Martin Chartier
Martin Chartier | |
|---|---|
| Born | June 1, 1655 |
| Died | April 1, 1718 (aged 62) |
| Nationality | French-Canadian |
| Occupation(s) | Explorer, fur trader, glovemaker |
| Known for | Travels with Louis Jolliet and René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle |
| Spouse | Sewatha Straight Tail (1660-1759) |
| Parent(s) | René Chartier (1621-1689);[1] Madeleine Ranger (1621?-1662) |
| Relatives | Children: Mary Seaworth (Sewatha) Chartier (1687-1732); Peter Chartier (1690-1759) |
Martin Chartier (1 June 1655 – Apr 1718)[2] was a French-Canadian explorer, a glove maker, and then a "white Indian", living much of his life amongst the Shawnee Native Americans.
Chartier accompanied Louis Jolliet on two of his journeys to the Illinois Territory, and went with René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle on his 1679-1680 journey to Lake Erie, Lake Huron, and Lake Michigan. Chartier assisted in the construction of Fort Miami and Fort Crèvecoeur[3] where, on April 16, 1680, Chartier, along with six other men, mutinied, looted, burned Fort Crèvecoeur, and fled. In a letter dated 1682, La Salle stated that Martin Chartier "was one of these who incited the others to do as they did."[4]
Chartier sometimes was written as Chartiere, Chartiers, Shartee or Shortive.
Early life
Martin Chartier was born in 1655 in St-Jean-de-Montierneuf, Poitiers, Vienne, Poitou-Charentes, France.[5] He arrived in Quebec in 1667 with his brother Pierre, his sister Jeanne Renée, and his father René.[6] On the transatlantic voyage, René and Martin became acquainted with René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle, who was also immigrating to Canada.[7][5] Some sources state that Martin spent the next several years in Montreal learning to make gloves,[3][Note 1] however there is also evidence that he was apprenticed to a carpenter.[9]
Louis Jolliet's 1672 expedition
In 1672, Martin Chartier, along with his brother Pierre, participated in Louis Jolliet's second expedition.[10] Jolliet was chosen by Intendant Jean Talon (who in turn had been delegated his power from Governor Louis de Buade de Frontenac) to explore the Mississippi River, which the Indians alleged flowed into the southern sea. In December of the same year Jolliet reached the Straits of Mackinac, where with Père Marquette, he spent the winter and the early spring questioning the Indians and preparing maps for his famous 1673 expedition, also with Père Marquette, to find the mouth of the Mississippi River and discover if it flowed into the Gulf of Mexico or the Pacific Ocean.[11]
Louis Jolliet's 1674 expedition
In 1674, Chartier accompanied Louis Jolliet to the Illinois Territory, where he became acquainted with the Pekowi Shawnee, who lived at that time on the Wabash River.[Note 2] In 1675, Chartier married Sewatha Straight Tail (1660-1759),[13] daughter of the Shawnee chief Straight Tail Meaurroway Opessa.[14] Their first child, a daughter, was born in 1676, according to a statement Chartier himself made in 1692.[12][8]
La Salle's 1679 expedition

Chartier went along with René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle on his 1679-1680 journey to Lake Erie, Lake Huron, and Lake Michigan. They were accompanied by the Belgian missionary Louis Hennepin and the French missionary Zenobius Membre.[15]

Chartier assisted in the construction of Le Griffon, a seven-cannon, 45-ton barque, on the upper Niagara River at or near Cayuga Creek. She was launched on August 7, 1679 and was the largest sailing vessel on the Great Lakes up to that time.[8] La Salle sailed in Le Griffon up Lake Erie to Lake Huron, then up to Michilimackinac and on to present-day Green Bay, Wisconsin. Le Griffon left for Niagara with a load of furs, but was never seen again. La Salle continued with his men in canoes down the western shore of Lake Michigan, rounding the southern end to the mouth of the St. Joseph River, where Chartier helped to build a stockade in November 1679. They called it Fort Miami (now known as St. Joseph, Michigan). There they waited for Henri de Tonti and his party, who had crossed the Lower Peninsula of Michigan on foot.
