Mi Teleférico
16°30′00″S 68°09′00″W / 16.50000°S 68.15000°W
| Mi Teleférico La Paz–El Alto Cable Car | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| File:Mi Teleférico logo.png | |||
| Overview | |||
| Native name | Mi Teleférico | ||
| Owner | Empresa Estatal de Transporte por Cable "Mi Teleférico" | ||
| Locale | La Paz, Bolivia | ||
| Transit type | Gondola lift | ||
| Number of lines | 10 (1 in planning)[1][2] | ||
| Number of stations | 36 (5 in planning)[1][2] | ||
| Website | www.miteleferico.bo | ||
| Operation | |||
| Began operation | 30 May 2014 | ||
| Operator(s) | Empresa Estatal de Transporte por Cable "Mi Teleférico" | ||
| Number of vehicles | 1398 gondola cars: 10 Person each 109 (Red Line) 169 (Yellow Line) 165 (Green Line) 208 (Blue Line)[3] 127 (Orange Line)[4] 131 (White Line)[5] 155 (Sky Blue Line) 190 (Purple Line) 27 (Brown Line) 117 (Silver Line) 106 (Gold Line) | ||
| Headway | 12 sec | ||
| Technical | |||
| System length | 30.6 km (19.0 mi) | ||
| Average speed | 11.2 mph (18.0 km/h) | ||
| Top speed | 13.4 mph (21.6 km/h) | ||
| |||
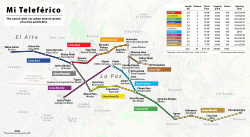
Mi Teleférico (Spanish pronunciation: [mi teleˈfeɾiko], English: My Cable Car), also known as Teleférico La Paz–El Alto (La Paz–El Alto Cable Car), is an aerial cable car urban transit system serving the La Paz–El Alto metropolitan area in Bolivia.[6] As of September 2018, the system consists of 25 stations along eight lines: Red, Yellow, Green, Blue, Orange, White, Sky Blue, and Purple. Another three lines are in planning or construction: Brown, Silver, and Gold.[2]
Upon the completion of the 10-kilometre (6.2 mi) Phase One (Red, Yellow, and Green Lines) in 2014, the system was considered to be the longest aerial cable car system in the world.[citation needed] Based on its master plan, the completed system, which is being built by the Doppelmayr Garaventa Group,[7] is intended to reach a length of 33.8 km (21.0 mi) with 11 lines and 30 stations.[8] While other urban transit cable cars like Medellín's Metrocable complement existing rapid transit systems, Mi Teleférico is the first system to use cable cars as the backbone of the urban transit network.[9] In 2018, Mi Teleférico won a Latam Smart City Award in the category of "Sustainable urban development and mobility".[10]
Mi Teleférico was planned in order to address a number of problems, including a precarious public transit system that could not cope with growing user demands, the high cost in time and money of traveling between La Paz and El Alto, chaotic traffic with its subsequent environmental and noise pollution, and a growing demand for gasoline and diesel fuel, which are subsidized by the state. The Red, Yellow, and Purple lines connect the neighboring cities of La Paz and El Alto, which are separated by a steep slope about 400 m (1,300 ft) tall, and which were previously only connected by winding, congested roads.
History
Background
The neighboring cities of El Alto and La Paz are the second and third most populous cities in Bolivia. Despite their proximity, travel between the two has always been a challenge, due to a difference in elevation of about 400 m (1,300 ft). La Paz, the national capital of Bolivia, is located in a canyon on the Choqueyapu River, while El Alto, a poorer but growing city with a majority indigenous population, is located above it on the Altiplano plateau. Prior to the construction of the cable car, travel between La Paz and El Alto was limited to heavily crowded, winding streets, and the only public transit consisted of buses and minibuses that often got stuck in traffic.[9] In order to alleviate this situation, the idea of connecting the two cities with a cable car has been proposed several times since the 1970s.
In the 1970s, a team planned an aerial cable car route connecting the neighborhoods of La Ceja in El Alto and La Florida in La Paz.
