Hochjuvalt Castle
| Hochjuvalt Castle | |
|---|---|
Niderjuvalt, Ausserjuvalt, Alt-Juvalt | |
| Rothenbrunnen | |
 Hochjuvalt Castle | |
| Coordinates | 46°46′40″N 9°25′15″E / 46.77778°N 9.42083°E |
| Type | hill castle |
| Code | CH-GR |
| Height | 805 m above the sea |
| Site information | |
| Condition | ruin |
| Site history | |
| Built | 12th century |
| Materials | rubble stone |
Hochjuvalt Castle (also Niderjuvalt[1] or Ausser-Juvalt[2]) is a castle in the municipality of Rothenbrunnen of the Canton of Graubünden in Switzerland. It is a Swiss heritage site of national significance.[3]
History
The castle consists of two sections, the upper castle on a rocky spur above the valley and the lower castle along the trade road on the valley floor. The spur created a natural pinch point in the valley, forcing traffic from the Septimer, Splügen and San Bernardino Passes to pass through the customs post in the lower castle. The von Juvalt family first appears in records in 1140[2] and the castle is first mentioned in 1149.[4] The von Juvalt family were vassals of the Bishop of Chur and had estates from Feldis/Veulden to Scharans. Around 1250 they built Innerjuvalt Castle about 2 km (1.2 mi) south-east of Hochjuvalt to improve their control over the area.
By the 14th century the castle passed, probably through inheritance, to the Rietberg family. Following the death of the last male heir, Johann von Reitberg, in 1349 the castle was supposed to pass to his relative, the Freiherr von Landenberg. However, the Bishop of Chur claimed Hochjuvalt as well as other Reitberg estates in the region. In 1352 the Bishop forced the Landenbergs to sign away their claims to the castle. Another claimant, the Freiherr of Lumbrein agreed to drop his claims for 250 gulden. Over the following century, the Bishops used the castle and its estates as collateral for loans from a number of wealthy families. In 1451 a war broke out between the residents of the Schams valley and Counts of Werdenberg-Sargans. Several castles in the area were partially destroyed in the war, though it is unknown if Hochjuvalt was one of them. It was last granted to Eberhard Ringg von Baldenstein in 1454, though its condition was not recorded. By 1500 the castle was completely abandoned and around 1550 was described as a ruin.[2]
During World War II the site was reoccupied and fortified. In 1940 guns were emplaced near the old upper castle and tank barriers were added around the lower.[2]
In 2011-12 the castle was reinforced and repaired and a new footpath was added to the upper castle.[2]
Castle site
The oldest part of the castle is the residence tower high above the valley. Most of three sides of the tower have collapsed, leaving an "L" shaped five story wall still standing. The castle was surrounded by a ring wall that probably enclosed the entire top of the spur. Today only a few traces of this wall remain. The castle was protected by two ditches on the mountain side of the spur.
The lower castle stretches between the base of the spur and the river banks. There are three doors in the wall, one toward Chur, one toward the Viamala road and one toward the Rhine river.[5] Inside the wall, the only remaining building is a 9 m × 9 m (30 ft × 30 ft) tower in the south-west corner. The foundations of a similar tower are visible in north-west corner.[2]
Gallery
-
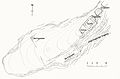
Floor plan of the upper castle
-
Drawing of the lower castle in 1896
-
Ruins of the tower from the upper castle
-
Hochjuvalt during repairs in 2011
-
Lower castle during repairs in 2011
-
Lower castle
See also
References
- ^ Juvalta in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- ^ a b c d e f "Burg Hoch-Juvalt". www.burgenwelt.ch. Retrieved 8 March 2017.
- ^ "Kantonsliste A-Objekte". KGS Inventar (in German). Federal Office of Civil Protection. 2009. Archived from the original on 28 June 2010. Retrieved 25 April 2011.
- ^ "Hochjuvalt". Federal Office of Civil Protection. Retrieved 8 March 2017.
- ^ "Graubuenden :Schloss Nieder Juvalt". www.swisscastles.ch. Retrieved 8 March 2017.