Tonti arrived on November 20; on December 3, the entire party set off up the St. Joseph, which they followed until they had to take a portage at present-day South Bend, Indiana. They crossed to the Kankakee River and followed it to the Illinois River, where they started construction on Fort Crèvecoeur on January 15, 1680.[16] Father Hennepin went with a small party to seek the junction of the St. Joseph and the Mississippi rivers; he was captured by Sioux warriors and held for several months.[15]
The 1680 mutiny at Fort Crèvecoeur
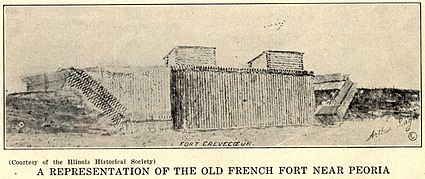
Chartier assisted in the construction of Fort Crèvecoeur,[3][12] which was built along the Illinois River near the present-day site of Peoria, Illinois. The fort was the first public building erected by white men within the boundaries of the modern state of Illinois and the first fort built in the West by the French.[16] La Salle also started building another 40-ton barque to replace Le Griffon.[17] On March 1, 1680, La Salle set off on foot for Fort Frontenac for supplies,[16] leaving Henri de Tonti to hold Fort Crèvecoeur in Illinois.[18] While on his return trip up the Illinois River, La Salle concluded that Starved Rock might provide an ideal location for another fortification and sent word downriver to Tonti regarding this idea. Following La Salle's instructions, Tonti took five men and departed up the river to evaluate the suitability of the Starved Rock site. Shortly after Tonti's departure, on April 16, 1680, the seven members of the expedition who remained at Fort Crevecoeur mutinied, plundering the provisions and ammunition, throwing into the river all the arms, goods, and stores which they could not carry off, and then burning the fort to the ground.[19][20] In a letter dated 1682, La Salle blamed Chartier as one of the main instigators "who incited the others to do as they did."[21]

The mutiny was probably caused by the men's fear of being killed by Iroquois raiding parties, who were devastating the local Illinois communities at the height of the Beaver Wars. The men were demanding that La Salle return with them to Montreal, which he was unwilling to do.[17] In addition, one of the mutineers who was later captured, the shipbuilder Moyse Hillaret, testified that "some [of the men] had had no pay for three years," and alleged that La Salle had mistreated them.[8][22]
At Fort St. Louis (Starved Rock), two men who had been at the fort told Tonti of its destruction. Tonti sent messengers to La Salle in Canada to report the events. Tonti then returned to Fort Crèvecoeur to collect any tools not destroyed[20] and moved them to the Kaskaskia Village at Starved Rock. Later La Salle captured a few of the mutineers on Lake Ontario, but not Chartier, who followed the south shore of Lake Ontario headed for Albany, New York, as a part of a second group of deserters, while the others, who were eventually captured, were pursuing La Salle, intending to kill him.[12]
Crèvecoeur means "heart break" in French, and Fort Crèvecoeur was given this name because of the many difficulties the French had in its construction, including Chartier's mutiny.
