Super-server
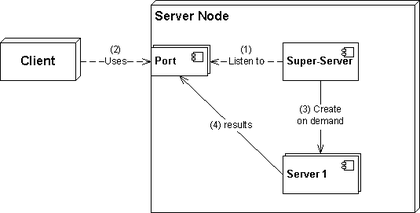

A super-server or sometimes called a service dispatcher is a type of daemon run generally on Unix-like systems.
Usage
A super-server starts other servers when needed, normally with access to them checked by a TCP wrapper. It uses very few resources when in idle state. This can be ideal for workstations used for local web development, client/server development[citation needed] or low-traffic daemons with occasional usage (such as ident and SSH).
Performance
There is a slight delay in connecting to the sub-daemons. Thus, when compared to standalone servers, a super-server setup may perform worse, especially when under high load. Some servers, such as tftpd-hpa, therefore take over the internet socket and listen on it themselves for some specified interval, anticipating more connections to come.
