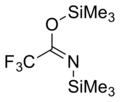
BSTFA
Appearance
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
trimethylsilyl 2,2,2-trifluoro-N-trimethylsilylethanimidate
| |||
| Other names
BSTFA, N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.807 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H18F3NOSi2 | |||
| Molar mass | 257.403 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colourless | ||
| Density | 0.96 | ||
| Melting point | −10 °C (14 °F; 263 K) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA) is a chemical compound that is used to derivatise labile groups such as hydroxyl on other chemicals, with the more stable trimethylsilyl group, which protects the labile group and allows the compound to be used for analytical purposes or as a chemical reagent for synthesis of more complex molecules.[1] Siloxanes are usually more volatile than the corresponding hydroxyl compounds, and thus can be analyzed with gas chromatography better than the parent compound.