Rheobatrachus silus
| Rheobatrachus silus | |
|---|---|

| |
| A specimen of a southern gastric-brooding frog | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Myobatrachidae |
| Genus: | †Rheobatrachus |
| Species: | †R. silus
|
| Binomial name | |
| †Rheobatrachus silus (Liem, 1973)
| |
Rheobatrachus silus, commonly called southern gastric-brooding frog, is a extinct species of gastric-brooding frog native to Australia.
Distribution
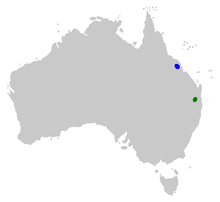
The southern gastric-brooding frog was discovered in 1972 and described in 1973,[2] though there is one publication suggesting that the species was discovered in 1914 (from the Blackall Range).[3] Rheobatrachus silus was restricted to the Blackall Range and Conondale Ranges in southeast Queensland, north of Brisbane, between elevations of 350 and 800 metres (1,150 and 2,620 ft) above sea level.[4] The areas of rainforest, wet sclerophyll forest and riverine gallery open forest that it inhabited were limited to less than 1,400 km2 (540 sq mi). They were recorded in streams in the catchments of the Mary, Stanley and Mooloolah Rivers.[5]
Description
The southern gastric-brooding frog was a medium-sized species of dull colouration, with large protruding eyes positioned close together and a short, blunt snout. Its skin was moist and coated with mucus. The fingers were long, slender, pointed and unwebbed and the toes were fully webbed. The arms and legs were large in comparison to the body. In both species the females were larger than the males.

The southern gastric-brooding frog was a dull grey to slate coloured frog that had small patches, both darker and lighter than the background colouration, scattered over dorsal surface (back). The ventral surface was white or cream, occasionally with yellow blotches. The arms and legs had darker brown barring above and were yellow underneath. There was a dark stripe that ran from the eye to the base of the forelimb. The ventral surface (belly) was white with large patches of cream or pale yellow. The toes and fingers were light brown with pale brown flecking. The end of each digit had a small disc and the iris was dark brown. The skin was finely granular and the tympanum was hidden. The male Southern Gastric Brooding Frog was 33 to 41 millimetres (1.3 to 1.6 in) in length and the female 44 to 54 millimetres (1.7 to 2.1 in) in length.[6]
Ecology and behaviour
The southern gastric-brooding frog lived in areas of rainforest, wet sclerophyll forest and riverine gallery open forest. They were a predominately aquatic species closely associated with watercourses and adjacent rock pools and soaks. Streams that the southern gastric-brooding frog were found in were mostly permanent and only ceased to flow during years of very low rainfall.[7] Sites where southern gastric-brooding frogs were found usually consisted of closed forests with emergent eucalypts, however there was sites where open forest and grassy ground cover were the predominant vegetation. There is no record for this species occurring in cleared riparian habitat. Searches during spring and summer showed that the favored diurnal habitat was at the edge of rock pools, either amongst leaf litter, under or between stones or in rock crevices. They were also found under rocks in shallow water. Winter surveys of sites where southern gastric-brooding frogs were common only recovered two specimens, and it is assumed that they hibernated during the colder months. Adult males preferred deeper pools than the juveniles and females which tended to inhabit shallower, newly created (after rain) pools that contained stones and/or leaf litter. Individuals only left themselves fully exposed while sitting on rocks during light rain.[5]
The call of the southern gastric-brooding frog has been described as an "eeeehm...eeeehm" with an upward inflection. It lasts for around 0.5 s and was repeated every 6–7 seconds.