Life with the Shawnee
After the mutiny at Fort Crèvecoeur, Chartier was now an outlaw, however he apparently returned to Montreal,[12] from where he journeyed in 1685 to Lake Michigan, then to the Cumberland River in Tennessee, evidently in search of his wife and adolescent daughter:
In August, he resolved to follow [the Shawnees], and took a canoe and went after them three hundred leagues (about 900 miles) in forty days ... He guessed the way, and was guided by the course of the river, and found water in all places ... And when he came to them [the Shawnee] they made him very welcome.[8]
After reuniting with his family, he visited the future site of Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, then crossed the Alleghenies and traveled along the Susquehanna River. His daughter Mary Seaworth (Sewatha) Chartier (1687-1732) was born in Frederick County, Virginia in 1687.[23][24]
Birth of Peter Chartier

In 1689, Chartier established a trading post at French Lick on the Cumberland River in northeastern Tennessee, near the present-day site of Nashville, Tennessee.[25][26][27] His son Peter (Pierre) Chartier was born there in 1690.[28][29][30] Peter Chartier went on to become a leader of the Pekowi Shawnee and campaigned against the sale of alcohol in indigenous communities in Pennsylvania.[31][32]
After Peter's birth, Martin and his Shawnee family established a fur trading post where the Ohio River forks into the Monongahela River and the Allegheny River, the present-day site of Pittsburgh, where they spent two years.[7]
Relocation to Maryland and Pennsylvania
In the spring of 1692, Chartier led a group of 192 Shawnee and an unknown number of Susquehannock (Conestoga) Indians east to Cecil County, Maryland on the Potomac River.[8][12][33] The Shawnee were relocating after a series of violent conflicts with Illinois and Miami Indians. The Susquehannocks, having recently been defeated by the Iroquois, formed an alliance with the Shawnee and, with the help of Chartier, intended to use the Susquehanna River to transport furs for the growing North American Fur Trade.[32] Although he was French by birth, Chartier wanted to exploit the rivalry between the French and the British to benefit his Shawnee family.
Suspecting that Chartier was actually employed by the French, colonial officials in Annapolis ordered Chartier's arrest and he was jailed in St. Mary's and Anne Arundel Counties as "a spy or party with designs of mischief." He was released to await trial but he escaped, was recaptured in August of 1692 and sentenced to three months in prison.[Note 3] He was released on October 29, 1692.[9]
In defense of Chartier, Casperus Augustine Herman, son of Augustine Herman and Lord of Bohemia Manor, wrote to Governor Lionel Copley on February 15, 1693 that Martin Chartier was "a man of excellent parts" and that he spoke several languages and had been apprenticed to a carpenter as a young man.[9]
Nonetheless, Chartier and his band of Shawnees felt unwelcome in Maryland and in 1694 they moved north into Pennsylvania and eventually settled at a place known as Chartier's Old Town (on the site of what is now Tarentum, Pennsylvania).[34] He maintained a good relationship with the Provincial Government, and acted at times as an interpreter,[31] serving as an unofficial liaison between the government and the Indians.[8][35]
The Chartier and Conestoga alliance
In 1701, Chartier and his Shawnee community invited the Conestoga, who had been decimated by war and a major epidemic, to live with them. Both the Conestoga and the Shawnee appeared before William Penn and on 23 April 1701 they were granted formal permission for this arrangement.[36][37][38] They established the community of Conestoga Town near Manor Township, Lancaster County, Pennsylvania.[39][40] The descendants of these Indians were killed by the Paxton Boys in December, 1763.[41]
French traders in Pennsylvania

By the late 17th century, French settlers and fur traders were moving into the Ohio Valley (then part of New France) to take advantage of the opportunities for commerce among various Native American tribes that were concentrated there as a result of having been pushed away from the east coast by European colonization. Experienced in frontier life and fluent in several Native American languages, Chartier and his old colleagues from expeditions in Canada, Peter Bisaillon,[42] Nicole Godin, and Jacques Le Tort, Le Tort's son James and his wife Ann, were six of the most prominent who established the earliest trading posts,[43] but the British Provincial Government suspected that they were "very dangerous persons" who "kept private correspondence with the Canida Indians and the French," and who "entertained strange Indians in remote and obscure places," and who "uttered suspicious words."[44] They were harassed, arrested and imprisoned, often on false or minor charges. Chartier only escaped persecution after he agreed to assist in the arrest of Nicole Godin.[45]
