146 Lucina
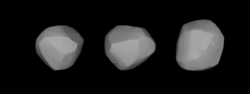 A three-dimensional model of 146 Lucina based on its light curve. | |
| Discovery[1] | |
|---|---|
| Discovered by | Alphonse Borrelly |
| Discovery date | 8 June 1875 |
| Designations | |
| Main belt | |
| Orbital characteristics[2][3] | |
| Epoch 31 July 2016 (JD 2457600.5) | |
| Uncertainty parameter 0 | |
| Observation arc | 130.35 yr (47610 d) |
| Aphelion | 2.89945 AU (433.752 Gm) |
| Perihelion | 2.53641 AU (379.442 Gm) |
| 2.71793 AU (406.597 Gm) | |
| Eccentricity | 0.066786 |
| 4.48 yr (1636.6 d) | |
Average orbital speed | 18.04 km/s |
| 198.102° | |
| 0° 13m 11.863s / day | |
| Inclination | 13.0947° |
| 83.9692° | |
| 146.982° | |
| Earth MOID | 1.53233 AU (229.233 Gm) |
| Jupiter MOID | 2.14062 AU (320.232 Gm) |
| TJupiter | 3.319 |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Dimensions | 132.21±2.4 km[3] 131.893 km[4] |
| Mass | 2.4×1018 kg |
Mean density | 2.0 g/cm³ |
Equatorial surface gravity | 0.0369 m/s² |
Equatorial escape velocity | 0.0699 km/s |
| 18.557 h (0.7732 d) | |
| 0.0531±0.002[3] 0.0496 ± 0.0107[4] | |
| Temperature | ~169 K |
| C[4] (Tholen) | |
| 8.20,[3] 8.277[4] | |
146 Lucina is a main-belt asteroid that was discovered by Alphonse Borrelly on June 8, 1875, and named after Lucina, the Roman goddess of childbirth. It is large, dark and has a carbonaceous composition.
Photometric observations of this asteroid made during 1979 and 1981 gave a light curve with a period of 18.54 hours.[5]
Two stellar occultations by Lucina have been observed so far, in 1982 and 1989. During the first event, a possible small satellite with an estimated 5.7 km diameter was detected at a distance of 1,600 km from 146 Lucina.[6] A 1992 search using a CCD failed to discover a satellite larger than 0.6 km, although it may have been obscured by occultation mask.[7] Further evidence for a satellite emerged in 2003, this time based on astrometric measurements.[8]
References
- ^ [1]
- ^ "The Asteroid Orbital Elements Database". astorb. Lowell Observatory.
- ^ a b c d Yeomans, Donald K., "146 Lucina", JPL Small-Body Database Browser, NASA Jet Propulsion Laboratory, retrieved 12 May 2016.
- ^ a b c d Pravec, P.; et al. (May 2012), "Absolute Magnitudes of Asteroids and a Revision of Asteroid Albedo Estimates from WISE Thermal Observations", Asteroids, Comets, Meteors 2012, Proceedings of the conference held May 16–20, 2012 in Niigata, Japan, no. 1667, Bibcode:2012LPICo1667.6089P. See Table 4.
- ^ Schober, H. J. (July 1983), "The large C-type asteroids 146 Lucina and 410 Chloris, and the small S-type asteroids 152 Atala and 631 Philippina - Rotation periods and lightcurves", Astronomy and Astrophysics Supplement Series, vol. 53, pp. 71–75, Bibcode:1983A&AS...53...71S.
- ^ Arlot, J. E.; et al. (February 1985), "A possible satellite of (146) Lucina", Icarus, vol. 61, pp. 224–231, Bibcode:1985Icar...61..224A, doi:10.1016/0019-1035(85)90104-6.
- ^ Stern, S. Alan; Barker, Edwin S. (December 1992), "A CCD search for distant satellites of asteroids 3 Juno and 146 Lucina", In Lunar and Planetary Inst., Asteroids, Comets, Meteors 1991, pp. 577–581, Bibcode:1992acm..proc..577S.
- ^ Kikwaya, J.-B.; et al. (March 2003), "Does 146 Lucina Have a Satellite? An Astrometric Approach", 34th Annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, March 17–21, 2003, League City, Texas, abstract no.1214, Bibcode:2003LPI....34.1214K.
External links
