Vitebsk Region
Vitebsk Region
Віцебская вобласць (in Belarusian) Витебская область (in Russian) | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Administrative center | Vitebsk |
| Largest cities | Vitebsk - 369,933 Orsha - 115,938 Navapolatsk - 102,288 |
| Raions | 21 Cities - 19 Urban localities - 26 |
| City raions | 5 |
| Area | |
| • Total | 40,049.99 km2 (15,463.39 sq mi) |
| Population (2019 census) | |
| • Total | 1,135,731 |
| • Density | 28/km2 (73/sq mi) |
| ISO 3166 code | BY-VI |
| HDI (2017) | 0.785[1] high · 6th |
| Website | www.vitebsk-region.gov.by |
Vitebsk Region, Vitsebsk Voblast, or Vitebsk Oblast (Belarusian: Ві́цебская во́бласць, Viciebskaja vobłasć, pronounced [ˈvʲit͡sʲɛpskaja ˈvɔblast͡sʲ]; Russian: Ви́тебская о́бласть, romanized: Vitebskaya oblast, IPA: [ˈvʲitʲɪpskəjə ˈobləsʲtʲ]) is a region (voblast) of Belarus with its administrative center being Vitebsk (Vitsebsk). It is located near the border with Russia.
As of a 2019, the region had a population of 1,135,731.[2] It has the lowest population density in Belarus at 30.6 p/km².
Important cities within the region include Vitebsk, Orsha, and Polotsk/Navapolatsk.
Geography

Vitebsk Region covers an area of 40,000 km²,[2] which is about 19.4% of the national total. It is bordered on the north by Pskov Oblast of Russia, by Smolensk Oblast of Russia on the east, on the south by Minsk Region and by Mogilev Region, on the southwest by Minsk Region and Grodno Region, and on the west and northwest by Vilnius and Utena counties of Lithuania and Dagda, Daugavpils, Krāslava and Zilupe municipalities of Latvia.
The northern extreme point of Belarus is situated in Verkhnyadzvinsk District of Vitebsk Region, north of Lake Osveya.[3]
In 2000 Belarusian scientists Alexey Solomonov and Valery Anoshko published a report in which they stated that the geographic centre of Europe was located near Lake Sho (Belarusian: Шо) in the Vitebsk Region. [1][better source needed]
The region is known for its numerous lakes. The largest lakes of the Vitebsk Region are: Osveyskoye (2nd largest in Belarus), Lukomskoye (4th largest), Drivyaty (5th largest in Belarus and the largest of Braslav Lakes), Nescherdo, Snudy, Lisno, Ezerische, Strusto, Richi, Losvido, Lepelskoye.[4]
The region has more national parks, nature reserves, and wildlife preserves of national importance than any other region of Belarus. Braslav Lakes and Naroch National Parks and Berezinski Biosphere Reserve comprise 3,4% of the whole region's territory, and 22 wildlife preserves of national importance make up 4,1% of the region.[5]
Economy
The main industry of the region is petrochemical. "Naftan" (Navapolatsk) is one of the biggest oil refineries in Belarus and a major polymer manufacturer, "LLK-Naftan" (Navapolatsk) produces oil additives. Share of the food industry in the regional industrial output is estimated at 14-15%. Share of textile, garment and shoe factories (light industry) is estimated at 5-6%, the major factories are "Belvest" (shoes), "Marko" (shoes; both in Vitebsk), Orsha flax factory, "Vitebsk carpets", "Znamya industrializacyi" garment factory in Vitebsk, "Bell Bimbo" (baby clothes manufacturer). The biggest electrical and machinery plants (5-6% of the regional industrial output) are "Vityas" in Vitebsk (TV sets and household appliances), "Vistan" machine tool factory, Vitebsk factory of electrical measuring instruments, Vitebsk factory of tractor spare parts, "Red fighter" machine tool factory in Orsha.[6]
Lukoml power station is the biggest power plant in Belarus.
Vitebsk Region has a number of important transport connections with Russia, Ukraine, the Baltic countries, and Poland.
Tourism
The number of travel agencies in Vitebsk Region has been growing, from 25 in 2000 to 83 in 2010; most provide both agent and operator activities.[7][8] The numerous lake resorts attract tourists for several-night stays. Polotsk and Vitebsk are the most popular cultural tourism destinations of the region.
Administrative subdivisions
The Vitebsk Region is subdivided into 21 districts, 2 cities of oblast subordinance, 19 additional cities, 249 selsovets, and 26 urban-type settlements.
