Canon de 340 modèle 1912 à berceau
| Canon de 340 modèle 1912 à berceau | |
|---|---|
 A Canon de 340 modèle 1912 à berceau in US service Haussimont, France. | |
| Type | Railway gun |
| Place of origin | France |
| Service history | |
| In service | 1916-1945 |
| Used by | |
| Wars | World War I World War II |
| Production history | |
| Designed | 1915 |
| Produced | 4 during 1915 2 during 1917 |
| No. built | 6 |
| Specifications | |
| Mass | 166 t (163 long tons; 183 short tons) |
| Length | 33.7 m (111 ft) |
| Barrel length | 15.3 m (50 ft) L/45[1] |
| Shell | Separate loading bagged charges and projectiles |
| Caliber | 34 cm (13.4 in) |
| Breech | Interrupted screw breech |
| Recoil | Cradle recoil[1] |
| Carriage | Two six-axle rail bogies |
| Elevation | 0 to +37° |
| Traverse | None |
| Rate of fire | 1 round every six minutes |
| Muzzle velocity | 927 m/s (3,040 ft/s) |
| Maximum firing range | 37.6 km (23.4 mi)[1] |
The Canon de 340 modèle 1912 à berceau was a French railway gun used by the French Army and the United States Army during World War I. The guns were used again by the French Army during World War II.
History
Although the majority of combatants had heavy field artillery prior to the outbreak of the First World War, none had adequate numbers of heavy guns in service, nor had they foreseen the growing importance of heavy artillery once the Western Front stagnated and trench warfare set in. Since aircraft of the period were not yet capable of carrying large diameter bombs the burden of delivering heavy firepower fell on the artillery. Two sources of heavy artillery suitable for conversion to field use were surplus coastal defense guns and naval guns.[2]
However, a paradox faced artillery designers of the time; while large caliber naval guns were common, large caliber land weapons were not due to their weight, complexity, and lack of mobility. Large caliber field guns often required extensive site preparation because the guns had to be broken down into multiple loads light enough to be towed by a horse team or the few traction engines of the time and then reassembled before use. Building a new gun could address the problem of disassembling, transporting and reassembling a large gun, but it did not necessarily address how to convert existing heavy weapons to make them more mobile. Rail transport proved to be the most practical solution because the problems of heavy weight, lack of mobility and reduced setup time were addressed.[2]
Design
The Canon de 340 modèle 1912 à berceau started life as six 340mm/45 Modèle 1912 naval guns as used on the Bretagne class of super-dreadnoughts. The guns converted were surplus guns that were made available when the Normandie class were canceled. The guns were typical built-up guns of the period with steel construction consisting of a rifled steel liner with several layers of reinforcing hoops and an interrupted screw breech.[3]
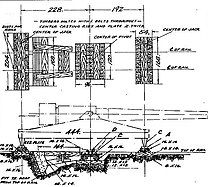
The carriages consisted of a large rectangular steel base, which was suspended on two six-axle railroad bogies manufactured by St. Chamond. The number of axles was determined by the weight limit for European railways of 17 tonnes per axle.[2] These were the longest range guns available to the French and US Army during the first world war and although well regarded they were time-consuming to set up with 2–5 days of site preparation being required. The site preparation consisted of excavating a large pit underneath the breech of the gun and lining it with timbers to accommodate the recoil of the gun at high angles of elevation +37°.