In 1990, a feasibility study was undertaken for a cable car between La Ceja in El Alto and the Plaza de San Francisco in La Paz. The most controversial aspects of the plan were the fare, the low passenger capacity, and the proximity to the Basilica of San Francisco. During the 1991 municipal elections, the Conciencia de Patria (CONDEPA) party candidate argued against a cable car, claiming it would cost minibus drivers their livelihoods and impact privacy.
In the 1993 municipal elections, mayoral candidate Mónica Medina, also of the CONDEPA party, made aerial transit one of her campaign promises, modifying the original idea of a single line into a system of interconnected cable car lines with a hub on Lainkakota hill.
In 2003, the project returned to the table, but details such as tower placement stalled the work.[11] The planned San Francisco terminal was moved to the Zapata soccer field near the Higher University of San Andrés, but the idea was still too controversial to move ahead.
In 2011, the Municipal Government of La Paz carried out a study on potential ridership demand, and found that the city handles 1.7 million trips per day, including 350,000 trips between La Paz and El Alto.
Phase One
In July 2012, Bolivian President Evo Morales Ayma drafted a bill for the construction of a cable car to connect El Alto with the center and south of La Paz and sent it to the Plurinational Legislative Assembly. Morales called together the mayor of La Paz, Luis Revilla, the mayor of El Alto, Édgar Patana, and the governor of the La Paz Department, César Cocarico, to participate in the project. The project was financed by the country's National Treasury with an internal loan from the Central Bank of Bolivia.
The system's Phase One consisted of the Red Line (Línea Roja), Yellow Line (Línea Amarilla), and Green Line (Línea Verde), which are also the colors of the Bolivian flag. Phase One was inaugurated and began operation on 30 May 2014.
Phase Two
On 1 July 2014, Evo Morales announced five new interconnected lines to be built in the coming years. On 26 January 2015, the law permitting construction of Phase Two was passed, increasing the number of new lines to six and committing US $450 million to the project. A seventh line was announced in February 2016,[12] and an eighth was announced in July 2016.[13][14] Phase Two will extend the system by over 20 km (12 mi).[15][16] On 13 July 2017, it was announced that the cost of Phase 2 would be increased to US $506 million.[17]
Phase Two began operation in 2017 with the inauguration of the Blue Line (Línea Azul) on 3 March 2017,[3][18][19] followed by the Orange Line (Línea Naranja) on 29 September 2017.[20][4][21] On 24 March 2018, the White Line (Línea Blanca) and the first section of the Sky Blue Line (Línea Celeste) were opened.[22][23][5] The second and final section of the Sky Blue Line was opened on 14 July 2018.[citation needed] The remaining five lines will be the Purple Line (Línea Morada), the Brown Line (Línea Café), the Silver Line (Línea Plateada), and the Gold Line (Línea Dorada).[2][24] As of March 2018, the Purple and Silver Lines are under construction.[25]
Other cities
Oruro
