Battle of Burdigala
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2023) |
| Battle of Burdigala | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Cimbrian War | |||||||
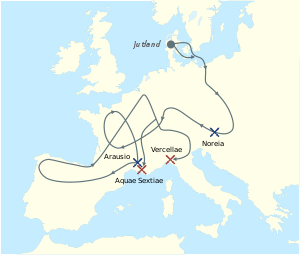 Map of the invasion route of the Cimbrian and Teuton territory | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
A combined Germanic-Celtic army including:
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
Lucius Cassius Longinus † Lucius Calpurnius Piso † Gaius Popillius Laenas | Divico | ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 40,000[1] | unknown but severely outnumbering the Romans[2] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
| 10,000[1] | Relatively low | ||||||
The Battle of Burdigala (the Roman name for Bordeaux, with stress on the 'i') was a battle of the Cimbrian War that occurred in the year 107 BC. The battle was fought between a combined Germanic-Celtic army including the Helvetian Tigurini under the command of Divico, and the forces of the Roman Republic under the command of Lucius Cassius Longinus, Lucius Caesoninus, and Gaius Popillius Laenas. Longinus and Caesoninus were killed in the action and the battle resulted in a victory for the combined tribes.
Context
In 113 BC, the Germanic tribes of the Cimbri and the Teutons invaded Roman territory, defeating an army under the command of Gnaeus Papirius Carbo in Noricum at the Battle of Noreia. The Germanic tribes demanded to be given the right to settle in Roman territory. When denied, the Germanic force marched all the way to Gallia Narbonensis where they defeated another Roman army under the command of Marcus Junius Silanus at an unknown location. It was thereafter that the Germans forged an alliance with the Tigurini tribe and Rome prepared for an invasion of the lower peninsula that did not come.
Prelude
In 107 BC, the Roman Senate launched another campaign under Lucius Cassius Longinus, Lucius Caesoninus, and Gaius Popillius Laenas (son of Publius Popillius Laenas), to defend one of their allied tribes. At first, all went well for Rome. Just outside Tolosa, the combatants met and, despite the huge numbers of Germans and their allies, Longinus defeated them and they retreated in disorder, leaving behind a large number of baggage wagons. Flushed with his success, Longinus followed them, but was reluctant to leave behind the captured baggage train, which slowed his army down significantly.[1]
The battle
By the time he reached Burdigala, it was heavily fortified and the barbarians had been reinforced. Longinus made a camp on a defensible hilltop near Burdigala and decided to attack the oppidum. He put the camp under the command of Popillius Laenas and marched on Burdigala, but did so without tightening ranks or marching in squares. He apparently did not even bother to send out scouts. Near Burdigala, Longinus and his army were ambushed by the combined tribes. He was killed in the action along with 10,000 of his men. The remaining Roman forces were saved from the same fate by Laenas, who was forced to surrender a majority of the army's supplies in return for permission to retire from the field "under the yoke".[1]
Aftermath
When news of the Roman defeat reached the Gallic countryside, several towns rose in revolt including Toulouse. The following year, another consul, Quintus Servilius Caepio, marched on the rebellious Gallic forces and captured Toulouse, capturing the Gold of Tolosa (Aurum Tolosanum) amongst other spoils. Much of these spoils "vanished" whilst being transferred to Massilia. In 105 BC, the Germanic forces and the Tigurini won a further victory against the Romans at the Battle of Arausio.
References
Bibliography
- Gaius Sallustius Crispus. Jugarta, ch. 32.
- Titus Livius. Epítome, ch. 65.
- Paulus Orosius. Historias. Libro V, ch. 15.
- Julius Caesar. Commentaries on the Gallic Wars Book I, ch. 7 (leer).
- Publius Cornelius Tacitus. Germania, ch. 37.
External links
- "The Cimbrian War". Archived from the original on 4 January 2010. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
