Edge-notched card
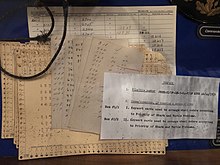
Edge-notched cards or edge-punched cards are a system used to store a small amount of binary or logical data on paper index cards, encoded via the presence or absence of notches in the edges of the cards.[1] The notches allowed efficient sorting and selecting of specific cards matching multiple desired criteria, from a larger number of cards in a paper-based database of information. In the mid-20th century they were sold under names such as Cope-Chat cards, E-Z Sort cards, McBee Keysort cards,[2] and Indecks cards.[3] They are also informally called needle cards since they can be sorted with long knitting needles.
Overview



Edge-notched cards are a manual data storage and manipulation technology used for specialized data storage and cataloging applications through much of the 20th century. An early instance of something like this methodology appeared in 1904.[4] While there were many variants, by the mid-20th century a popular version consisted of 5-by-8-inch (13 by 20 cm) paperboard cards with holes punched at regular intervals along all four edges, a short distance in from the edges. The center of the card might be blank space for information to be written, or contain a pre-printed form, or contain a microform image in the case of edge-notched aperture cards.[5][6]
To record data, the paper stock between a hole and the nearest edge was removed by a special notching tool. The holes were assigned a meaning dependent upon a particular application. For example, one hole might record the answer to a yes/no question on a survey, with the presence of a notch meaning "yes". More-complex data was encoded using a variety of schemes, often using a superimposed code which allows more distinct categories to be coded than the number of holes available.
To allow a visual check that all cards in a deck were oriented the same way, one corner of each card was beveled, much like Hollerith punched cards. Edge-notched cards, however, were not intended to be read by machines such as IBM card sorters. Instead, they were manipulated by passing one or more slim needles through selected holes in a group of cards. As the needles were lifted, the cards that were notched in the hole positions where the needles were inserted would be left behind as rest of the deck was lifted by the needles. Using two or more needles produced a logical and function. Combining the cards from two different selections produced a logical or. Quite complex manipulations, including sorting were possible using these techniques.[7]
Applications
Before the widespread use of computers, some public libraries used a system of small edge-notched cards in paper pockets in the back of library books to keep track of them.[8][9] Edge-notched cards were used for course scheduling in some high schools and colleges during the same era.[10]
The corporate library of a division of E. I. du Pont de Nemours and Company maintained a subject catalog on two-level edge-punched cards (Royal-McBee Keysort cards) that grew to 15,000 cards before the librarians began to consider keeping the catalog on a computer.[11]
See also
Notes
- ^ Casey 1958.
- ^ Casey 1958, p. v.
- ^ Kelly 2008.
- ^ Casey 1958, p. 4.
- ^ Ellsworth 1951.
- ^ Cady 1999, p. 182.
- ^ For example: Robert S. Casey & James W. Perry, "Elementary manipulations of hand-sorted punched cards", in Casey 1958, pp. 12–29.
- ^ Kilgour 1939.
- ^ "An old library book card". plakboek.livejournal.com. Retrieved 2011-03-29. An example of an edge-notched library card.
- ^ Anderson & Van Dyke 1963.
- ^ Grandine, Starr & Putscher 1961.
References
- Anderson, Lester W.; Van Dyke, Lauren Andrew (1963). "Machine and marginal punch card programming and registration". Secondary school administration. Boston: Houghton Mifflin. pp. 178–180. OCLC 186532.
- Cady, Susan A. (1999). "Microfilm technology and information systems". In Bowden, Mary Ellen; Hahn, Trudi Bellardo; Williams, Robert Virgil (eds.). Proceedings of the 1998 Conference on the History and Heritage of Science Information Systems. ASIS monograph series. Medford, NJ: Published for the American Society for Information Science and the Chemical Heritage Foundation by Information Today. pp. 177–186. CiteSeerX 10.1.1.99.3796. ISBN 1573870803. OCLC 42022214.
Early aperture cards were sometimes mounted on McBee Keysort cards that could be notched on the margins to indicate an index term and then sorted manually with tools resembling knitting needles.
- Casey, Robert S., ed. (1958) [1951]. Punched cards: their applications to science and industry (2nd ed.). New York: Reinhold Pub. Corp. OCLC 574357. Edge-notched cards are mentioned in multiple chapters in this collection.
- Ellsworth, Russell S. (October 1951). "New horizons with microfilm". American Documentation. 2 (4): 221–228. doi:10.1002/asi.5090020407. An article that describes the use of microform images in edge-notched aperture cards.
- Grandine, Joseph D.; Starr, Eva M.; Putscher, Richard E. (July 1961). "Report index searching on the Bendix G-15D computer". Journal of Chemical Documentation. 1 (2): 79–83. doi:10.1021/c160002a020.
- Kelly, Kevin (17 June 2008). "One dead media". kk.org. Retrieved 2008-06-18. An article on edge-notched cards that mentions their use in the production of The Last Whole Earth Catalog in the 1970s, among other projects. Kelly observed that as a medium edge-notched cards were "dead", but some commenters on the article suggested otherwise.
- Kilgour, Frederick G. (15 February 1939). "A new punched card for circulation records". Library Journal. 64 (4): 131–133. An article introducing McBee Keysort edge-notched cards for use in library circulation records. The author, a technology early adopter, later became a pioneer in library computerization.