Arrest of Nicole Godin
In the aftermath of the Beaver Wars (1629-1701), both French and British colonial governments were trying to influence Native American communities to take one side or the other, for trading relations as well as political control. Many white fur traders and other merchants participated in this, one of them being the trader Nicole Godin, an Englishman born of a French father in London. After 1701 he operated a trading post near Martin Chartier's homestead, and became well-known for "using endeavors to incense these people [the local Shawnees], to stir them up to enmity against the subjects of the Crown; and to join with our public enemy, the French, to our destruction."[46] On May 15, 1704, Chartier was summoned to Philadelphia and questioned by William Penn "in regard to his relations with the Indians, he being 'a Frenchman, who has lived long among the Shawanah Indians and upon Conestoga.'"[47] Although there is no record of this interrogation, some of it likely pertained to Godin's activities. On 1 July 1707, Pennsylvania Governor John Evans persuaded Chartier (a friend of Godin's from their days at Fort St. Louis) to lure Godin into a trap near Paxtang, Pennsylvania, where Godin was arrested. Godin was tried for treason in Philadelphia in 1708, but the results of the trial are unknown.[12]
Later life
In 1717, Governor Penn granted Chartier a 300-acre tract of land along the Conestoga River in Lancaster County, Pennsylvania.[29][3][35] He and his son Peter Chartier established a trading post near a Shawnee village on Pequea Creek in Pennsylvania.[5][48] That same year, he accompanied Christoph von Graffenried, 1st Baron of Bernberg on a journey to Sugarloaf Mountain[49] and then to the Shenandoah Valley, where they visited Massanutten Mountain.[50]
Death
Martin Chartier died in April, 1718, on his farm in Dekanoagah, Pennsylvania.[51] His funeral was attended by James Logan, the future Mayor of Philadelphia.[35] Logan said of Martin that "he was a very decent man, but too generous to grow rich."[52] Immediately after the funeral, Logan seized Martin Chartier's 250-acre estate on the grounds that Martin owed him a debt of 108 pounds, 19 shillings and 3 and 3/4 pence. He later sold the property to Stephen Atkinson for 30 pounds.[53]
In 1873, Chartier's grave was accidentally discovered by the then owner of the property, John Stehman. Chartier was evidently buried in traditional Shawnee style, but with his helmet, a cutlass, and several small cannon balls.[54] A historical marker, erected in 1925, stands on the site of his burial, in Washington Boro, Pennsylvania, at the intersection of River Road and Charlestown Road.[29]
Notes
- ^ Evidence that Chartier was actually a glovemaker is very tenuous, but has become a traditional part of his biography. In fact, it appears that from 1667 to 1669 he was apprenticed to a house carpenter, a skill that would have made him useful on Jolliet's and La Salle's expeditions.[8]
- ^ The subgroup of the Shawnee that Chartier lived with is referred to in some sources as the "Stabbernowles," but this may be an alternate designation for the Pekowi.[12]
- ^ During his deposition before the court, Chartier (who is also referred to as "Martin Shortive") was identified by the tattoo "MC" on his chest, and stated that he had two Native American wives and a daughter, aged 16.[12]
External links
- Excerpts from Charles Augustus Hanna, The Wilderness Trail: or The ventures and adventures of the Pennsylvania traders on the Allegheny path, pertaining to Martin Chartier.
- Martin Chartier, Nashville's First White Person
References
- ^ Chartier Family Association: René Chartier
- ^ Martin Chartier at Find a Grave
- ^ a b c d Zuber Family Tree: Martin Chartier
- ^ History of Fort Crevecoeur Archived 2009-01-02 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c Don Greene, Shawnee Heritage II: Selected Lineages of Notable Shawnee (Lulu.com: Fantasy ePublications, 2008), Lulu.com: Fantasy ePublications, 2008; pp. 44-45 and 70.
- ^ René Chartier (1625 - 1689)
- ^ a b Jean Chartier Robert, The Chartier Families (A Complete Record of the Chartier Families in North America), edited by the American Section of the Chartier Family Association, Portland, Oregon, 1982. Printed in Montreal Canada 1982.
- ^ a b c d e f g Harriette Simpson Arnow, Seedtime on the Cumberland, Michigan State University Press. (2013)
- ^ a b c Historical Papers and Addresses of the Lancaster County Historical Society, Lancaster County Historical Society (Pa.), 1919; p. 70.
