Phosphoramide
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Phosphoric triamide
| |
| Other names
Phosphoric amide; Diaminophosphorylamine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| H6N3OP | |
| Molar mass | 95.042 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | white solid |
| good | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
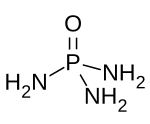
Phosphoramide is a chemical compound with the molecular formula O=P(NH2)3. It is a derivative of phosphoric acid in which each of the hydroxyl groups have been replaced with an amino group. Phosphoramide arises from the reaction of phosphoryl chloride with ammonia. It is a white solid that is soluble in polar solvents. In moist air, it hydrolyzes to an ammonium salt:
- 2 H2O + OP(NH2)3 → NH4+[HPO3(NH2)] + NH3
It reacts with sodium hydroxide with loss of ammonia:[1]
- NaOH + OP(NH2)3 → NaO2P(NH2)2 + NH3
The related thiophosphoryl compound P(=S)(NH2)3 was made from the reaction of thiophosphoryl chloride with ammonia.
Phosphoramides
Phosphoramide is also the parent compound for a range of derivatives called phosphoramides.[2] An example compound is the polar solvent hexamethylphosphoramide (HMPA).
References
- ^ "Phosphoroxy‐triamid und Phosphorthio‐triamid". Chemische Berichte. 87: 333–340. 1954. doi:10.1002/cber.19540870308.
{{cite journal}}: Cite uses deprecated parameter|authors=(help) - ^ IUPAC, Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. (the "Gold Book") (1997). Online corrected version: (2006–) "phosphoramides". doi:10.1351/goldbook.A00484
External links
 Media related to phosphoramides at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to phosphoramides at Wikimedia Commons The dictionary definition of phosphoramide at Wiktionary
The dictionary definition of phosphoramide at Wiktionary
