Yerkes (crater)
 LRO image | |
| Coordinates | 14°36′N 51°42′E / 14.6°N 51.7°E |
|---|---|
| Diameter | 36 km |
| Depth | None |
| Colongitude | 310° at sunrise |
| Eponym | Charles T. Yerkes |

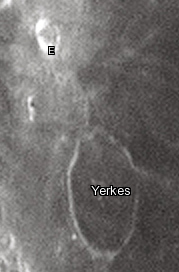
Yerkes is a lunar impact crater near the western edge of Mare Crisium. It was named after American financier Charles Yerkes.[1] To the east of Yerkes is the crater Picard, and farther to the north is Peirce.
In the past the interior of this crater has been almost completely inundated by lava, leaving only a shallow remnant of a rim above the mare. The rim is widest on the western and southern portions, and barely existent to the east, forming a thin curve in the surface. A low ridge runs from the north rim to Yerkes E in the north-northwest. The floor has a similar albedo to the nearby mare, so the feature is not sharply distinguished from the surroundings.
Satellite craters
By convention these features are identified on lunar maps by placing the letter on the side of the crater midpoint that is closest to Yerkes.
| Yerkes | Latitude | Longitude | Diameter |
|---|---|---|---|
| E | 15.90° N | 50.67° E | 9.91 km |
| V | 15.24° N | 50.49° E | 3.7 km |
References
- ^ "Yerkes (crater)". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology Research Program.
- Andersson, L. E.; Whitaker, E. A. (1982). NASA Catalogue of Lunar Nomenclature. NASA RP-1097.
- Bussey, B.; Spudis, P. (2004). The Clementine Atlas of the Moon. New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-81528-4.
- Cocks, Elijah E.; Cocks, Josiah C. (1995). Who's Who on the Moon: A Biographical Dictionary of Lunar Nomenclature. Tudor Publishers. ISBN 978-0-936389-27-1.
- McDowell, Jonathan (July 15, 2007). "Lunar Nomenclature". Jonathan's Space Report. Retrieved 2007-10-24.
- Menzel, D. H.; Minnaert, M.; Levin, B.; Dollfus, A.; Bell, B. (1971). "Report on Lunar Nomenclature by the Working Group of Commission 17 of the IAU". Space Science Reviews. 12 (2): 136–186. Bibcode:1971SSRv...12..136M. doi:10.1007/BF00171763. S2CID 122125855.
- Moore, Patrick (2001). On the Moon. Sterling Publishing Co. ISBN 978-0-304-35469-6.
- Price, Fred W. (1988). The Moon Observer's Handbook. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-33500-3.
- Rükl, Antonín (1990). Atlas of the Moon. Kalmbach Books. ISBN 978-0-913135-17-4.
- Webb, Rev. T. W. (1962). Celestial Objects for Common Telescopes (6th revised ed.). Dover. ISBN 978-0-486-20917-3.
- Whitaker, Ewen A. (1999). Mapping and Naming the Moon. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-62248-6.
- Wlasuk, Peter T. (2000). Observing the Moon. Springer. ISBN 978-1-85233-193-1.
