Ornithine oxoglutarate
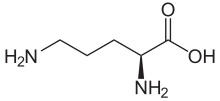 | |
 Ornithine (top) and ketoglutaric acid (bottom) | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.047.261 100.023.615, 100.047.261 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C10H18N2O7 |
| Molar mass | 278.261 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Ornithine oxoglutarate (OGO) or ornithine α-ketoglutarate (OKG) is a drug used in liver therapy. It is the salt formed from ornithine and alpha-ketoglutaric acid. It is also used to improve nutritional health in elderly patients.[1][2]
References
- ^ Blonde-Cynober, F; Aussel, C; Cynober, L (2003). "Use of ornithine α-ketoglutarate in clinical nutrition of elderly patients". Nutrition. 19 (1): 73–5. doi:10.1016/S0899-9007(02)00849-3. PMID 12507647.
- ^ Patrice Brocker; Bruno Vellas; Jean-Louis Albarede; Thierry Poynard (July 1994). "A two-centre, randomized, double-blind trial of ornithine oxoglutarate in 194 elderly, ambulatory, convalescent subjects". Age and Ageing.
