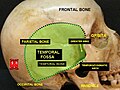
Temporal fossa
Appearance
| Temporal fossa | |
|---|---|
 The temporal fossa is clearly visible in this picture | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | fossa temporalis |
| TA98 | A02.1.00.022 |
| TA2 | 426 |
| FMA | 75307 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The temporal fossa is a fossa (shallow depression) on the side of the skull bounded by the temporal lines and terminating below the level of the zygomatic arch.
Boundaries
- Medial: frontal bone, parietal bone, temporal bone, and sphenoid bone.
- Lateral: Temporal fascia
- Anterior: Posterior surface of the frontal process of the zygomatic bone and the posterior surface of the zygomatic process of the frontal bone.
- Superior: Pair of temporal lines (superior and inferior temporal lines) that arch across the skull from the zygomatic process of the frontal bone to the supramastoid crest of the temporal bone
- Inferior: Zygomatic arch laterally and by the infratemporal crest of the greater wing of the sphenoid medially.
Temporal & Infratemporal Fossa
- Osteology
- Temporal fossa, boundaries & contents
- Infratemporal fossa, boundaries & contents
- Muscles of mastication
- Maxillary artery
- Pterygoid venous plexus
- Mandibular nerve
- Temporomandibular Joint
Contents
- Temporalis muscle
- Deep temporal arteries
- Deep temporal nerves
- Superficial temporal artery (from external carotid)
- Zygomaticotemporal nerve
Clinical significance
The pterion is located in the temporal fossa, Clinically the pterion is an important area because it overlies the anterior division of the middle meningeal artery and vein.Trauma in this region can lead to an extradural haematoma, which can result in herniation of brain tissue and ischemia
Additional images
-
Temporal fossa
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Temporal fossa.