Mi Teleférico contributed to the construction of the Teleférico Turístico "Virgen del Socavón" (Our Lady of the Mines Tourist Cable Car) in Oruro, Bolivia. The cable car connects the city center to the Virgen del Socavón statue and shrine on nearby Santa Bárbara hill, which plays an important role in the city's carnaval celebrations. The cable car, which opened on 7 February 2018, consists of a single 800-metre (2,600 ft) line with two stations and 16 cars. It has a capacity of 1000 passengers per hour, and a one-way trip takes approximately 3 minutes.[26][27] The project was originally due to open in November 2016, but it suffered repeated delays until Mi Teleférico took over construction work in 2017.[28]
Sucre
As of 2017, the Empresa Estatal de Transporte por Cable "Mi Teleférico" was in the process of planning a cable car system for the city of Sucre.[29]
Lines
Lines in operation


The Mi Teleférico system consists of monocable aerial cable car lines. Most lines have a maximum capacity of 3000 passengers per hour, while the Sky Blue Line has a capacity of 4000 passengers per hour.[30] The network has a total of seven lines, with 443 cars on the Red, Green, and Yellow Lines, 208 on the Blue Line,[3] 127 on the Orange Line,[4] 131 on the White Line,[5] and 155 on the Sky Blue Line.[citation needed] Each car seats 10 passengers. Cars depart every 12 seconds, and the network is open 17 hours a day.[31]
According to Mi Teleférico, the Red, Yellow, and Green Lines combined transport between 80,000 and 90,000 passengers per day. Of these, the Yellow and Red Lines, the two lines that link La Paz and El Alto, account for some 70,000 rides. During its opening week, the Blue Line moved 41,000 passengers in one day, and it has increased ridership on the Red Line by 15%.[32]
| Line | Terminus stations | Length | Travel time | Stations | Cabins | Capacity | Speed | Towers | Opened |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Red Line | 16 de Julio/Jach'a Qhathu – Estación Central/Taypi Uta | 2.4 km (1.5 mi) | 10 min | 3 | 109 | 3000 pphpd | 5 m/s | 19 | 30 May 2014 |
| Yellow Line | Mirador/Qhana Pata – Chuqui Apu/Libertador | 3.9 km (2.4 mi) | 13.5 min | 4 | 169 | 3000 pphpd | 5 m/s | 31 | 15 September 2014 |
| Green Line | Chuqui Apu/Libertador – Irpawi/Irpavi | 3.7 km (2.3 mi) | 16.6 min | 4 | 165 | 3000 pphpd | 5 m/s | 27 | 4 December 2014 |
| Blue Line | Rio Seco/Waña Jawira – 16 de Julio/Jach'a Qhathu | 4.7 km (2.9 mi) | 17 min[33] | 5 | 208 | 3000 pphpd | 5 m/s | 38 | 3 March 2017[3][18][19] |
| Orange Line | Estación Central/Taypi Uta – Héroes de la Revolución/Villarroel | 2.6 km (1.6 mi)[20] | 10 min | 4 | 127 | 3000 pphpd | 5 m/s | 26 | 29 September 2017[20] |
| White Line | Plaza Villarroel – San Jorge | 2.9 km (1.8 mi) | 13.1 min | 4 | 131 | 3000 pphpd | 5 m/s | 26 | 24 March 2018 |
| Sky Blue Line | El Prado – Chuqui Apu/Libertador | 2.6 km (1.6 mi) | 11.8 min | 4 | 155 | 4000 pphpd | 6 m/s | 26 | Section 1: 24 March 2018 Complete Line: 14 July 2018 |
| Purple Line | 6 de Marzo – San Jose | 4.3 km (2.7 mi) | 16.2 min | 3 | 190 | 4000 pphpd | 6 m/s | 34 | 28 September 2018 |
| Brown Line | Monumento Busch – Las Villas[1][16] | 0.7 km (0.43 mi) | 3.8 min | 2 | 27 | 2000 pphpd | 5 m/s | 7 | 20 December 2018 |
| Silver Line | 16 de Julio/Jach'a Qhathu – Mirador/Qhana Pata[12] | 2.6 km (1.6 mi) | 11.7 min | 3 | 117 | 3000 pphpd | 5 m/s | 21 | 9 March 2019 |
Future lines
| Line | Terminus stations | Length | Travel time | Stations | Cabins | Capacity | Speed | Towers | Planned opening |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gold Line | Irpawi/Irpavi – Cota Cota[2][24] | 2.2 km (1.4 mi) | 7.6 min | 3 | 106 | 3000 pphpd | 5 m/s | 2020 |
Stations



All stations have both a Spanish name and an Aymara name.
