Panobacumab
Appearance
| Monoclonal antibody | |
|---|---|
| Type | Whole antibody |
| Source | Human |
| Target | Pseudomonas aeruginosa serotype IATS O11 |
| Clinical data | |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C38714H60189N10637O12187S322 |
| Molar mass | 879959.96 g·mol−1 |
| | |
Panobacumab (proposed INN) is a monoclonal antibody designed as an antibacterial against Pseudomonas aeruginosa.[1]
It is a fully human pentameric IgM antibody with a mouse J chain.[1]
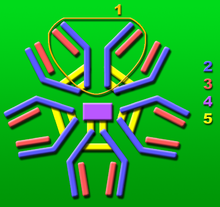
1: Base unit.
2: Heavy chains.
3: Light chains.
4: J chain.
5: Intermolecular disulfide bonds.
Development
Panobacumab is being developed by Aridis Pharmaceuticals. As of November 15th it is in phase 2 clinical trials. The originator was Berna Biotech.[2]
The mechanism of action is as a lipopolysaccharide inhibitor.[2]
References
- ^ a b International Nonproprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Substances (INN, prepublication copy), World Health Organization.
- ^ a b https://adisinsight.springer.com/drugs/800024401. Retrieved 15 November 2019.
{{cite web}}: Missing or empty|title=(help)
