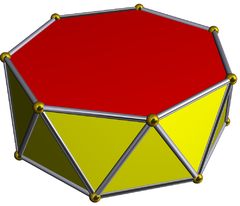
Heptagonal antiprism
| Uniform heptagonal antiprism | |
|---|---|
| |
| Type | Prismatic uniform polyhedron |
| Elements | F = 16, E = 28 V = 14 (χ = 2) |
| Faces by sides | 14{3}+2{7} |
| Schläfli symbol | s{2,14} sr{2,7} |
| Wythoff symbol | | 2 2 7 |
| Coxeter diagram | |
| Symmetry group | D7d, [2+,14], (2*7), order 28 |
| Rotation group | D7, [7,2]+, (722), order 14 |
| References | U77(e) |
| Dual | Heptagonal trapezohedron |
| Properties | convex |
 Vertex figure 3.3.3.7 | |
In geometry, the heptagonal antiprism is the fifth in an infinite set of antiprisms formed by an even-numbered sequence of triangle sides closed by two polygon caps.
Antiprisms are similar to prisms except the bases are twisted relative to each other, and that the side faces are triangles, rather than quadrilaterals.
In the case of a regular 7-sided base, one usually considers the case where its copy is twisted by an angle 180°/n. Extra regularity is obtained by the line connecting the base centers being perpendicular to the base planes, making it a right antiprism. As faces, it has the two n-gonal bases and, connecting those bases, 2n isosceles triangles.
If faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.
See also
| Antiprism name | Digonal antiprism | (Trigonal) Triangular antiprism |
(Tetragonal) Square antiprism |
Pentagonal antiprism | Hexagonal antiprism | Heptagonal antiprism | ... | Apeirogonal antiprism |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyhedron image | ... | |||||||
| Spherical tiling image | Plane tiling image | |||||||
| Vertex config. | 2.3.3.3 | 3.3.3.3 | 4.3.3.3 | 5.3.3.3 | 6.3.3.3 | 7.3.3.3 | ... | ∞.3.3.3 |
External links
- Virtual Reality Polyhedra www.georgehart.com: The Encyclopedia of Polyhedra
- VRML model
- Conway Notation for Polyhedra Try: "A7"