- ^ Tanya Larkin (2003). Jacques Marquette and Louis Jolliet: Explorers of the Mississippi. The Rosen Publishing Group. p. 6. ISBN 978-0-8239-3625-0. Retrieved 28 June 2013.
- ^ "Louis Joliet," Catholic Encyclopedia, New Advent
- ^ a b c d e f g h Charles Augustus Hanna, The Wilderness Trail: Or, The Ventures and Adventures of the Pennsylvania Traders on the Allegheny Path, Volume 1, Putnam's sons, 1911
- ^ Chief Straight Tail, posted Aug 22, 2011.
- ^ American-Canadian Genealogist, (New Hampshire: American Canadian Genealogical Society), Vol 19, No 2, p. 61: "The Chartiers: An Indian Life".
- ^ a b Jean-Roch Rioux, "Louis Hennepin," Dictionary of Canadian Biography, University of Toronto/Université Laval, 2003
- ^ a b c "The Site of Fort de Crèvecoeur", University of Illinois, 1925.
- ^ a b Francis Parkman, "La Salle And The Discovery Of The Great West," American Heritage, April 1957, Volume 8, Issue 3.
- ^ "La Salle," New International Encyclopedia, Volume 13, Second Edition, Dodd, Mead, 1915; p. 581.
- ^ "Henri de Tonti, Founder of Peoria"
- ^ a b "Fort Crevecoeur - built in 1680". Fort Crevecoeur Park and Campground. April 1, 2015. Archived from the original on November 12, 2015.
- ^ Francis Parkman, La Salle and the Discovery of the Great West: France and England in North America. Part Third, vol. V-VI; Little, Brown, 1897.
- ^ "Déclaration faite par devant le Sr. Duchesneau, Intendant en Canada, par Moyse Hillaret, charpentier de barque cy-devant au service du Sr. de la Salle, Aoust, 1680." cited in Francis Parkman, La Salle and the Discovery of the Great West: France and England in North America. Part Third, vol. V-VI; Little, Brown, 1897.
- ^ Mary Seaworth Chartier
- ^ Zuber Family Tree: Mary Chartier
- ^ Martin Chartier, Nashville's First White Person
- ^ Robert Trail, "Livingston County, Kentucky: Stepping Stone to Illinois," The Register of the Kentucky Historical Society, Vol. 69, No. 3 (July, 1971), pp. 239-272.
- ^ "Alvin Wirt, "The Upper Cumberland of Pioneer Times," 1954" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 2015-10-10. Retrieved 2018-07-22.
- ^ Chartier Family Association family tree "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 2014-05-12. Retrieved 2016-05-17.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ a b c Martin Chartier Historical Marker
- ^ Sherman Day, Historical Collections of the State of Pennsylvania: Containing a Copious Selection of the Most Interesting Facts, Traditions, Biographical Sketches, Anecdotes, Etc., Relating to Its History and Antiquities, Both General and Local, with Topographical Descriptions of Pennsylvania county and regional histories, G. W. Gorton, 1843; p. 391.
- ^ a b William Albert Hunter, "Peter Chartier: Knave of the Wild Frontier; The adventures of the first private owner of the site of New Cumberland and a record of subsequent landowners to 1814." Paper presented before the Cumberland County Historical Society on February 16, 1973. New Cumberland, PA: Historical Papers of the Cumberland County Historical Society Vol 9, no. 4 (1973); Cumberland County National Bank and Trust Co.
- ^ a b Stephen Warren, Worlds the Shawnees Made: Migration and Violence in Early America, UNC Press Books, 2014 ISBN 1469611732
- ^ Nancy Capace, Encyclopedia of Tennessee, Volume 21 of Encyclopedia of the United States, Somerset Publishers, Inc., 2000; pp. 52 & 71. ISBN 040309349X
- ^ "Strange Stories Hidden in Names: Indian Nomenclature Embodies Records of Old Time Events." Altoona Tribune, 11 Sep, 1923, p. 7
- ^ a b c William Henry Egle, Historical Register: Notes and Queries, Historical and Genealogical, Relating to Interior Pennsylvania, Volumes 1-2. L. S. Hart, printer., 1883; p. 251.