Districts of Vitebsk Region
Cities and towns
Population of cities and towns in Vitebsk Region
| English | Belarusian | Russian | Pop. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vitebsk | Belarusian: Ві́цебск | Russian: Ви́тебск | 342,400 |
| Orsha | Belarusian: О́рша | Russian: О́рша | 125,300 |
| Navapolatsk | Belarusian: Наваполацк | Russian: Новополоцк | 101,300 |
| Polotsk | Belarusian: По́лацк | Russian: По́лоцк | 82,800 |
| Pastavy | Belarusian: Паставы | 20,500 | |
| Hlybokaye | Belarusian: Глыбокае | 19,600 | |
| Lepel | Belarusian: Ле́пель | Russian: Ле́пель | 18,800 |
| Novalukoml | 14,900 | ||
| Haradok | Belarusian: Гарадок | Russian: Городок | 14,000 |
| Baran | 12,300 | ||
| Talachyn | Belarusian: Талачын | 10,500 | |
| Braslaw | Belarusian: Браслаў | Russian: Браслав | 10,100 |
| Chashniki | Belarusian: Чашнікі | 9,800 | |
| Dubroŭna | Belarusian: Дуброўна | 9,100 | |
| Myory | Belarusian: Мёры | 9,000 | |
| Syanno | Belarusian: Сянно | 8,400 | |
| Beshankovichy | Belarusian: Бешанко́вічы | 8,200 | |
| Verkhnyadzvinsk | Belarusian: Верхнядзвінск | 7,300 | |
| Dokshytsy | Belarusian: Докшыцы | 7,000 | |
| Ushachyu.t.s. | Belarusian: Ушачы | 5,600 | |
| Disna | 2,400 | ||
| Koptyusht. | Belarusian: Капцюгі | ||
| Suraž t. | Belarusian: Сураж |
Notes:
t. - town
u.t.s. - urban-type settlement
Towns
Demographics
As of 2008, the birth rate was 9.7 per 1000, while the death rate was 15.5 per 1000.[9] As of 2017, the birth rate was 9.6 and the death rate was 14.4. Rasony District, Shumilina District, Verkhnyadzvinsk District had the highest birth rates (over 11), while the city of Navapolatsk (Novopolotsk), Beshankovichy District, Haradok District had the lowests birth rates (less than 9).[10] 16.1% of the population were under working age, 56.6% in working age, 27.3% over working age (averages in Belarus — 17.7%, 57.2%, 25.1%).[11]
In 2017, the region had negative net migration rates for both internal and international migrations (-2,102 and -63 respectively). 5,227 of those who departed from the region in 2017 arrived in Minsk, 2,021 in the Minsk Region, 1,630 in the Mahilioŭ (Mogilev) Region, less than 700 — in each of the other regions. 3,858 people arrived in the region from Minsk, 1,731 from the Mahilioŭ (Mogilev) Region, 1,355 from the Minsk Region, less than 750 — from each of the other regions.[12]
As of 2018, 53.7% of the region's population were female, 46.3% were male (averages in Belarus — 53.4% and 46.6% respectively).[13]
Share of urban population in the region is increasing continuously since 1950 (21.5% in 1950, 77.4% in 2018).[14]
| Year | 1939 | 1950 | 1955 | 1960 | 1965 | 1970 | 1975 | 1980 | 1985 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Population (thousands)[14] | 1,702.5 | 1,256.2 | 1,243.3 | 1,289.9 | 1,313.5 | 1,368.8 | 1,384.1 | 1,386.1 | 1,402.3 |
| Year | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
| Population (thousands)[14] | 1,415.7 | 1,426.3 | 1,366.4 | 1,289.5 | 1,273.8 | 1,259.4 | 1,247.3 | 1,237.5 | 1,229.4 |
| Year | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 |
| Population (thousands)[14][15] | 1,221.8 | 1,214.1 | 1,208 | 1,202.1 | 1,198.5 | 1,193.5 | 1,188 | 1,180.2 | 1,171.5 |
| Birth & death rates | 1950 | 1960 | 1970 | 1980 | 1985 | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Birth rate[16] | 24 | 21.6 | 14.6 | 14.2 | 14.8 | 13.2 | 9.1 | 8.5 | 8.4 | 10.1 | 10.1 | 10.9 | 11.1 | 11.1 | 11.2 | 11.1 | 9.6 |
| Death rate[16] | 7.8 | 7 | 8.5 | 11.3 | 12.3 | 12.5 | 14.9 | 15.1 | 16.5 | 16.7 | 16.2 | 15.4 | 15.4 | 14.7 | 14.7 | 14.6 | 14.4 |
| Life expectancy at birth | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Overall[17] | 71 | 68 | 68.4 | 68.1 | 69.5 | 72.9 | 73.3 | 73.3 |
| female[17] | 76.3 | 74.9 | 75.6 | 75.7 | 77 | 78.9 | 79.4 | 79.3 |
| male[17] | 67.3 | 64.4 | 64.2 | 63.3 | 65.1 | 69.2 | 69.4 | 69.4 |
| Marriages and divorces | 1950 | 1960 | 1970 | 1980 | 1990 | 1995 | 2000 | 2005 | 2010 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Marriages (total)[18] | 11,589 | 15,275 | 12,645 | 13,908 | 13,480 | 10,571 | 7,936 | 9,037 | 9,542 | 9,803 | 7,536 | 7,582 |
| Marriages (per 1000 population)[18] | 9.2 | 11.9 | 9.2 | 10 | 9.5 | 7.4 | 5.8 | 7.1 | 7.8 | 8.2 | 6.3 | 6.4 |
