Search results
Appearance
The page "Modified Lewis acid" does not exist. You can create a draft and submit it for review or request that a redirect be created, but consider checking the search results below to see whether the topic is already covered.
- A Lewis acid (named for the American physical chemist Gilbert N. Lewis) is a chemical species that contains an empty orbital which is capable of accepting...22 KB (2,761 words) - 09:58, 2 June 2024
- In Lewis acid catalysis of organic reactions, a metal-based Lewis acid acts as an electron pair acceptor to increase the reactivity of a substrate. Common...44 KB (5,017 words) - 06:20, 11 November 2023
- Mechoulam R (1985). "Boron trifluoride etherate on alumuna – a modified Lewis acid reagent. An improved synthesis of cannabidiol". Tetrahedron Letters...123 KB (11,382 words) - 16:03, 6 September 2024
- DNA (redirect from Desoxyribonucleic acid)nucleic acid – Synthetic nucleic acid analogues "deoxyribonucleic acid". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster. Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff...166 KB (17,865 words) - 10:19, 31 August 2024
- nitrogenous base. The two main classes of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA). If the sugar is ribose, the polymer is...24 KB (2,853 words) - 22:25, 28 July 2024
- Pentetic acid or diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (DTPA) is an aminopolycarboxylic acid consisting of a diethylenetriamine backbone with five carboxymethyl...15 KB (1,657 words) - 23:16, 18 August 2023
- acids are steroid acids found predominantly in the bile of mammals and other vertebrates. Diverse bile acids are synthesized in the liver. Bile acids...36 KB (4,587 words) - 11:51, 6 September 2024
- Sialic acids are a class of alpha-keto acid sugars with a nine-carbon backbone. The term "sialic acid" (from Greek σίαλον (síalon) 'saliva') was first...29 KB (3,328 words) - 08:07, 3 June 2024
- the first genetically modified organism in 1973, a bacterium resistant to the antibiotic kanamycin. The first genetically modified animal, a mouse, was...223 KB (24,607 words) - 23:09, 19 August 2024
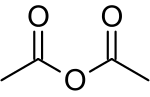
- Acetic anhydride (redirect from Acetic acid anhydride)applications, Lewis acidic scandium salts have also proven effective catalysts. Aromatic rings are acetylated by acetic anhydride. Usually acid catalysts...17 KB (1,392 words) - 13:43, 19 July 2024
- Monomer (section Amino acids)example, the formation of many nylons requires equal amounts of a dicarboxylic acid and diamine. In the case of addition polymerizations, the comonomer content...6 KB (654 words) - 17:11, 7 July 2024
- gamma-Hydroxybutyric acid (GHB) (or γ-hydroxybutyric acid), also known as 4-hydroxybutanoic acid is a naturally occurring neurotransmitter and a depressant...89 KB (9,446 words) - 08:06, 5 September 2024
- Protein metabolism (redirect from Amino acid metabolism)biochemical processes responsible for the synthesis of proteins and amino acids (anabolism), and the breakdown of proteins by catabolism. The steps of protein...27 KB (2,828 words) - 13:35, 3 August 2024
- Peptide (redirect from Amino acid chain length)Peptides are short chains of amino acids linked by peptide bonds. A polypeptide is a longer, continuous, unbranched peptide chain. Polypeptides that have...22 KB (2,418 words) - 23:33, 30 July 2024
- Dissociation constant (section Acid–base reactions)the deprotonation of acids, K is known as Ka, the acid dissociation constant. Strong acids, such as sulfuric or phosphoric acid, have large dissociation...20 KB (3,119 words) - 03:51, 29 February 2024
- carboxy tail, C-terminal end, or COOH-terminus) is the end of an amino acid chain (protein or polypeptide), terminated by a free carboxyl group (-COOH)...6 KB (607 words) - 07:14, 3 September 2024
- groups that can be appended to the ene and enophile moieties. Many useful Lewis acid-catalyzed ene reactions have been also developed, which can afford high...27 KB (3,345 words) - 20:30, 22 July 2024
- Chlorine (redirect from Dephlogisticated marine acid)deposition chambers. It can act as a fluoride ion donor or acceptor (Lewis base or acid), although it does not dissociate appreciably into ClF+ 2 and ClF−...117 KB (13,028 words) - 19:18, 26 August 2024
- In chemistry, an acid dissociation constant (also known as acidity constant, or acid-ionization constant; denoted K a {\displaystyle K_{a}} ) is a...103 KB (11,513 words) - 19:58, 26 August 2024
- Lipid metabolism (section Fatty acid biosynthesis)second step is the addition of fatty acids to the backbone to make phosphatidic acid. Phosphatidic acid is further modified with the attachment of different...23 KB (2,461 words) - 13:32, 23 August 2024
- treated with tannic acid developed roots. The hydrochloric-acid bulb died, and the sulphuric-acid bulb a month later. After the tannic-acid one, a bulb treated
- Churchill (14 February 1939), quoted in Julia Namier, Lewis Namier: A Biography (1971), p. 230 Now the acid test will be applied to the friendship and devotion
- that an acid is a proton donor, while a base is a proton acceptor. Another common definition is the Lewis definition, which indicates that an acid is an