Red Line (Línea Roja)
| Aymara name[1] | Spanish name | Connections | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taypi Uta | Estación Central | Orange Line | La Paz | former central railway station |
| Ajayuni | Cementerio | La Paz | main cemetery | |
| Jach'a Qhathu | 16 de julio | Blue and Silver Lines | El Alto |
Yellow Line (Línea Amarilla)
| Aymara name[1] | Spanish name | Connections | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chuqui Apu | Libertador | Green and Sky Blue Lines | La Paz | |
| Suphu Kachi | Sopocachi | La Paz | ||
| Quta Uma | Buenos Aires | La Paz | ||
| Qhana Pata | Mirador | Silver Line | El Alto |
Green Line (Línea Verde)
| Aymara name[1] | Spanish name | Connections | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irpawi | Irpavi | Gold Line (2020) | La Paz | |
| Aynacha Obrajes | Obrajes | La Paz | a free funicular provides access from Calle 17 to the station[34] | |
| Pata Obrajes | Alto Obrajes | La Paz | ||
| Chuqui Apu | Libertador | Yellow and Sky Blue Lines | La Paz |
Blue Line (Línea Azul)
| Aymara name[33] | Spanish name[19] | Connections | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jach'a Qhathu | 16 de julio | Red and Silver Lines | El Alto | |
| Qhana Thaki | Plaza Libertad | El Alto | ||
| Suma Qamaña | Plaza La Paz | El Alto | ||
| Yatina Uta | Plaza UPEA | El Alto | Universidad Pública de El Alto | |
| Waña Jawira | Río Seco | El Alto |
Orange Line (Línea Naranja)
| Aymara name | Spanish name | Connections | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Taypi Uta | Estación Central | Red Line | La Paz | former central railway station |
| Riosinho Pampa | Armentia | La Paz | ||
| Apachita | Periférica | La Paz | ||
| Villarroel | Héroes de la Revolución | White Line | La Paz | underground station |
White Line (Línea Blanca)
| Aymara name[22] | Spanish name | Connections | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jalsuri | San Jorge | Sky Blue Line | La Paz | |
| Kimsachata | Triangular | La Paz | ||
| Qhuirwa Uma | Busch | Brown Line | La Paz | |
| Inalmama | Villarroel | Orange Line | La Paz | underground station |
Sky Blue Line (Línea Celeste)
| Aymara name | Spanish name | Connections | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Chuqui Apu | Del Libertador | Yellow and Green Lines | La Paz | |
| Arce | Avenida Poeta | White Line | La Paz | |
| Cancha Zapata | Teatro al Aire Libre | La Paz | ||
| Prado | Camacho | La Paz |
Purple Line (Línea Morada)
| Aymara name | Spanish name | Connections | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| San José | Edificio Correos | Sky Blue Line | La Paz | |
| Complejo de Integración Faro Murillo | Silver Line | El Alto | ||
| 6 de Marzo | Terminal de Transporte | El Alto |
Brown Line (Línea Café)
| Aymara name | Spanish name | Connections | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Qhuirwa Uma | Monumento a Busch | White Line | La Paz | |
| Las Villas | Villa Copacabana / Villa San Antonio | La Paz |
Silver Line (Línea Plateada)
| Aymara name | Spanish name | Connections | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jach'a Qhathu | 16 de julio | Red and Blue Lines | El Alto | |
| Complejo de Integración Faro Murillo | Purple Line | El Alto | ||
| Qhana Pata | Mirador | Yellow Line | El Alto |
Gold Line (Línea Dorada)
| Aymara name[1] | Spanish name | Connections | City | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Irpawi | Irpavi | Green Line | La Paz | |
| Achumani | San Miguel | La Paz | ||
| Cota Cota | UMSA | La Paz |
Incidents
When the system first opened, riders experienced delays of 2 to 25 minutes, which the government attributed to technical problems and riders holding doors.[citation needed]
On February 14, 2015, a eucalyptus tree fell, striking an empty cabin on the Yellow Line, dislocating the cable and leaving passengers stranded for three hours. Nineteen passengers suffered bruises and other minor injuries, but there were no major injuries, and only minor damage to three cabins.[35]
On May 9, 2016, a tower from the construction of the Blue Line fell, with nine injured and no deaths.
Intermodal transfers
Beginning in December 2014, the Mi Teleférico and La Paz Bus systems began allowing passenger transfers at the Chuqui Apu station.[36]
Mobile application
Mi Teleférico has released a mobile application for Android and Apple with information about existing and future lines.[37][38]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g "Almanaque Mi Teleférico" [Mi Teleférico Calendar] (PDF) (in Spanish). Empresa Estatal de Transporte por Cable "Mi Teleférico". Retrieved February 2, 2015.
- ^ a b c d e "Red de Integración Metropolitana" [Metropolitan Integration Network]. Mi Teleférico (in Spanish). 7 March 2016. Retrieved 5 March 2017.
- ^ a b c d "Bolivia Inaugurates New Cable Car Line". Prensa Latina. 3 March 2017. Retrieved 5 March 2017.
