Barium acetylacetonate
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
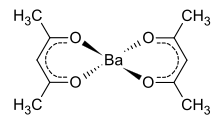
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Barium(2+); (Z)-4-oxopent-2-en-2-olate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.031.944 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C10H14BaO4 | |
| Molar mass | 335.545 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | White |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H332 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P301+P312, P304+P312, P304+P340, P312, P330, P501 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Barium acetylacetonate is a compound with formula Ba(C5H7O2)2. It is the barium complex of the anion of acetylacetone.
Uses
Barium acetylacetonate has uses in metal organic chemical vapour deposition. It is the source barium in the production of polycrystalline BaTiO3 thin films, alongside diisopropoxy-titanium-bis-(acetylacetonate) as the source of titanium.[2]
References
- ^ "Barium Acetylacetonate C10H14BaO4 | AMERICAN ELEMENTS ® Supplier & Info". Americanelements.com. Retrieved 2013-10-02.
- ^ Lee, C. H.; Park, S. J. (1990-12-01). "Preparation of ferroelectric BaTiO3 thin films by metal organic chemical vapour deposition". Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics. 1 (4): 219–224. doi:10.1007/BF00696081.
