Inborn errors of steroid metabolism
| Inborn error of steroid metabolism | |
|---|---|
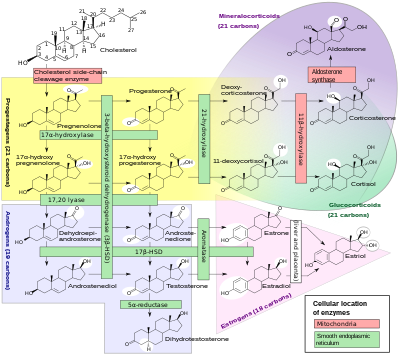 | |
| Steroidogenesis | |
| Specialty | Medical genetics, endocrinology |
An inborn error of steroid metabolism is an inborn error of metabolism due to defects in steroid metabolism.
Types
A variety of conditions of abnormal steroidogenesis exist due to genetic mutations in the steroidogenic enzymes involved in the process, of which include:
Generalized
- 20,22-Desmolase (P450scc) deficiency: blocks production of all steroid hormones from cholesterol
- 3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 2 deficiency: impairs progestogen and androgen metabolism; prevents the synthesis of estrogens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids; causes androgen deficiency in males and androgen excess in females
- Combined 17α-hydroxylase/17,20-lyase deficiency: impairs progestogen metabolism; prevents androgen, estrogen, and glucocorticoid synthesis; causes mineralocorticoid excess
- Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase deficiency: prevents production of numerous but not all sex steroids [1], as well as other metabolic reactions
Androgen- and estrogen-specific
- Isolated 17,20-lyase deficiency: prevents androgen and estrogen synthesis [2].
- Cytochrome b5 deficiency: subtype of isolated 17,20-lyase deficiency; additionally results in elevated methemoglobin and/or methemoglobinemia
- 17β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 3 deficiency: impairs androgen and estrogen metabolism; results in androgen deficiency in males and androgen excess and estrogen deficiency in females
- 5α-Reductase 2 deficiency: prevents the conversion of testosterone to dihydrotestosterone; causes androgen deficiency in males
- Aromatase deficiency: prevents estrogen synthesis; causes androgen excess in females
- Aromatase excess: causes excessive conversion of androgens to estrogens; results in estrogen excess in both sexes and androgen deficiency in males
Glucocorticoid- and mineralocorticoid-specific
- 21-Hydroxylase deficiency: prevents glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid synthesis; causes androgen excess in females
- 11β-Hydroxylase 1 deficiency: impairs glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid metabolism; causes glucocorticoid deficiency and mineralocorticoid excess as well as androgen excess in females
- 11β-Hydroxylase 2 deficiency: impairs corticosteroid metabolism; results in excessive mineralocorticoid activity
- 18-Hydroxylase deficiency: prevents mineralocorticoid synthesis; results in mineralocorticoid deficiency
- 18-Hydroxylase overactivity: impairs mineralocorticoid metabolism; results in mineralocorticoid excess
Miscellaneous
In addition, several conditions of abnormal steroidogenesis due to genetic mutations in receptors, as opposed to enzymes, also exist, including:
- Gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) insensitivity: prevents synthesis of sex steroids by the gonads in both sexes
- Follicle-stimulating (FSH) hormone insensitivity: prevents synthesis of sex steroids by the gonads in females; merely causes problems with fertility in males
- Luteinizing hormone (LH) insensitivity: prevents synthesis of sex steroids by the gonads in males; merely causes problems with fertility in females
- Luteinizing hormone (LH) oversensitivity: causes androgen excess in males, resulting in precocious puberty; females are asymptomatic
No activating mutations of the GnRH receptor in humans have been described in the medical literature,[3] and only one of the FSH receptor has been described, which presented as asymptomatic.[4][5]
See also
- Inborn error of metabolism
- Disorders of sex development
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
- Adrenal insufficiency
- Hypogonadism (hypoandrogenism and hypoestrogenism)
- Hypergonadism (hyperandrogenism and hyperestrogenism)
- Delayed puberty and precocious puberty
- Intersex
- Steroid hormone
- Corticosteroid (glucocorticoid, mineralocorticoid)
- Sex steroid (androgen, estrogen, and progestogen)
- Neuroactive steroid
- Hypothalamus and pituitary gland
- Adrenal cortex and gonad (testicle and ovary)
- HPA axis and HPG axis
References
- ^ Parween, Shaheena; Fernández-Cancio, Mónica; Benito-Sanz, Sara; Camats, Núria; Rojas Velazquez, Maria Natalia; López-Siguero, Juan-Pedro; Udhane, Sameer S; Kagawa, Norio; Flück, Christa E; Audí, Laura; Pandey, Amit V (April 2020). "Molecular Basis of CYP19A1 Deficiency in a 46,XX Patient With R550W Mutation in POR: Expanding the PORD Phenotype". The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism. 105 (4): e1272–e1290. doi:10.1210/clinem/dgaa076.
- ^ Fernández-Cancio, Mónica; Camats, Núria; Flück, Christa E.; Zalewski, Adam; Dick, Bernhard; Frey, Brigitte M.; Monné, Raquel; Torán, Núria; Audí, Laura (2018-04-29). "Mechanism of the Dual Activities of Human CYP17A1 and Binding to Anti-Prostate Cancer Drug Abiraterone Revealed by a Novel V366M Mutation Causing 17,20 Lyase Deficiency". Pharmaceuticals. 11 (2): 37. doi:10.3390/ph11020037. PMC 6027421. PMID 29710837.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Karges B, Karges W, de Roux N (2003). "Clinical and molecular genetics of the human GnRH receptor". Human Reproduction Update. 9 (6): 523–30. doi:10.1093/humupd/dmg040. PMID 14714589.
- ^ Eberhard Nieschlag; Hermann M. Behre; Susan Nieschlag (3 December 2009). Andrology: Male Reproductive Health and Dysfunction. Springer. p. 226. ISBN 978-3-540-78354-1. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- ^ Mark A. Sperling (25 April 2008). Pediatric Endocrinology E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 35. ISBN 978-1-4377-1109-7. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
Further reading
- Miller WL, Auchus RJ (February 2011). "The molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology of human steroidogenesis and its disorders". Endocrine Reviews. 32 (1): 81–151. doi:10.1210/er.2010-0013. PMC 3365799. PMID 21051590.
External links
This template is no longer used; please see Template:Endocrine pathology for a suitable replacement
