The Lesser Key of Solomon
The Lesser Key of Solomon, also known as Clavicula Salomonis Regis[note 1] or Lemegeton, is an anonymous grimoire (or spell book) on demonology. It was compiled in the mid-17th century, mostly from materials a couple of centuries older.[1][2] It is divided into five books—the Ars Goetia, Ars Theurgia-Goetia, Ars Paulina, Ars Almadel, and Ars Notoria.[1]
Ars Goetia

Etymology
Goetia or Goëtia is a practice that includes the conjuration of demons. The Ancient Greek word γοητεία (goēteía) means "charm, jugglery, sorcery",[3] from γόης (góēs) "sorcerer, wizard" (plural: γόητες góētes).[4] The meaning of "sorcerer" is attested in a scholion, or commentary, referring to the Dactyli, a mythical race, stating that according to Pherecydes of Syros and Hellanicus of Lesbos, those to the left are goētes, while those to the right are deliverers from sorcery.[5][page needed] The word may be ultimately derived from the verb γοάω "groan, bewail" (goáō). Derivative terms are γοήτευμα "a charm" (goḗteuma, plural γοητεύματα goēteúmata) and γοητεύω "to bewitch, beguile" (goēteúō).
Γοητεία was a term for the magic in the Greco-Roman world. Its Latinized form is goëtia; in the 16th century, English adopted it as goecie or goety (and the adjectival form goetic), via French goétie.[citation needed]
During the Renaissance, goëtia was sometimes contrasted with magia, as "evil magic" vs. "good magic" or "natural magic",[6] or sometimes with theurgy.[7] Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa, in his Three Books of Occult Philosophy, writes "Now the parts of ceremonial magic are goetia and theurgia. Goetia is unfortunate, by the commerces of unclean spirits made up of the rites of wicked curiosities, unawful charms, and deprecations, and is abandoned and execrated by all laws."[8]
Sources
The most obvious source for the Ars Goetia is Johann Weyer's Pseudomonarchia Daemonum in his De praestigiis daemonum. Weyer does not cite, and is unaware of, any other books in the Lemegeton, suggesting that the Lemegeton was derived from his work, not the other way around.[1][9] The order of the spirits changed between the two, four additional spirits were added to the later work, and one spirit (Pruflas) was omitted. The omission of Pruflas, a mistake that also occurs in an edition of Pseudomonarchia Daemonum cited in Reginald Scot's The Discoverie of Witchcraft, indicates that the Ars Goetia could not have been compiled before 1570. Indeed, it appears that the Ars Goetia is more dependent upon Scot's translation of Weyer than on Weyer's work in itself. Additionally, some material came from Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa's Three Books of Occult Philosophy, the Heptameron by pseudo-Pietro d'Abano,[note 2][1][10] and the Magical Calendar.[11]
Weyer's Officium Spirituum, which is likely related to a 1583 manuscript titled The Office of Spirits,[12] appears to have ultimately been an elaboration on a 15th-century manuscript titled Le Livre des Esprits (30 of the 47 spirits are nearly identical to spirits in the Ars Goetia).[2][10]
In a slightly later copy made by Thomas Rudd (1583?–1656), this portion was labelled "Liber Malorum Spirituum seu Goetia", and the seals and demons were paired with those of the 72 angels of the Shem HaMephorash[13] which were intended to protect the conjurer and to control the demons he summoned.[14] The angelic names and seals derived from a manuscript by Blaise de Vigenère, whose papers were also used by Samuel Liddell MacGregor Mathers (1854-1918) in his works for the Hermetic Order of the Golden Dawn[10] (1887–1903). Rudd may have derived his copy of Liber Malorum Spirituum from a now-lost work by Johannes Trithemius,[10] who taught Agrippa, who in turn taught Weyer.
This portion of the work was later translated by Samuel Liddell MacGregor Mathers and published by Aleister Crowley in 1904 under the title The Book of the Goetia of Solomon the King. Crowley added some additional invocations previously unrelated to the original work (including some evocations in the Enochian language), as well as essays describing the rituals as psychological exploration instead of demon summoning.[15][16]
The Seventy-Two Demons
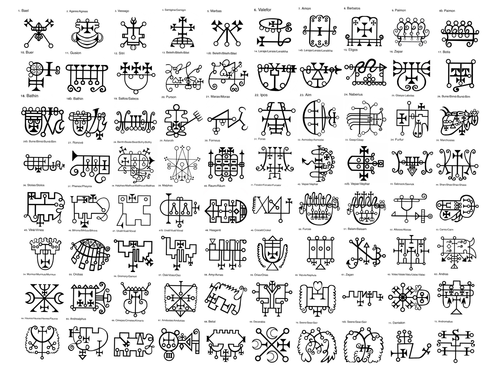
The demons' names (given below) are taken from the Ars Goetia, which differs in terms of number and ranking from the Pseudomonarchia Daemonum of Weyer. As a result of multiple translations, there are multiple spellings for some of the names, which are given in the articles concerning them.