[3] Sections of the rail bed were also reinforced in front of and behind the carriage to provide a level surface for the gun. Once on site the carriage was positioned over the gun pit and four screw jacks attached to the corners of the carriage and one under the center were lowered to take weight off of the axles which allowed the rail bogies to be removed from under the carriage. The carriage then rested on these jacks and the gun had to be aligned with the target ahead of time because there was no traverse. The gun barrels were held in a gun cradle that was trunnioned far to the rear in order to provide the greatest amount of elevation possible and a large counterweight near the breech balanced the preponderance of the barrel which was well forward. The guns used a berceau or cradle recoil system with five hydro-pneumatic recoil cylinders arranged around the barrel. To load the guns were lowered and a derrick at the rear of the carriage could be used to lift projectiles from the ammunition wagon.[3]
World War I
The first four guns were built during 1915 and came into service in 1916 with another two being built in 1917 and coming into service during 1918. Two of the guns were assigned to the US Army. One gun was sent to the Italian Front during 1917 to reinforce the Italians.[4] All six of the guns survived World War I and were placed in reserve after the war.[5]
World War II
All six guns were mobilized by the French Army during World War II. Two guns were assigned to the 2nd battery of Heavy Artillery Regiment 372° of the ALVF near Metzange. Two guns were assigned to the 7th battery of Heavy Artillery Regiment 372° of the ALVF (Artillerie Lourde sur Voie Ferrée) near Le Pont-de-Claix. Two guns were assigned to the 8th battery of Heavy Artillery Regiment 372° of the ALVF near Lutterbach.[6] All six guns survived the Fall of France and three were given to the Italians who gave them the designation Cannoni da 340/45 Mod. 1912 ALVF and considered using them for the defense of their naval base at Taranto but were only evaluated due to a lack of ammunition. Three guns were used by the Germans under the designation 34 cm Kanone (Eisenbahn) in Wiegenlafette 674(f) and were employed by a Kriegsmarine coastal defense battery at Plouharnel near the port of Lorient.[7]
Ammunition
The guns fired separate loading bagged charges and projectiles. The propellant charge weighed approximately 150 kg (330 lb).
| Designation | Weight |
|---|---|
| HE15A | 465 kg (1,025 lb) |
| HE17 FATO | 445 kg (981 lb) |
| HE32-6 FATO | 432 kg (952 lb)[8] |
Gallery
-
A diagram showing the carriage details and the gun pit.
-
A French gun in a revetment and covered with camouflage netting at Glisy, France.
-
A gun assigned to the US Army in a revetment. It has been jacked up and the bogies are being removed.
-
A gun with its bogies removed showing its screw jacks.
-
A camouflaged US Army gun in action.
References
- ^ a b c Batchelor, John (1973). Rail gun. Hogg, Ian. New York: Scribner. p. 18. ISBN 0684133423. OCLC 760898.
- ^ a b c Hogg, Ian (2004). Allied Artillery of World War One. Ramsbury: Crowood. pp. 129–134 & 218. ISBN 1861267126. OCLC 56655115.
- ^ a b c Harry W, Miller (1921). "Railway Artillery Guns 1921". eugeneleeslover.com. Retrieved 2019-04-15.
- ^ "340 mm Modèle 1912 à berceau dit "plate-forme"". www.artillerie.asso.fr. Retrieved 2019-04-15.
- ^ Romanych, Marc (2017-08-24). Railway Guns of World War I. Heuer, Greg,, Noon, Steve. London: Osprey. pp. 13–24. ISBN 9781472816412. OCLC 999616340.
- ^ "Wikimaginot - Le wiki de la ligne Maginot". wikimaginot.eu. Retrieved 2019-04-16.
- ^ Zaloga, Steve (2016). Railway Guns of World War II. Dennis, Peter. Oxford: Osprey. pp. 3–7. ISBN 978-1472810687. OCLC 907965829.
- ^ "France 34 cm/45 (13.4") Model 1912 and Model 1912M - NavWeaps". www.navweaps.com. Retrieved 2019-04-14.
- ^ "53rd Artillery CAC". freepages.rootsweb.com. Retrieved 2019-04-15.





![A gun of the 53rd Coastal Artillery, 80th division near Verdun, France. Four shot were fired at a German rail head 30 km away and aerial observers confirmed four hits.[9]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/b/b8/111-SC-24753_-_NARA_-_55209117_%28cropped%29.jpg/247px-111-SC-24753_-_NARA_-_55209117_%28cropped%29.jpg)