Celtis lindheimeri
Appearance
| Celtis lindheimeri | |
|---|---|
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | Plantae |
| Clade: | Tracheophytes |
| Clade: | Angiosperms |
| Clade: | Eudicots |
| Clade: | Rosids |
| Order: | Rosales |
| Family: | Cannabaceae |
| Genus: | Celtis |
| Species: | C. lindheimeri
|
| Binomial name | |
| Celtis lindheimeri Engelm. ex K. Koch
| |
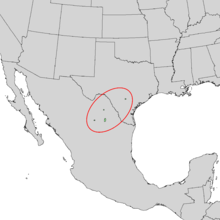
| |
| Natural range of Celtis lindheimeri | |
Celtis lindheimeri, also called Lindheimer's hackberry,[2] is a species of tree in the family Cannabaceae. It is typically found in areas of central Texas and northeastern Mexico. It has a height averaging 9 meters, and produces a reddish-brown berry. It is a species closely related to netleaf hackberry which is common in western United States. The Spanish common name is "palo blanco", meaning "white tree", which is commonly used to identify this tree. It is named after its discoverer Ferdinand Lindheimer, a German-born botanical collector and Texas newspaper editor.

References
[edit]- ^ Samain, M.-S.; Fuentes, A.C.D.; Martínez Salas, E. (2021). "Celtis lindheimeri". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2021: e.T34001A126290816. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2021-1.RLTS.T34001A126290816.en. Retrieved 15 November 2021.
- ^ USDA, NRCS (n.d.). "Celtis lindheimeri". The PLANTS Database (plants.usda.gov). Greensboro, North Carolina: National Plant Data Team. Retrieved 28 June 2016.

