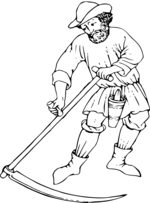
Scythe

- Toe
- Chine
- Beard
- Heel
- Tang
- Ring
- Snath or snaith
- Grips
A scythe is an agricultural hand tool for mowing grass or reaping crops. It has largely been replaced by horse-drawn and then tractor machinery, but is still used in some areas of Europe and Asia.
The word "scythe" derives from Old English siðe.[1][further explanation needed] In Middle English and after it was usually spelt sithe or sythe. However, in the 15th century some writers began to use the sc- spelling as they thought (wrongly) the word was related to the Latin scindere (meaning "to cut").[2] Nevertheless, the sithe spelling lingered and notably appears in Noah Webster's dictionaries.[3][4]

A scythe consists of a shaft about 170 centimetres (67 in) long called a snaith, snath, snathe or sned, traditionally made of wood but now sometimes metal. Simple snaiths are straight with offset handles, others have an "S" curve or are steam bent in three dimensions to place the handles in an ergonomic configuration but close to shaft. The snaith has either one or two short handles at right angles to it, usually one near the upper end and always another roughly in the middle. The handles are usually adjustable to suit the user. A curved, steel blade between 60 to 90 centimetres (24 to 35 in) long is mounted at the lower end at 90°, or less, to the snaith. Scythes almost always have the blade projecting from the left side of the snaith when in use, with the edge towards the mower; left-handed scythes are made but cannot be used together with right-handed scythes as the left-handed mower would be mowing in the opposite direction and could not mow in a team.
Use

The use of a scythe is traditionally called mowing, now often scything to distinguish it from machine mowing. The mower holds the top handle in the left hand and the central one in the right, with the arms straight, the blade parallel and very close to the ground and the uncut grass to the right. The body is then twisted to the right, the blade hooks the grass and is swung steadily to the left in a long arc ending in front of the mower and depositing the cut grass neatly to the left. The mower takes a small step forward and repeats the motion, proceeding with a steady rhythm, stopping at frequent intervals to hone the blade. The correct technique has a slicing action on the grass, cutting a narrow strip with each stroke, leaving a uniform stubble on the ground and forming a regular windrow on the left.[5]
The mower moves along the mowing-edge with the uncut grass to the right and the cut grass laid in a neat row to the left, on the previously mown land. Each strip of ground mown by a scythe is called a swathe (pronounced /sweɪð/: rhymes with "bathe") or swath (/swɒθ/: rhymes with "Goth"). Mowing may be done by a team of mowers, usually starting at the edges of a meadow then proceeding clockwise and finishing in the middle. Mowing grass is easier when it is damp, and so hay-making traditionally began at dawn and often stopped early, the heat of the day being spent raking and carting the hay cut on previous days or peening the blades.
Scythes are designed for different tasks. A long, thin blade 90 to 100 centimetres (35 to 39 in) is most efficient for mowing grass or wheat, while a shorter, more robust scythe 60 to 70 centimetres (24 to 28 in) is more appropriate for clearing weeds, cutting reed or sedge and can be used with the blade under water for clearing ditches and waterways. Skilled mowers using traditional long-bladed scythes honed very sharp were used to maintain short lawn grass until the invention of the lawnmower. Many cultures have used a variety of 'cradles' to catch cut different kinds of grain stems, keeping the seed heads aligned and laying them down in an orderly fashion to make them easier to sheaf and winnow.
Mowing with a scythe is a skilled task that takes time to fully learn. Long-bladed traditional scythes, typically around 90 centimetres (35 in) (such as in the example below) and suitable for mowing grass or wheat are harder to use at first, consequently, beginners usually start on shorter blades, say 70 centimetres (28 in) or less. Common beginner's errors include: setting up the snaith with the handles in the wrong locations to suit the body, setting the blade at the wrong turn-in and turn-up angles to suit the conditions, choosing a blade that is too long for the skill level, failing to start with a sharp edge and persevering with a dull one during use, chopping or hacking at the grass, trying to cut too wide a strip of grass at once and striking the ground with the blade. Traditionally, beginners relied on mentors to help them set up and maintain their scythe and to teach them to mow comfortably and efficiently.
The mowing action
-
Typical stance; the pouch at belt contains a whetstone
-
1. Start of the stroke after stepping forward into the swathe. Mowing rye in 1945
-
2. Swinging left into the cut and deepening the swathe
-
3. Finish of the stroke and depositing on the windrow to the left
Sharpening
The cutting edge of a tensioned scythe blade is traditionally maintained by occasional peening followed by frequent honing. Peening reforms the malleable edge, by hammering, to create the desired profile, to locally work-harden the metal, and to remove minor nicks and dents. For mowing fine grass the bevel angle may be peened extremely fine, while for coarser work a larger angle is created to give a more robust edge. Peening requires some skill and is done using a peening hammer and special anvils or by using a peening jig. Historically, a peening station was set up on the edge of the field during harvest but now more likely back in the workshop.
In the example below, a short scythe blade, being used to clear brambles, is being sharpened. Before going to the forest the blade is peened back in the workshop; this reforms the malleable steel to create an edge profile that can then be honed. Peening is done only occasionally; how often depends on the hardness of the steel and the nature of the work. The Austrian blade shown is being used to cut tough-stemmed brambles and it is being peened about every thirty hours of work. Nicks and cuts to the blade edge can usually be worked out of the blade by peening and a new edge profile formed for honing. A peening jig is being used here but blades can be free-peened using various designs of peening anvils. The peening jig shown has two interchangeable caps that set different angles; a coarse angle is set first about 3 mm back from the edge and the fine angle is then set on the edge, leaving an edge that lends itself to being easily honed. The blade is then honed using progressively finer honing stones and then taken to the field. In the field the blade is honed using a fine, ovoid whetstone (or rubber), fine-grained for grass, coarser for cereal crops. Honing is done the moment the mower senses that the edge has gone off; this may be every half hour or more depending on the conditions. The laminated honing stone shown here has two grades of stone and is carried into the field soaking in a water-filled holster on the belt. A burr is set up on the outside of the blade by stroking the blade on the inside, the burr is then taken off by gently stroking it on the outside. There are a great many opinions, regional traditions and variations on exactly how to do this; some eastern European countries even set up the burr on the inside.[6][7]
-
A peening jig anvil. Note the two colour-coded caps.
-
Peening a scythe blade using the jig
-
A typical ovoid honing stone soaking in a water-filled sheath
-
Setting up a burr on the outside of the blade by honing on the inside
-
Taking the burr off the outside of the blade by honing on the outside
-
The finished blade
-
Image from a 1945 rye harvest, showing a very long blade being honed on the job. Setting up the burr
-
Removing the burr on the outside face, ready to mow again
Unlike continental European blades, typical American, English, and Nordic style blades are made of harder steel and are not usually peened for risk of cracking them. The harder blade holds an edge longer and requires less frequent honing in the field but after heavy use or damage the edge must be reshaped by grinding. Because of the greater wear resistance of the hard steel, and the reduced need for honing as a result, this usually only needs to be done 1–3 times a season. Many examples have a laminated construction with a hard, wear-resistant core providing the edge and softer sides providing strength. In American and English blades the edge steel is typically clad on either side with the tough iron, while some Nordic laminated blades have a layer of iron on the top only, with the edge steel comprising the bottom layer.
History

