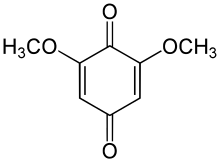
2,6-Dimethoxybenzoquinone
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,6-Dimethoxycyclohexa-2,5-diene-1,4-dione
| |
| Other names
2,6-Dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone; 2,6-DMBQ
| |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.007.714 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C8H8O4 | |
| Molar mass | 168.148 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
2,6-Dimethoxybenzoquinone (2,6-DMBQ) is a benzoquinone, a chemical compound found in Rauvolfia vomitoria[1] and in Tibouchina pulchra.[2]
Toxicity
2,6-DMBQ is mutagenic,[3][4] cytotoxic,[4] genotoxic,[5] and hepatotoxic.[6][7][8]
References
- ^ A note on the occurrence of 2,6-dimethoxybenzoquinone in Rauwolfia vomitoria. S. Morris Kupchan and Mang E. Obasi, Journal of the American Pharmaceutical Association, Volume 49, Issue 4, pages 257–258, April 1960, doi:10.1002/jps.3030490421
- ^ Plant anticancer agents. XI. 2,6-dimethoxybenzoquinone as a cytotoxic constituent of Tibouchina pulchra. Jones E., Ekundayo O. and Kingston D.G.I., Journal of natural products, Jul-Aug 1981, doi:10.1021/np50016a019
- ^ Canonero R; Poggi C Mutagenic activity of 2,6-dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone, produced during the nitrosation of dimethophrine, in V 79 cells. Bollettino della Societa italiana di biologia sperimentale (1988), 64(1), 61-8
- ^ a b Brambilla G; Robbiano L; Cajelli E; Martelli A; Turmolini F; Mazzei M Cytotoxic, DNA-damaging and mutagenic properties of 2,6-dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone, formed by dimethophrine-nitrite interaction. The Journal of pharmacology and experimental therapeutics (1988), 244(3), 1011-5
- ^ Mazzei M; Roma G; Balbi A; Sottofattori E; Robbiano L Formation of 2,6-dimethoxy-1,4-benzoquinone, a highly genotoxic compound, from the reaction of sodium nitrite with the sympathomimetic drug dimethophrine in acidic aqueous solution. Il Farmaco; edizione scientifica (1988), 43(6), 523-38
- ^ Moore, Gregory A.; Rossi, Luisa; Nicotera, Pierluigi; Orrenius, Sten; O'Brien, Peter J. Quinone toxicity in hepatocytes: studies on mitochondrial calcium release induced by benzoquinone derivatives. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics (1987), 259(2), 283-95.
- ^ Siraki, Arno G.; Chan, Tom S.; O'Brien, Peter J. Application of Quantitative Structure-Toxicity Relationships for the Comparison of the Cytotoxicity of 14 p-Benzoquinone Congeners in Primary Cultured Rat Hepatocytes Versus PC12 Cells. Toxicological Sciences (2004), 81(1), 148-159
- ^ Chan, Katie; Jensen, Neil; O'Brien, Peter J. Structure-activity relationships for thiol reactivity and rat or human hepatocyte toxicity induced by substituted p-benzoquinone compounds. Journal of Applied Toxicology (2008), 28(5), 608-620.