- King Bael
- Duke Agares
- Prince Vassago
- Marquis Samigina
- President Marbas
- Duke Valefor
- Marquis Amon
- Duke Barbatos
- King Paimon
- President Buer
- Duke Gusion
- Prince Sitri
- King Beleth
- Marquis Leraje
- Duke Eligos
- Duke Zepar
- Count/President Botis
- Duke Bathin
- Duke Sallos
- King Purson
- Count/President Marax
- Count/Prince Ipos
- Duke Aim
- Marquis Naberius
- Count/President Glasya-Labolas
- Duke Buné
- Marquis/Count Ronové
- Duke Berith
- Duke Astaroth
- Marquis Forneus
- President Foras
- King Asmoday
- Prince/President Gäap
- Count Furfur
- Marquis Marchosias
- Prince Stolas
- Marquis Phenex
- Count Halphas
- President Malphas
- Count Räum
- Duke Focalor
- Duke Vepar
- Marquis Sabnock
- Marquis Shax
- King/Count Viné
- Count Bifrons
- Duke Vual
- President Haagenti
- Duke Crocell
- Knight Furcas
- King Balam
- Duke Alloces
- President Caim
- Duke/Count Murmur
- Prince Orobas
- Duke Gremory
- President Ose
- President Amy
- Marquis Orias
- Duke Vapula
- King/President Zagan
- President Valac
- Marquis Andras
- Duke Flauros
- Marquis Andrealphus
- Marquis Kimaris
- Duke Amdusias
- King Belial
- Marquis Decarabia
- Prince Seere
- Duke Dantalion
- Count Andromalius
The demons are described as being commanded by four kings of the cardinal directions: Amaymon (East), Corson (West), Ziminiar (North), and Gaap (South). A footnote in one variant edition instead lists them as Oriens or Uriens, Paymon or Paymonia, Ariton or Egyn, and Amaymon or Amaimon, alternatively known as Samael, Azazel, Azael, and Mahazael (purportedly their preferred rabbinic names).[17] Agrippa's Occult Philosophy lists the kings of the cardinal directions as Urieus (East), Amaymon (South), Paymon (West), and Egin (North); again providing the alternate names Samuel (i.e. Samael), Azazel, Azael, and Mahazuel. The Magical Calendar lists them as Bael, Moymon, Poymon, and Egin,[18][19] though Peterson notes that some variant editions instead list '"Asmodel in the East, Amaymon in the South, Paymon in the West, and Aegym in the North"; "Oriens, Paymon, Egyn, and Amaymon"; or "Amodeo [sic] (king of the East), Paymon (king of the West), Egion (king of the North), and Maimon."'[18]
Ars Theurgia Goetia
The Ars Theurgia Goetia mostly derives from Trithemius's Steganographia, though the seals and order for the spirits are different due to corrupted transmission via manuscript.[10][20] Rituals not found in Steganographia were added, in some ways conflicting with similar rituals found in the Ars Goetia and Ars Paulina. Most of the spirits summoned are tied to points on a compass, four Emperors are tied to the cardinal points (Carnesiel in the East, Amenadiel in the West, Demoriel in the North and Caspiel in the South), and sixteen Dukes are tied to cardinal points, inter-cardinal points, and additional directions between those. There are an additional eleven Wandering Princes, totalling thirty-one spirit leaders who each rule several to a few dozen spirits.[21]
Ars Paulina
Derived from book three of Trithemius's Steganographia and from portions of the Heptameron, but purportedly delivered by Paul the Apostle instead of (as claimed by Trithemius) Raziel. Elements from The Magical Calendar, astrological seals by Robert Turner's 1656 translation of Paracelsus's Archidoxes of Magic, and repeated mentions of guns and the year 1641 indicate that this portion was written in the later half of the seventeenth century.[22][23] Traditions of Paul communicating with heavenly powers are almost as old as Christianity itself, as seen in some interpretations of 2 Corinthians 12:2–4 and the apocryphal Apocalypse of Paul. The Ars Paulina is in turn divided into two books, the first detailing twenty-four angels aligned with the twenty-four hours of the day, the second (derived more from the Heptameron) detailing the 360 spirits of the degrees of the zodiac.[23]
Ars Almadel
Mentioned by Trithemius and Weyer, the latter of whom claimed an Arabic origin for the work. A 15th-century copy is attested to by Robert H.Turner, and Hebrew copies were discovered in the 20th century. The Ars Almadel instructs the magician on how to create a wax tablet with specific designs intended to contact angels via scrying.[24][25]
Ars Notoria
The oldest known portion of the Lemegeton, the Ars Notoria (or Notory Art) was first mentioned by Michael Scot in 1236 (and thus was written earlier). The Ars Notoria contains a series of prayers (related to those in The Sworn Book of Honorius) intended to grant eidetic memory and instantaneous learning to the magician. Some copies and editions of the Lemegeton omit this work entirely;[26][27] A. E. Waite ignores it completely when describing the Lemegeton.[9] It is also known as the Ars Nova.