The scythe may have dated back as far as c. 5000 BC, and seems to have been used since Cucuteni–Trypillia settlements, becoming wide spread with agricultural developments. Initially used mostly for mowing hay, it had replaced the sickle for reaping crops by the 16th century as the scythe was better ergonomically and consequently more efficient. In about 1800 the grain cradle, was sometimes added to the standard scythe when mowing grain; the cradle was an addition of light wooden fingers above the scythe blade which kept the grain stems aligned and the heads together to make the collection and threshing easier. In the developed world the scythe has largely been replaced by the motorised lawn mower and combine harvester. However, the scythe remained in common use for many years after the introduction of machines because a side-mounted finger-bar mower, whether horse or tractor drawn, could not mow in front of itself and scythes were still needed to open up a meadow by clearing the first swathe to give the mechanical mower room to start.


The Dictionary of Greek and Roman Antiquities of Sir William Smith argues that the scythe, known in Latin as the falx foenaria as opposed to the sickle, the falx messoria, was used by the ancient Romans. According to ancient Greek mythology, Gaia the Greek goddess and mother of the Titans gave a sickle made out of the strongest metal to her youngest son Kronos, who is also the youngest of the Titans and god of the harvest, to seek vengeance against her husband Ouranos for torturing their eldest sons. To illustrate this, Smith cites an image of Saturn holding a scythe, from an ancient Italian cameo. The Grim Reaper and the Greek Titan Cronus were often depicted carrying or wielding a scythe. According to Jack Herer and Flesh of The Gods (Emboden, W. A. Jr., Praeger Press, New York, 1974), the ancient Scythians grew hemp and harvested it with a hand reaper that we still call a scythe.
The Abbeydale Industrial Hamlet in Sheffield, England, is a museum of a scythe-making works that was in operation from the end of the 18th century until the 1930s.[8] This was part of the former scythe-making district of north Derbyshire, which extended into Eckington.[9] Other English scythe-making districts include that around Belbroughton.[10]
The German Renaissance scythe sword, the Greek and Roman harpe and the Egyptian khopesh were scythes or sickles modified as weapons or symbols of authority. An improvised conversion of the agricultural scythe to a war scythe by re-attaching the blade parallel to the snaith, similar to a bill has also been used throughout history as a weapon. See Scythes in art below for an example.
In national cultures
The scythe is still an indispensable tool for farmers in developing countries and in mountainous terrain.
In Romania, for example, in the highland landscape of the Transylvanian Apuseni mountains,[11] scything is a very important annual activity, taking about 2–3 weeks to complete for a regular house. As scything is a tiring physical activity and is relatively difficult to learn, farmers help each other by forming teams. After each day's harvest, the farmers often celebrate by having a small feast where they dance, drink and eat, while being careful to keep in shape for the next day's hard work. In other parts of the Balkans, such as in Serbian towns, scything competitions are held where the winner takes away a small silver scythe.[12] In small Serbian towns, scything is treasured as part of the local folklore, and the winners of friendly competitions are rewarded richly[13] with food and drink, which they share with their competitors.
Among Basques scythe-mowing competitions are still a popular traditional sport, called segalaritza (from Spanish verb segar: to mow). Each contender competes to cut a defined section of grown grass before his rival does the same.
