that uses the piezoelectric effect to measure pressure, acceleration, strain or force by converting them to an electrical signal.
Applications

Piezoelectric sensors have proven to be versatile tools for the measurement of various processes. They are used for quality assurance, process control and for research and development in many different industries. Although the piezoelectric effect was discovered by Curie in 1880, it was only in the 1950s that the piezoelectric effect started to be used for industrial sensing applications. Since then, this measuring principle has been increasingly used and can be regarded as a mature technology with an outstanding inherent reliability. It has been successfully used in various applications, such as in medical, aerospace, nuclear instrumentation, and as a pressure sensor in the touch pads of mobile phones. In the automotive industry, piezoelectric elements are used to monitor combustion when developing internal combustion engines. The sensors are either directly mounted into additional holes into the cylinder head or the spark/glow plug is equipped with a built in miniature piezoelectric sensor [1].
The rise of piezoelectric technology is directly related to a set of inherent advantages. The high modulus of elasticity of many piezoelectric materials is comparable to that of many metals and goes up to 10e6 N/m² [dubious – discuss]. Even though piezoelectric sensors are electromechanical systems that react to compression, the sensing elements show almost zero deflection. This is the reason why piezoelectric sensors are so rugged, have an extremely high natural frequency and an excellent linearity over a wide amplitude range. Additionally, piezoelectric technology is insensitive to electromagnetic fields and radiation, enabling measurements under harsh conditions. Some materials used (especially gallium phosphate [2] or tourmaline) have an extreme stability even at high temperature, enabling sensors to have a working range of up to 1000°C. Tourmaline shows pyroelectricity in addition to the piezoelectric effect; this is the ability to generate an electrical signal when the temperature of the crystal changes. This effect is also common to piezoceramic materials.
| Principle | Strain Sensitivity [V/µ*] | Threshold [µ*] | Span to threshold ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Piezoelectric | 5.0 | 0.00001 | 100,000,000 |
| Piezoresistive | 0.0001 | 0.0001 | 2,500,000 |
| Inductive | 0.001 | 0.0005 | 2,000,000 |
| Capacitive | 0.005 | 0.0001 | 750,000 |
One disadvantage of piezoelectric sensors is that they cannot be used for truly static measurements. A static force will result in a fixed amount of charges on the piezoelectric material. While working with conventional readout electronics, imperfect insulating materials, and reduction in internal sensor resistance will result in a constant loss of electrons, and yield a decreasing signal. Elevated temperatures cause an additional drop in internal resistance and sensitivity. The main effect on the piezoelectric effect is that with increasing pressure loads and temperature, the sensitivity is reduced due to twin-formation. While quartz sensors need to be cooled during measurements at temperatures above 300°C, special types of crystals like GaPO4 gallium phosphate do not show any twin formation up to the melting point of the material itself.
However, it is not true that piezoelectric sensors can only be used for very fast processes or at ambient conditions. In fact, there are numerous applications that show quasi-static measurements, while there are other applications with temperatures higher than 500°C.
Piezoelectric sensors are also seen in nature. Dry bone is piezoelectric, and is thought by some to act as a biological force sensor.[3][4]
Principle of operation
Depending on how a piezoelectric material is cut, three main modes of operation can be distinguished: transverse, longitudinal, and shear.[2]
- Transverse effect
- A force is applied along a neutral axis (y) and the charges are generated along the (x) direction, perpendicular to the line of force. The amount of charge depends on the geometrical dimensions of the respective piezoelectric element. When dimensions apply,
- ,
- where is the dimension in line with the neutral axis, is in line with the charge generating axis and is the corresponding piezoelectric coefficient.[5]
- Longitudinal effect
- The amount of charge produced is strictly proportional to the applied force and is independent of size and shape of the piezoelectric element. Using several elements that are mechanically in series and electrically in parallel is the only way to increase the charge output. The resulting charge is
- ,
- where is the piezoelectric coefficient for a charge in x-direction released by forces applied along x-direction (in pC/N). is the applied Force in x-direction [N] and corresponds to the number of stacked elements .
- Shear effect
- Again, the charges produced are strictly proportional to the applied forces and are independent of the element’s size and shape. For elements mechanically in series and electrically in parallel the charge is
- .
In contrast to the longitudinal and shear effects, the transverse effect opens the possibility to fine-tune sensitivity on the force applied and the element dimension.
Electrical properties

A piezoelectric transducer has very high DC output impedance and can be modeled as a proportional voltage source and filter network. The voltage V at the source is directly proportional to the applied force, pressure, or strain.[3] The output signal is then related to this mechanical force as if it had passed through the equivalent circuit.

