Posterior scrotal nerves
| Posterior scrotal nerves | |
|---|---|
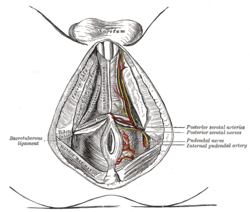 The superficial branches of the internal pudendal artery. (Posterior scrotal nerves labeled at center right.) | |
 Sacral plexus of the right side. (Posterior scrotal nerves not labeled, but visible at bottom right.) | |
| Details | |
| From | perineal nerve |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervi scrotales posteriores |
| TA98 | A14.2.07.040M |
| TA2 | 6559 |
| FMA | 21867 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The posterior scrotal branches (in men) or posterior labial branches (in women) are two in number, medial and lateral. They are branches of the perineal nerve, which is itself a branch of the pudendal nerve. The pudendal nerve arises from spinal roots S2 through S4, travels through the pudendal canal on the fascia of the obturator internus muscle, and gives off the perineal nerve in the perineum. The major branch of the perineal nerve is the posterior scrotal/posterior labial.
They pierce the fascia of the urogenital diaphragm, and run forward along the lateral part of the urethral triangle in company with the posterior scrotal branches of the perineal artery; they are distributed to the skin of the scrotum or labia and communicate with the perineal branch of the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 968 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 968 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- perineum at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (analtriangle3)
- figures/chapter_32/32-2.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School
- figures/chapter_32/32-3.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School