Editions
- Crowley, Aleister (ed.), S. L. MacGregor Mathers (transcribed) The Book of the Goetia of Solomon the King. Translated into the English tongue by a dead hand (Foyers, Inverness: Society for the Propagation of Religious Truth, 1904) 1995 reprint: ISBN 0-87728-847-X.
- Greenup, A. W., "The Almadel of Solomon, according to the text of the Sloane MS. 2731" The Occult Review vol. 22 no. 2, August 1915, 96–102.
- Henson, Mitch (ed.) Lemegeton. The Complete Lesser Key of Solomon (Jacksonville: Metatron Books, 1999) ISBN 978-0-9672797-0-1. Noted by Peterson to be "uncritical and indiscriminate in its use of source material".[15]
- de Laurence, L. W. (ed.), The Lesser Key Of Solomon, Goetia, The Book of Evil Spirits (Chicago: de Laurence, Scott & Co., 1916) 1942 reprint: ISBN 978-0-7661-0776-2; 2006 reprint: ISBN 978-1-59462-200-7. A plagiarism of the Mathers/Crowley edition.[28]
- Peterson, Joseph H. (ed.), The Lesser Key of Solomon: Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis (York Beach, ME: Weiser Books, 2001). Considered "the definitive version"[29] and "the standard edition".[30]
- Runyon, Carroll, The Book of Solomon’s Magick (Silverado, CA: C.H.S. Inc., 1996). Targeted more toward practicing magicians than academics, claims that the demons were originally derived from Mesopotamian mythology.[31]
- Shah, Idries, The Secret Lore of Magic (London: Abacus, 1972). Contains portions of Ars Almandel and split sections the Goetia, missing large portions of the rituals involved.[15]
- Skinner, Stephen & Rankine, David (eds.), The Goetia of Dr Rudd: The Angels and Demons of Liber Malorum Spirituum Seu Goetia (Sourceworks of Ceremonial Magic) (London and Singapore: The Golden Hoard Press 2007) ISBN 978-0-9547639-2-3
- Thorogood, Alan (ed.), Frederick Hockley (transcribed), The Pauline Art of Solomon (York Beach, ME: The Teitan Press, 2016)
- Waite, Arthur Edward, The Book of Black Magic and of Pacts. Including the rites and mysteries of goëtic theurgy, sorcery, and infernal necromancy, also the rituals of black magic (Edinburgh: 1898). Reprinted as The Secret Tradition in Goëtia. The Book of Ceremonial Magic, including the rites and mysteries of Goëtic theurgy, sorcery, and infernal necromancy (London: William Rider & Son, 1911). Includes the Goetia, Pauline Art and Almadel.[15]
- White, Nelson & Anne (eds.) Lemegeton: Clavicula Salomonis: or, The complete lesser key of Solomon the King (Pasadena, CA: Technology Group, 1979). Noted by Peterson to be "almost totally unreadable".[15]
- Wilby, Kevin (ed.) The Lemegetton. A Medieval Manual of Solomonic Magic (Silian, Lampeter: Hermetic Research Series, 1985)
- Veenstra, Jan R. “The Holy Almandal. Angels and the intellectual aims of magic” in Jan N. Bremmer and Jan R. Veenstra (eds.), The Metamorphosis of Magic from Late Antiguity to the Early Modern Period (Leuven: Peeters, 2002), pp. 189–229. The Almadel is transcribed at pp. 217–229.
See also
Notes
- ^ The Clavicula Salomonis, or Key of Solomon is an earlier text referring to different material.
- ^ The latter republished spuriously as a purported Fourth Book of Agrippa.
