Vena comitans
| Vena comitans | |
|---|---|
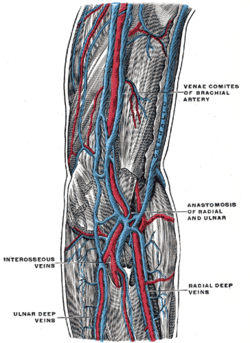 The deep veins of the arm. (Venae comitantes labeled as venae comites at upper right.) | |
| Identifiers | |
| TA98 | A12.0.00.031 |
| TA2 | 3905 |
| FMA | 76841 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
Vena comitans is Latin for accompanying vein and is also known as a satellite vein.[1] It refers to a vein that is usually paired, with both veins lying on the sides of an artery. They are found in close proximity to arteries so that the pulsations of the artery aid venous return. Because they are generally found in pairs, they are often referred to by their plural form: venae comitantes.
Venae comitantes are usually found with certain smaller arteries, especially those in the extremities. Larger arteries, on the other hand, generally do not have venae comitantes. They usually have a single, similarly sized vein which is not as intimately associated with the artery.
Examples
Examples of arteries and their venae comitantes:
- Radial artery and radial veins
- Ulnar artery and ulnar veins
- Brachial artery and brachial veins
- Anterior tibial artery and anterior tibial veins
- Posterior tibial artery and posterior tibial veins
- Fibular artery and fibular veins
Examples of arteries that do not have venae comitantes (i.e. those that have "regular" veins):
- Axillary artery and the axillary vein
- Subclavian artery and the subclavian vein
References
- ^ Standring, Susan (2016). Gray's anatomy : the anatomical basis of clinical practice (Forty-first ed.). [Philadelphia]. p. 131. ISBN 9780702052309.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link)
