2022 Slovenian parliamentary election
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
All 90 seats to the National Assembly 46 seats needed for a majority | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Parliamentary elections will be held in Slovenia no later than 5 June 2022.
Electoral system
The 90 members of the National Assembly are elected by two methods. 88 are elected by open list proportional representation in eight 11-seat constituencies and seats are allocated to the parties at the constituency level using the Droop quota. The elected Deputies are identified by ranking all of a party's candidates in a constituency by the percentage of votes they received in their district. The seats that remain unallocated are allocated to the parties at the national level using the D'Hondt method with an electoral threshold of 4%.[1] Although the country is divided into 88 electoral districts, deputies are not elected from all 88 districts. More than one deputy is elected in some districts, which results in some districts not having an elected deputy (for instance, 21 of 88 electoral districts did not have an elected deputy in the 2014 elections).[2] Parties must have at least 35% of their lists from each gender, except in cases where there are only three candidates. For these lists, there must be at least one candidate of each gender.[3][4]
Two additional deputies are elected by the Italian and Hungarian minorities. Voters rank all of the candidates on the ballot paper using numbers (1 being highest priority). A candidate is awarded the most points (equal to the number of candidates on the ballot paper) when a voter ranks them first. The candidate with most points wins.[5][1]
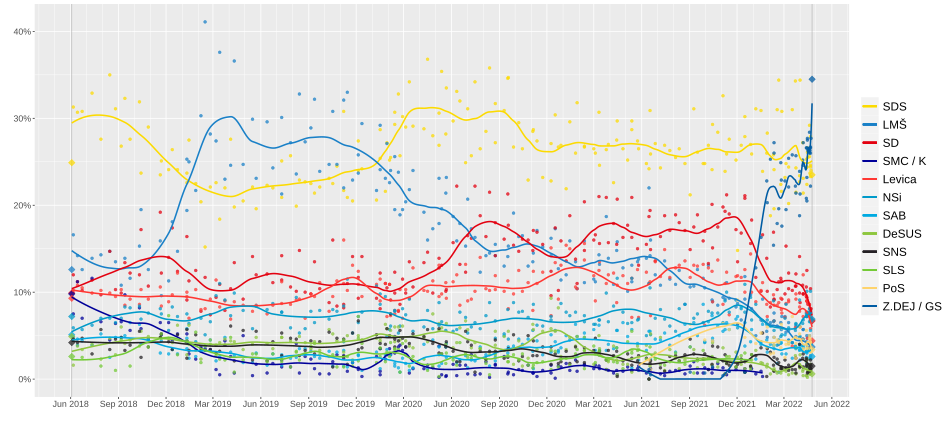
Opinion polls
References
- ^ a b National Assembly of the Republic of Slovenia State Election Commission
- ^ "Imamo sploh legalno volilno zakonodajo za državni zbor?". Časnik Večer d.o.o. (in Slovenian). Retrieved 2018-03-18.
- ^ Electoral system IPU
- ^ "Zakon o volitvah v državni zbor (ZVDZ)". pisrs. Retrieved 2018-03-17.
- ^ "Navodila in rokovnik - DZ 2018 | Državna volilna komisija". Državna volilna komisija. Retrieved 2018-06-16.









