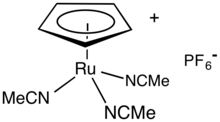
Tris(acetonitrile)cyclopentadienylruthenium hexafluorophosphate
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.152.130 |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| C11H14N3RuPF6 | |
| Molar mass | 434.28 |
| Appearance | yellow/brown solid |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Tris(acetonitrile)cyclopentadienylruthenium hexafluorophosphate is an organoruthenium compound with the formula [(C5H5)Ru(NCCH3)3]PF6, abbreviated [CpRu(NCMe)3]PF6. It is a yellow-brown solid that is soluble in polar organic solvents. The compound is a salt consisting of the hexafluorophosphate anion and the cation [CpRu(NCMe)3]+. In coordination chemistry, it is used as a source of RuCp+ for further derivitization.[1] In organic synthesis, it is a homogeneous catalyst. It enables C-C bond formation and promotes cycloadditions.[2] The cyclopentadienyl ligand (Cp) is bonded in an η5 manner to the Ru(II) center.
Preparation
The title complex is synthesized in two steps from the (benzene)ruthenium dichloride dimer. In the first step, the Cp− group is installed using cyclopentadienylthallium:[1]
- [(C6H6)RuCl2]2 + 2 TlCp + 2 NH4PF6 → 2 [Cp(C6H6)Ru]PF6 + 2 TlCl + 2 NH4Cl
The second step entails photochemical displacement of the benzene ligand, which is replaced by three equivalents of acetonitrile (MeCN):
- [Cp(C6H6)Ru]PF6 + 3 MeCN → [CpRu(NCMe)3]PF6 + C6H6
References
- ^ a b Gill, Thomas P; Mann, Kent R (1982). "Photochemical Properties of the Cyclopentadienyl(benzene)ruthenium(II) Cation. The Synthesis and Reactions of a Synthetically Useful Intermediate: the Cyclopentadienyltris (acetonitrile) ruthenium (II) Cation". Organometallics. 1: 485–488. doi:10.1021/om00063a014.
- ^ Trost, Barry M.; Toste, F. Dean; Pinkerton, Anthony B. (2001). "Non-Metathesis Ruthenium-Catalyzed C−C Bond Formation". Chem. Rev. 101: 2067–2096. doi:10.1021/cr000666b.