References
- ^ a b c d Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis: The Lesser Key of Solomon, Detailing the Ceremonial Art of Commanding Spirits Both Good and Evil; ed. Joseph H. Peterson; Weiser Books Maine; 2001. p.xi-xvii
- ^ a b The Goetia of Dr Rudd; Thomas Rudd, Eds. Stephen Skinner & David Rankine; 2007, Golden Hoard Press. p. 399.
- ^ "LSJ". Perseus.tufts.edu. Retrieved 2013-10-18.
- ^ "LSJ". Perseus.tufts.edu. Retrieved 2013-10-18.
- ^ Muller, Carl Otfried; Müller, Theodor; Carl, Müller (2010). Fragmenta Historicorum Graecorum. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 9781108016605.
Ἀριστεροὶ μὲν, ὥς φησι Φερεκύδης, οἱ γόητες αὐτῶν· οἱ δὲ ἀναλύοντες, δεξιοὶ, ὡς Ἑλλάνικος.
- ^ Mebane, John S. (1992). Renaissance magic and the return of the Golden Age : the occult tradition and Marlowe, Jonson, and Shakespeare. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press. pp. 44, 45. ISBN 9780803281790.
- ^ Thorndike, Lynn (2003). History of magic and experimental science. [Whitefish, Mont.]: Kessinger. p. 505. ISBN 9780766143135.
- ^ Nettesheim, written by Henry Cornelius Agrippa of; edited, completely annotated with modern commentary ; translated by James Freake; Tyson, annotated by Donald (1993). Three books of occult philosophy (1st ed.). St. Paul, MN, U.S.A.: Llewellyn. p. 695. ISBN 9780875428321.
{{cite book}}:|last2=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b The Book of Ceremonial Magic, Part I, Chapter III, section 2: "The Lesser Key of Solomon"; Arthur Edward Waite; London, 1913; available online at The Internet Sacred Text Archive, (direct link to section).
- ^ a b c d e Rudd, Ed. Skinner & Rankine; pp. 31–43
- ^ Rudd, Ed. Skinner & Rankine; p.82
- ^ A Book of the Office of Spirits; John Porter, Trans. Frederick Hockley, Ed. Colin D. Campbelll; Teitan Press, 2011. p. xiii–xvii
- ^ Rudd, Ed. Skinner & Rankine; p.14-19
- ^ Rudd, Ed. Skinner & Rankine; p. 71
- ^ a b c d e Peterson, 2001, pp. xviii–xx
- ^ Stephen Skinner & David Rankine, The Goetia of Dr. Rudd, Golden Hoard Press, 2007, pp. 47–50
- ^ Peterson, 2001, p. 40
- ^ a b First footnote by Joseph H. Peterson to Trithemius's The art of drawing spirits into crystals
- ^ The Magical Calendar; Johann Baptist Grossschedel, trans. and ed. Adam McLean; Phanes Press, 1994. p. 35.
- ^ Peterson, 2001, p.xv.
- ^ Rudd, ed. Skinner & Rankine; p.53-57
- ^ Peterson, 2001, p. xv–xvi
- ^ a b Rudd, ed. Skinner & Rankine; pp. 57–59
- ^ Peterson, 2001, p. xvi
- ^ Rudd, ed. Skinner & Rankine; p.59-60
- ^ Peterson, 2001, p. xvii
- ^ Rudd, ed. Skinner & Rankine; p.60-63.
- ^ Rudd, ed. Skinner & Rankine; p.50,
- ^ Rudd, ed. Skinner & Rankine; p.8
- ^ Rudd, ed. Skinner & Rankine; p.52
- ^ Rudd, ed. Skinner & Rankine; p.51–52
Bibliography
- E. J. Langford Garstin, Theurgy or The Hermetic Practice: A Treatise on Spiritual Alchemy. Berwick: Ibis Press, 2004. (Published posthumously)
- Aleister Crowley (ed.), Samuel Liddell Mathers (trans.), The Goetia: The Lesser Key of Solomon the King. York Beach, ME : Samuel Weiser (1995) ISBN 0-87728-847-X.
- Stephen Skinner, & David Rankine, The Goetia of Dr Rudd: The Angels and Demons of Liber Malorum Spirituum Seu Goetia (Sourceworks of Ceremonial Magic). Golden Hoard Press, 2007. ISBN 978-0-9547639-2-3
External links
- J. B. Hare, online edition (2002, sacred-texts.com)
- Joseph H. Peterson, online edition (1999)
- Demon list with descriptions
