Rectovesical pouch
| Recto-vesical pouch | |
|---|---|
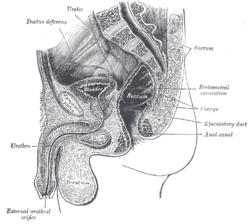 Median sagittal section of male pelvis. (Rectovesical excavation labeled at center right.) | |
 Male pelvic organs seen from right side. Bladder and rectum distended; relations of peritoneum to the bladder and rectum shown in blue. The arrow points to the rectovesical pouch. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Excavatio rectovesicalis |
| TA98 | A10.1.02.513M |
| TA2 | 3727 |
| FMA | 14727 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The recto-vesical pouch is the pocket that lies between the rectum and the urinary bladder in human males and other male mammals. It is lined by peritoneum and at its base is the rectoprostatic fascia (Denonvillier's fascia). When a man is upright or supine, the recto-vesical pouch is the lowest part of his peritoneal cavity. Because of this, peritoneal fluid and other fluids that enter the peritoneal cavity, including ascites, blood and pus, tend to collect in this pouch.
In women, the uterus lies between the rectum and the bladder. Therefore, women do not have a recto-vesical pouch, but instead have a recto-uterine pouch and vesico-uterine pouch.
Additional images
-
Median sagittal section of pelvis, showing arrangement of fasciae.
-
The peritoneum of the male pelvis.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1152 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1152 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- Anatomy photo:44:02-0201 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Male Pelvis: Distribution of the Peritoneum in the Male Pelvis"
- Anatomy photo:44:st-1501 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "The Male Pelvis: Rectovesical pouch"
- figures/chapter_35/35-1.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School