- ^ a b c "Bolivia inaugura la quinta línea del teleférico o "metro aéreo" de La Paz" [Bolivia inaugurates fifth cable car or "aerial metro" line in La Paz]. El Periódico (in Spanish). 30 September 2017. Retrieved 30 September 2017.
- ^ a b c "Mi Teleférico inaugura operaciones de la "Línea Blanca"" [Mi Teleférico inaugurates service on the "White Line"]. Página Siete (in Spanish). 24 March 2018.
- ^ Altamirano, Amalia (May 30, 2014). "Evo Morales inaugura teléferico que une La Paz y El Alto" [Evo Morales inaugurates cable car to connect La Paz and El Alto]. Prensa Latina (in Spanish).
- ^ Metcalfe, John (April 11, 2014). "Bolivia Deploys the World's Largest System of Cable Cars". CityLab. Atlantic Media.
- ^ Gondola Project. "La Paz Celebrates Three Years of Cable Car Operations". Gondola Project. Retrieved 23 November 2017.
- ^ a b Neuman, William (August 16, 2014). "With Subway in the Sky, Valley Meets Plateau". The New York Times. Retrieved February 6, 2015.
- ^ "Mi Teleférico gana el premio Latam Smart City Awards" [Mi Teleférico wins Latam Smart City Awards] (in Spanish). 14 September 2018. Retrieved 7 October 2018.
- ^ Villa, Micaela (July 12, 2012). "Evo anuncia millonaria inversión para teleférico La Paz-El Alto" [Evo announces multi-million-dollar investment in La Paz-El Alto cable car]. La Razón (in Spanish). La Paz, Bolivia.
- ^ a b Chu, Nick (February 18, 2016). "La Paz: Purple Line Starts Construction, Silver Line Announced". The Gondola Project. Creative Urban Projects. Retrieved February 21, 2016.
- ^ "110 millones de dólares más en teleféricos y parque cultural para el desarrollo de La Paz" [Another $110M for cable cars and cultural park for development in La Paz]. Mi Teleférico (in Spanish). 15 July 2016. Retrieved 5 March 2017.
- ^ Landsman, Peter (20 July 2016). "Mi Teleférico to Build 11th Gondola Line in La Paz". LiftBlog. Retrieved 5 March 2017.
- ^ "Evo autoriza la construcción de seis nuevas líneas de teleférico en La Paz y El Alto" [Evo authorizes construction of six new cable car lines in La Paz and El Alto]. Página Siete (in Spanish). La Paz, Bolivia. January 26, 2016.
- ^ a b Tapia, Guadalupe (January 27, 2015). "Elevan a 6 las líneas de fase II del teleférico; la Azul es la más larga" [Number of lines in cable car's phase two raised to six; Yellow to be the longest]. La Razón (in Spanish). La Paz, Bolivia.
- ^ Corz, Carlos (13 July 2017). "Comienzan obras de la línea Celeste del Teleférico y la inversión para la segunda fase sube a $us 506 MM" [Work begins on Mi Teleférico's Sky Blue Line and investment for second phase rises to US $506 million]. La Razón (in Spanish). Retrieved 14 July 2017.
- ^ a b "Línea Azul del Teleférico inicia operaciones comerciales" [Teleférico's Blue Line begins commercial operation]. Bolivia.com (in Spanish). 3 March 2017. Retrieved 5 March 2017.
- ^ a b c Corz, Carlos (3 March 2017). "La Línea Azul del teleférico inicia operaciones en El Alto en medio de dos homenajes" [Teleférico's Blue Line begins operations amidst two homages]. La Razón (in Spanish). Retrieved 5 March 2017.
- ^ a b c Corz, Carlos (29 September 2017). "Inicia operaciones la Línea Naranja del Teleférico con tarifa de Bs 3 y Bs 2 en sus conexiones" [Mi Teleférico Orange Line begins operations with fares of 3 bolivianos and 2 bolivianos at transfers]. La Razón (in Spanish). Retrieved 30 September 2017.
- ^ "Arranca la línea que une plaza Villarroel con Río Seco" [Line connecting Plaza Villarroel and Río Seco opens]. Página Siete (in Spanish). 30 September 2017. Retrieved 30 September 2017.