There is an international scything competition held at Goricko[14] where people from Austria, Hungary, Serbia and Romania, or as far away as Asia appear to showcase their culturally unique method of reaping crops.[15] In 2009, a Japanese gentleman showcased a wooden reaping tool with a metal edge, which he used to show how rice was cut. He was impressed with the speed of the local reapers, but said such a large scythe would never work in Japan.
The Norwegian municipality of Hornindal has three scythe blades in its coat-of-arms.
Scythes are beginning a comeback in American suburbs, since they "don't use gas, don't get hot, don't make noise, do make for exercise, and do cut grass".[16]
In art
-
1817 illustration of a Polish peasant sharpening a scythe. (Drawn by Jan Piotr Norblin, engraved by Philibert-Louis Debucourt)
-
Death and the woodcutter by Jean-François Millet, 1859
-
Niittomiehet (Mower men), by Pekka Halonen, 1891
-
Swedish boy with scythe by Per Södermark, second part of 19th century
See also
- Bagging hook, similar to the sickle
- Billhook, a version of the sickle used for cutting shrubs and branches
- Grain cradle, for aligning grain stems
- Harpe, a Greek or Roman long sickle or scythe which doubled as a weapon
- Kama (weapon), a Japanese hand scythe used in farming, and martial arts
- Khopesh, an Egyptian long sickle or scythe as a weapon
- Scythe sword, scythe blade converted to use as a weapon
- Sickle, the archetypal forerunner of the scythe
- War scythe, a polearm resembling a modified scythe
- String trimmer, a garden tool for cutting grass and groundcover which uses a flexible monofilament line instead of a blade.
References
- ^ "scythe". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ "Online Etymology Dictionary". etymonline.com.
- ^ "Browse 1828 => Word SITHE :: Search the 1828 Noah Webster's Dictionary of the English Language". 1828.mshaffer.com. 2012-06-03. Retrieved 2012-06-03.
- ^ "Browse 1913 => Word SITHE :: Search the 1913 Noah Webster's Dictionary of the English Language". 1913.mshaffer.com. 2012-06-03. Archived from the original on 2012-12-03. Retrieved 2012-06-03.
- ^ "How to Use a Scythe – Modern Homesteading – Mother Earth News".
- ^ "Peening and Sharpening – Scythe Cymru".
- ^ Tomlin, Steve (31 May 2016). "Learning to peen a scythe".
- ^ Sheffield Industrial Museums Trust Archived 2005-01-07 at the Wayback Machine. Simt.co.uk (2010-10-03). Retrieved on 2011-03-09.
- ^ K. M. Battye, "Sickle-makers and other metalworkers in Eckington 1534–1750: a study of metal workers tools, raw materials and made goods, using probate wills and inventories". Tools and Trades 12 (2000), 26–38.
- ^ P. W. King, "The north Worcestershire Scythe Industry" Historical Metallurgy 41(2), 124–147.
- ^ Reif, Albert; Ruşdea, Evelyn; Păcurar, Florin; Rotar, Ioan; Brinkmann, Katja; Auch, Eckhard; Goia, Augustin; Bühler, Josef (2008). "A Traditional Cultural Landscape in Transformation". Mountain Research and Development. 28: 18. doi:10.1659/mrd.0806.
- ^ Events in Serbia. Hay making on Rajac. Accommodation in Sumadija. Guaranted Tours. Visitserbia.org. Retrieved on 2011-03-09.
- ^ Serbian Scything Competition on Mt. Plavinac photo | stock photos Profimedia #0071934552. Profimedia.rs (2010-06-13). Retrieved on 2011-03-09.
- ^ Krajinski park Goričko. Park-goricko.org (2010-05-21). Retrieved on 2011-03-09.
- ^ Blog Archives. The One Scythe Revolution (2010-02-28). Retrieved on 2011-03-09.
- ^ Newman, Barry (June 29, 2012). "Who Needs a WeedWacker When You Can Use a Scythe? Grim Reaper Jokes Aside, Suburbanites Take Swing at Ancient Mower". Wall Street Journal. Retrieved 1 July 2012.
External links
- Scythe Network, a site dedicated to modern usage, with links to numerous equipment suppliers in North America.
 The dictionary definition of scythe at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of scythe at Wiktionary