Bacillus mycoides
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
| Bacillus mycoides | |
|---|---|
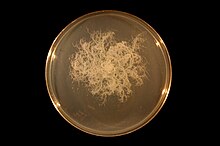
| |
| Bacillus mycoides growing clockwise on an agar plate. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Division: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | mycoides
|
| Binomial name | |
| Bacillus mycoides | |
Bacillus mycoides is a bacterium of the genus Bacillus.
Structure and compounds
Bacillus mycoides cells are usually larger than 3 micrometers. It forms chains of cells. It can form acid from glucose, this form is non motile. It's cell body does not swell when sporulating; Using Voges–Proskauer test, B. mycoides produces a positive result. It can also hydrolyse starch. B. mycoides is a common soil organism.[1]
Uses
Bacillus mycoides are found in common pesticides and are used to inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria and fungi. There seems to be no negative effects on humans or the environment.Citation needed
Nitrogen Cycle
Bacillus mycides is an ammonifying bacterium, and can convert peptone (protein, an organic nitrogen source) into ammonia. In water, ammonia becomes ammonium. This product is essential for nitrifying bacteria such as Nitrosococcus, which use the ammonia under aerobic conditions to make nitrite.
References