- ^ a b "Inauguran Línea Blanca y se anuncia proyección de Mi Teleférico al exterior" [White Line inaugurated and plans announced to expand Mi Teleférico abroad]. Erbol Digital (in Spanish). 24 March 2018.
- ^ "Extenso y panorámico, el teleférico boliviano atrae al mundo" [Extensive and panoramic, the Bolivian cable car attracts the world]. El Nuevo Diario (in Spanish). 25 March 2018.
- ^ a b Chuquimia, Leny (4 August 2016). "Mi Teleférico evalúa la reducción del trazo inicial de la línea Blanca" [Mi Teleférico evaluates reduction of the White Line's original length]. Página Siete (in Spanish). Retrieved 5 March 2017.
- ^ Corz, Carlos (20 October 2017). "Comienza la construcción de la Línea Plateada de Mi Teleférico" [Work begins on Mi Teleférico's Silver Line]. La Razón (in Spanish). Retrieved 29 October 2017.
- ^ "President inaugura teleférico turístico "Virgen del Socavón" en Oruro" [President inaugurates Our Lady of the Mines tourist cable car in Oruro]. Money.com.bo (in Spanish). 7 February 2018. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ^ Alanoca Paco, Jesús Reynaldo (7 February 2018). "Oruro estrena teleférico turístico 'Virgen del Socavón'" [Oruro opens Our Lady of the Mines tourist cable car]. El Deber. Retrieved 18 February 2018.
- ^ Columba, José Luis (13 September 2017). "Estatal Mi Teleférico asume la construcción del teleférico turístico en Oruro" [State company Mi Teleférico takes over construction of tourist cable car in Oruro]. La Razón (in Spanish).
- ^ "Mi Teleférico anunciará inicio de obras el jueves" [Mi Teleférico to announce groundbreaking on Thursday]. Correo del Sur (in Spanish). 17 December 2017.
- ^ "Mi Teleférico estrenará la "línea más veloz" el 14" [Mi Teleférico to open the "fastest line" on the 14th]. Página Siete (in Spanish). 3 July 2018. Retrieved 23 July 2018.
- ^ "Ficha técnica del proyecto teleférico" [Cable car project technical datasheet] (PDF) (in Spanish). Ministerio de Obras Públicas, Servicios y Vivienda, Bolivia. Retrieved January 3, 2014.
- ^ "Dockweiler: El teleférico es autosostenible y la Línea Azul llevó en un día 41 mil pasajeros" [Dockweiler: Cable car is self-sustaining and Blue Line carried 41 thousand passengers in one day]. Opinión.com.bo (in Spanish). 6 March 2017. Retrieved 25 March 2017.
- ^ a b "Mira el recorrido de la Línea Azul de Mi Teleférico" [Watch a trip on Mi Teleférico's Blue Line]. La Razón. 4 March 2017. Retrieved 5 March 2017.
- ^ Chuquimia, Leny (March 4, 2015). "Entrega del funicular de Obrajes cierra primera fase del teleférico" [Delivery of Obrajes funicular brings cable car's phase one to an end]. Página Siete (in Spanish). La Paz, Bolivia.
- ^ Imaña, Gabriela (February 15, 2016). "Caída de árbol saca de su eje cable del teleférico, hay heridos" [Fallen tree dislocates Mi Teleférico cable, injuries reported]. La Razón (in Spanish). La Paz, Bolivia.
- ^ "Acuerdan cambio bimodal entre el teleférico y los buses PumaKatari" [Agreement reached on intermodal transfers between cable car and PumaKatari buses]. La Razón (in Spanish). La Paz, Bolivia. November 18, 2014.
- ^ "Teleférico La Paz - Android Apps on Google Play". play.google.com. Retrieved 2016-04-03.
- ^ "Teleférico La Paz en el App Store". App Store. Retrieved 2016-04-03.
- MacGregor, Hilary (December 12, 2015). "La Paz's cable-car system Teleferico a heady ride that bridges Bolivia's values". Los Angeles Times.
External links
- Official website (Spanish)
- Teleférico La Paz Mobile App (Spanish)