A detailed model includes the effects of the sensor's mechanical construction and other non-idealities.[4] The inductance Lm is due to the seismic mass and inertia of the sensor itself. Ce is inversely proportional to the mechanical elasticity of the sensor. C0 represents the static capacitance of the transducer, resulting from an inertial mass of infinite size.[4] Ri is the insulation leakage resistance of the transducer element. If the sensor is connected to a load resistance, this also acts in parallel with the insulation resistance, both increasing the high-pass cutoff frequency.

For use as a sensor, the flat region of the frequency response plot is typically used, between the high-pass cutoff and the resonant peak. The load and leakage resistance need to be large enough that low frequencies of interest are not lost. A simplified equivalent circuit model can be used in this region, in which Cs represents the capacitance of the sensor surface itself, determined by the standard formula for capacitance of parallel plates.[4][5] It can also be modeled as a charge source in parallel with the source capacitance, with the charge directly proportional to the applied force, as above.[3]
Sensor design

Based on piezoelectric technology various physical quantities can be measured; the most common are pressure and acceleration. For pressure sensors, a thin membrane and a massive base is used, ensuring that an applied pressure specifically loads the elements in one direction. For accelerometers, a seismic mass is attached to the crystal elements. When the accelerometer experiences a motion, the invariant seismic mass loads the elements according to Newton’s second law of motion .
The main difference in the working principle between these two cases is the way forces are applied to the sensing elements. In a pressure sensor a thin membrane is used to transfer the force to the elements, while in accelerometers the forces are applied by an attached seismic mass.
Sensors often tend to be sensitive to more than one physical quantity. Pressure sensors show false signal when they are exposed to vibrations. Sophisticated pressure sensors therefore use acceleration compensation elements in addition to the pressure sensing elements. By carefully matching those elements, the acceleration signal (released from the compensation element) is subtracted from the combined signal of pressure and acceleration to derive the true pressure information.
Vibration sensors can also be used to harvest otherwise wasted energy from mechanical vibrations. This is accomplished by using piezoelectric materials to convert mechanical strain into usable electrical energy.[6]
Sensing materials
Two main groups of materials are used for piezoelectric sensors: piezoelectric ceramics and single crystal materials. The ceramic materials (such as PZT ceramic) have a piezoelectric constant / sensitivity that is roughly two orders of magnitude higher than those of single crystal materials and can be produced by inexpensive sintering processes. The piezoeffect in piezoceramics is "trained", so unfortunately their high sensitivity degrades over time. The degradation is highly correlated with temperature. The less sensitive crystal materials (gallium phosphate, quartz, tourmaline) have a much higher – when carefully handled, almost infinite – long term stability.
See also
References
- ^ Gautschi, G. (2002). Piezoelectric sensorics. Springer Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
- ^ "Piezoelectric sensors". Piezocryst website. Retrieved 2006-06-02.
- ^ a b "Interfacing Piezo Film to Electronics" (PDF). Measurement Specialties. 2006. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help)[dead link] - ^ a b c Alfredo Vázquez Carazo (2000). "Novel Piezoelectric Transducers for High Voltage Measurements". Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya: 242.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Karki, James (2000). "Signal Conditioning Piezoelectric Sensors" (PDF). Texas Instruments. Retrieved 2007-12-02.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) - ^ Ludlow, Chris (2008). "Energy Harvesting with Piezoelectric Sensors" (PDF). Mide Technology. Retrieved 2008-05-21.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|month=ignored (help) [dead link]
External links
- Material constants of gallium phosphate
- Langatate - new material for high-temperature piezoelectric sensors
- Piezoelectric multilayer sensors [6]
- Spark-Plug with integrated miniaturized piezoelectric pressure sensor [7]
- Overview of piezoelectric pressure sensors for automotive engine development [http://www.piezocryst.com/downloads/Product_Overview_Automotive_Sensors.pdf
- Using the Piezoelectric Effect in Sensors
- Using a piezoelectric sensor to create a vibration sensor.
- COMSOL Composite Piezoelectric Transducer FEA Model