| Divorces (total)[18] | 159 | 872 | 2,835 | 4,641 | 5,006 | 6,465 | 6,339 | 4,209 | 4,800 | 4,007 | 4,205 | 3,983 |
| Divorces (per 1000 population)[18] | 0.1 | 0.7 | 2.1 | 3.3 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 4.7 | 3.3 | 3.9 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 3.4 |
-
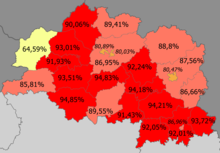
Belarusians in the region>90%85—90%80–85%<80% (64.59%)
-
Russians in the region>15% (15.51%)10–15%8–10%5–8%<5%
-
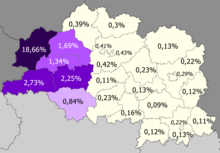
Poles in the region>5% (18.66%)2–5%1–2%0.5–1%<0.5%
-
Birth rate by district (2017)
See also
References
- ^ "Sub-national HDI - Area Database - Global Data Lab". hdi.globaldatalab.org. Retrieved 2018-09-13.
- ^ a b "Main Geographic Characteristics of the Republic of Belarus. Territory and population density of Belarus by region as of January 1, 2011". Land of Ancestors. The Scientific and Production State Republican Unitary Enterprise “National Cadastre Agency” of the State Property Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2011. Archived from the original on 27 September 2013. Retrieved 24 September 2013.
- ^ "Coordinates of the extreme points of the state frontier". Land of Ancestors. 2012. Archived from the original on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 30 August 2013.
- ^ "Main characteristics of the largest lakes of Belarus". Land of Ancestors. Data of the Research Laboratory for Lake Study of the Belarus State University. 2011. Archived from the original on 29 September 2013. Retrieved 29 September 2013.
- ^ "Nature reserves and national parks, wildlife preserves and nature sanctuaries". Land of Ancestors. Data of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Environmental Protection of the Republic of Belarus. 2011. Archived from the original on 29 September 2013. Retrieved 29 November 2013.
- ^ Промышленность (in Russian)
- ^ Ministry of Sports and Tourism of the Republic of Belarus. (2011). "Number of organizations engaged in tourist activities in 2010 in Belarus". Land of Ancestors. National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. Archived from the original on 13 October 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- ^ Ministry of Sports and Tourism of the Republic of Belarus. (2011). "Number of organisations engaged in tourist activities in Belarus by region". Land of Ancestors. National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. Archived from the original on 13 October 2013. Retrieved 9 October 2013.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2009-09-18. Retrieved 2008-12-29.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Демографический ежегодник Республики Беларусь [Demographic Yearbook of the Republic of Belarus]. Minsk: National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2018. p. 160—162.
- ^ Демографический ежегодник Республики Беларусь [Demographic Yearbook of the Republic of Belarus]. Minsk: National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2018. p. 81.
- ^ Демографический ежегодник Республики Беларусь [Demographic Yearbook of the Republic of Belarus]. Minsk: National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2018. p. 415—416.
- ^ Демографический ежегодник Республики Беларусь [Demographic Yearbook of the Republic of Belarus]. Minsk: National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2018. p. 42.
- ^ a b c d Демографический ежегодник Республики Беларусь [Demographic Yearbook of the Republic of Belarus]. Minsk: National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2018. p. 30.
- ^ Population by cities and districts (in Russian)
- ^ a b Демографический ежегодник Республики Беларусь [Demographical Yearbook of the Republic of Belarus]. Minsk: National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2018. p. 145.
- ^ a b c Демографический ежегодник Республики Беларусь [Demographical Yearbook of the Republic of Belarus]. Minsk: National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2018. p. 179.
- ^ a b c d Демографический ежегодник Республики Беларусь [Demographical Yearbook of the Republic of Belarus]. Minsk: National Statistical Committee of the Republic of Belarus. 2018. p. 188.
External links
- Viciebsk Region – The Land Of Artists And Terrorists
- (in English and Russian) Vitebsk Regional Executive Committee