- ^ Paula W. Wallace, Indians in Pennsylvania. DIANE Publishing Inc., 2007; p. 126. ISBN 1422314936
- ^ Charles Shearer Keyser, Penn's Treaty with the Indians, D. McKay, 1882; p. 26.
- ^ "Tuomi J. Forrest, "Penn and the Indians."". Archived from the original on 2018-09-04. Retrieved 2018-06-12.
- ^ William Brandon, The American heritage book of Indians, American Heritage Library. Edited by Alvin M. Josephy; American Heritage Pub. Co., Simon & Schuster, 1961.
- ^ Erika Quesenbery Sturgill, "Susquehannocks – The vanquished tribe,"
- ^ Brubaker, John H. (2010). Massacre of the Conestogas: On the Trail of the Paxton Boys in Lancaster County. History Press. pp. 23–24.
- ^ Francis Jennings, "Pierre Bisaillon," Dictionary of Canadian Biography, University of Toronto/Université Laval, 2003
- ^ John B. Keith and Mrs. C. Harold Johnson, History of Cumberland and Adams Counties, Pennsylvania, Containing History of the Counties, Their Townships, Towns, Villages, Schools, Churches, Industries, Etc.; Portraits of Early Settlers and Prominent men; Biographies; History of Pennsylvania, Statistical and Miscellaneous Matter, etc., Chicago, Warner Beers & Co.,1886.
- ^ James Hart Merrell, Into the American Woods: Negotiators on the Pennsylvania Frontier, W. W. Norton & Company, 2000. ISBN 0393319768
- ^ The Pennsylvania Magazine of History and Biography, Vol. XXIV, Historical Society of Pennsylvania, 1900; p. 17.
- ^ Samuel Hazard, Colonial Records of Pennsylvania, T. Fenn, 1838; p. 400
- ^ Charles Penrose Keith, Chronicles of Pennsylvania from the English Revolution to the Peace of Aix-la-Chapelle, 1688-1748, Vol. II, Patterson & White, Philadelphia, 1917; p. 475.
- ^ Feasibility Study on a Potential Susquehanna Connector Trail for the John Smith Historic Trail, Prepared for The Friends of the John Smith Chesapeake National Historic Trail, November 16, 2009, Bucknell University.
- ^ Thomas P. de Graffenried, History of the de Graffenried Family, from 1191 A.D. to 1925, Vail-Ballou Press, New York, 1925; pp. 101-102.
- ^ The Virginia Magazine of History and Biography, The Virginia Historical Society, Vol. XXX, December, 1922
- ^ Henry Frank Eshleman, Lancaster County Indians: Annals of the Susquehannocks and Other Indian Tribes of the Susquehanna Territory from about the Year 1500 to 1763, the Date of Their Extinction, Express Print Company, 1909; p. 193.
- ^ Simone Vincens, Madame Montour and the Fur Trade (1667–1752), Xlibris Corporation, 2011; p. 211. ISBN 145687375X
- ^ Francis Jennings, The Ambiguous Iroquois Empire: The Covenant Chain Confederation of Indian Tribes with English Colonies from Its Beginnings to the Lancaster Treaty of 1744, W. W. Norton & Company, 1984; p. 270. ISBN 0393303020
- ^ David H. Landis, "The Location of Susquehannock Fort," Papers Read Before the Lancaster County Historical Society, March 4, 1910.
- 1655 births
- 1718 deaths
- 1660s in New France
- 1670s in New France
- 1660s in Canada
- 1670s in Canada
- 17th-century explorers
- 17th-century French people
- Explorers of Canada
- French explorers of North America
- Explorers of the United States
- French explorers
- Interpreters
- Native American history of Illinois
- Native American history of Ohio
- Native American history of Pennsylvania
- People from Allegheny County, Pennsylvania
- People of New France
- People of Colonial French Louisiana
- Persons of National Historic Significance (Canada)
