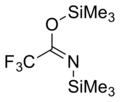
BSTFA
Appearance
| |||
| Names | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| IUPAC name
trimethylsilyl 2,2,2-trifluoro-N-trimethylsilylethanimidate
| |||
| Other names
BSTFA, N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.042.807 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| C8H18F3NOSi2 | |||
| Molar mass | 257.403 g·mol−1 | ||
| Appearance | colourless liquid | ||
| Density | 0.96 | ||
| Melting point | −10 °C (14 °F; 263 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 45–55 °C (113–131 °F; 318–328 K) 14 mm Hg | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA) is an organosilicon compound. It is a colorless liquid that is very sensitive to traces of water or alcohols.
It is often used to convert hydroxyl groups to trimethylsilyl ether groups (Me = CH3):
- ROH + CF3C(OSiMe3)NSiMe3 → CF3C(O)NH(SiMe3) + ROSiMe3
These silylated derivatives are amenable to analysis or further manipulation. Siloxanes are invariably more volatile than their hydroxyl precursors, and thus they can be more easily analyzed with gas chromatography.[1]
This reagent was first reported in 1968.[2]
Related compound
[edit]- Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide, MeC(OSiMe3)NSiMe3
References
[edit]- ^ Ito, Katsuji; Nakayama, Yuki (2001). "N,O-Bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA)". Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis. pp. 1–4. doi:10.1002/047084289X.rn01923. ISBN 9780470842898.
- ^ Stalling DL, Gehrke CW, Zumwalt RW. A new silylation reagent for amino acids bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide (BSTFA). Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications. 1968 May 23;31(4):616-22. PMID 5656249