13 Monocerotis
| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Monoceros |
| Right ascension | 06h 32m 54.22948s[1] |
| Declination | 7° 19′ 58.6942″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.498[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | A0 Ib[2] |
| U−B color index | −0.217[2] |
| B−V color index | +0.007[2] |
| Variable type | suspected[3] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | +11.80[4] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: -0.20[1] mas/yr Dec.: -3.48[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 0.83 ± 0.46 mas[1] |
| Distance | 780[5] pc |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | −4.80[6] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 12.0[7] M☉ |
| Radius | 34[6] R☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 2.15[2] cgs |
| Temperature | 10,000[2] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | −0.18[8] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 0[2] km/s |
| Age | 16[7] Myr |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
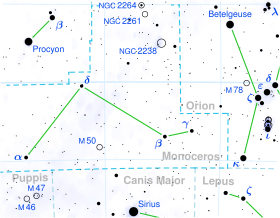
13 Monocerotis (13 Mon) is a class A0 Ib (white supergiant) star in the constellation Monoceros. Its apparent magnitude is 4.5 and it is approximately 780 parsecs (2,500 ly) away.
13 Mon lies within the Monoceros OB1 stellar association,[6] halfway between the Rosette Nebula and NGC 2264, at a distance of about 780 parsecs.[5] It is surrounded by a small reflection nebula listed as Van den Bergh 81 (VdB 81).[9]
13 Monocerotis has been used as a standard star for the A0 Ib spectral class.[10]
Extended photometry of 13 Monocerotis from 1997 to 2000 shows irregular variation of up to 0.04 magnitudes and also a slight trend to become fainter over the period.[11] All the bright A0 - A5 supergiants analysed using Hipparcos satellite data were found to be variable, but 13 Mon was the least variable.[12]
References
- ^ a b c d e Van Leeuwen, F. (2007). "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction". Astronomy and Astrophysics. 474 (2): 653. arXiv:0708.1752. Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V. doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357. Vizier catalog entry
- ^ a b c d e f g Firnstein, M.; Przybilla, N. (2012). "Quantitative spectroscopy of Galactic BA-type supergiants. I. Atmospheric parameters". Astronomy & Astrophysics. 543: A80. arXiv:1207.0308. Bibcode:2012A&A...543A..80F. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201219034.
- ^ Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; et al. (2009). "VizieR Online Data Catalog: General Catalogue of Variable Stars (Samus+ 2007-2013)". VizieR On-line Data Catalog: B/gcvs. Originally published in: 2009yCat....102025S. 1. Bibcode:2009yCat....1.2025S. Vizier catalog entry
- ^ Gontcharov, G. A. (2006). "Pulkovo Compilation of Radial Velocities for 35 495 Hipparcos stars in a common system". Astronomy Letters. 32 (11): 759. arXiv:1606.08053. Bibcode:2006AstL...32..759G. doi:10.1134/S1063773706110065.
- ^ a b Hovhannessian, R. Kh.; Hovhannessian, E. R. (2001). "Gas—Dust Shells around Some Early-Type Stars with an IR Excess (of Emission)". Astrophysics (English translation of Astrofizika). 44 (4): 454. Bibcode:2001Ap.....44..454H. doi:10.1023/A:1014244720865.
- ^ a b c Verdugo, E.; Talavera, A.; Gómez De Castro, A. I. (1999). "Understanding A-type supergiants. I. Ultraviolet and visible spectral atlas". Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement. 137 (2): 351. Bibcode:1999A&AS..137..351V. doi:10.1051/aas:1999487.
- ^ a b Tetzlaff, N.; Neuhäuser, R.; Hohle, M. M. (2011). "A catalogue of young runaway Hipparcos stars within 3 kpc from the Sun". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 410: 190. arXiv:1007.4883. Bibcode:2011MNRAS.410..190T. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17434.x.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) Vizier catalog entry - ^ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012). "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation". Astronomy Letters. 38 (5): 331. arXiv:1108.4971. Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A. doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015. Vizier catalog entry
- ^ Van Den Bergh, S. (1966). "A study of reflection nebulae". Astronomical Journal. 71: 990. Bibcode:1966AJ.....71..990V. doi:10.1086/109995.
- ^ Morgan, W. W.; Roman, Nancy G. (1950). "Revised Standards for Supergiants on the System of the Yerkes Spectral Atlas". Astrophysical Journal. 112: 362. Bibcode:1950ApJ...112..362M. doi:10.1086/145351.
- ^ Adelman, Saul J. (2001). "Differential uvby Photometry of 13 Mon (A0 Ib)". Baltic Astronomy. 10: 385. Bibcode:2001BaltA..10..385A. doi:10.1515/astro-2001-0305.
- ^ Adelman, S. J.; Albayrak, B. (1997). "On the Variability of Early A-Type Supergiants". Information Bulletin on Variable Stars. 4541: 1. Bibcode:1997IBVS.4541....1A.