Southern gastric-brooding frogs have been observed feeding on insects from the land and water. In aquarium situations Lepidoptera, Diptera and Neuroptera were eaten.[2]
Being a largely aquatic species the southern gastric-brooding frog was never recorded more than 4 m (13 ft) from water. Studies by Glen Ingram showed that the movements of this species were very restricted. Of ten juvenile frogs, only two moved more than 3 metres between observations. Ingram also recorded the distance moved along a stream by seven adult frogs between seasons (periods of increased activity, usually during summer). Four females moved between 1.8–46 metres (5 ft 11 in – 150 ft 11 in) and three males covered 0.9–53 m (2 ft 11 in – 173 ft 11 in). Only three individuals moved more than 5.5 m (18 ft) (46 m, 46 m and 53 m). It appeared that throughout the breeding season adult frogs would remain in the same pools or cluster of pools, only moving out during periods of flooding or increased flow.[5]
De-extinction attempt
Scientists are making progress in their efforts to bring the gastric-brooding frog species back to life using somatic-cell nuclear transfer (SCNT), a method of cloning.[8]
In March 2013, Australian scientists successfully created a living embryo from non-living preserved genetic material. These scientists from the University of Newcastle Australia led by Prof Michael Mahony, who was the scientist who first discovered the northern gastric-brooding frog, Simon Clulow and Prof Mike Archer from the University of New South Wales hope to continue using somatic-cell nuclear transfer methods to produce an embryo that can survive to the tadpole stage. "We do expect to get this guy hopping again," says UNSW researcher Mike Archer.[9]
The scientists from the University of Newcastle have also reported successful freezing and thawing (cryopreservation) of totipotent amphibian embryonic cells,[10] which along with sperm cryopreservation[11] provides the essential "proof of concept" for the use of cryostorage as a genome bank for threatened amphibians and also other animals.
References
- ^ IUCN SSC Amphibian Specialist Group (2022). "Rheobatrachus silus". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2022. IUCN: e.T19475A78430533.
- ^ a b Liem, David S. (1973). "A new genus of frog of the family Leptodactylidae from S. E. Queensland, Australia". Memoirs of the Queensland Museum. 16 (3): 459–470.
- ^ Ingram, G. J. (1991). "The earliest records of the extinct platypus frog". Memoirs of the Queensland Museum. 30 (3): 454.
- ^ Hines, H., Mahony, M. and McDonald, K. 1999. An assessment of frog declines in Wet Subtropical Australia. In: A. Campbell (ed.), Declines and Disappearances of Australian Frogs. Environment Australia.
- ^ a b c Ingram, G. J. (1983). "Natural History". In: M. J. Tyler (ed.), The Gastric Brooding Frog, pp. 16–35. Croom Helm, London.
- ^ "AmphibiaWeb - Rheobatrachus silus". amphibiaweb.org. Retrieved 2023-10-16.
- ^ Meyer, E., Hines, H. and Hero, J.-M. (2001). "Southern Gastric-brooding Frog, Rheobatrachus silus". In: Wet Forest Frogs of South-east Queensland, pp. 34–35. Griffith University, Gold Coast.
- ^ Nosowitz, Dan (15 March 2013) Scientists Resurrect Bonkers Extinct Frog That Gives Birth Through Its Mouth. popsci.com
- ^ Messenger, Stephen (15 March 2013) Scientists successfully create living embryo of an extinct species. treehugger.com
- ^ Moreira, Nei; Lawson, Bianca; Clulow, Simon; Mahony, Michael J.; Clulow, John (2013). "Towards gene banking amphibian maternal germ lines: short-term incubation, cryoprotectant tolerance and cryopreservation of embryonic cells of the frog, Limnodynastes peronii". PLOS ONE. 8 (4): e60760. Bibcode:2013PLoSO...860760L. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0060760. ISSN 1932-6203. PMC 3618038. PMID 23577155.
- ^ Browne, Robert; Mahony, Clulow (2002). "A comparison of sucrose, saline, and saline with egg-yolk diluents on the cryopreservation of cane toad (Bufo marinus) sperm". Cryobiology. 44 (251–157): 251–7. doi:10.1016/S0011-2240(02)00031-7. PMID 12237090.
Bibliography
- Barker, J.; Grigg, G. C.; Tyler, M. J. (1995): A Field Guide to Australian Frogs. Surrey Beatty & Sons.
- Pough, F. H.; Andrews, R. M.; Cadle, J. E.; Crump, M.; Savitsky, A. H. & Wells, K. D. (2003): Herpetology (3rd ed.). Pearson Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, New Jersey.
- Ryan, M. (ed.) (2003): Wildlife of Greater Brisbane. Queensland Museum, Brisbane.
- Ryan, M. & Burwell, C. (eds.) (2003): Wildlife of Tropical North Queensland. Queensland Museum, Brisbane.
- Tyler, M. J. (1984): There's a frog in my throat/stomach. William Collins Pty Ltd, Sydney. ISBN 0-00-217321-2
- Tyler, M. J. (1994): Australian Frogs – A Natural History. Reed Books.
- Zug, G. E.; Vitt, L. J. & Caldwell, J. P. (2001): Herpetology (2nd ed.). Academic Press, San Diego, California.

