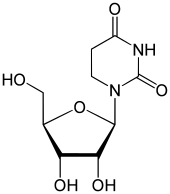
Dihydrouridine
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]-1,3-diazinane-2,4-dione
| |
| Other names
5,6-dihydrouridine
1,3,5,6-tetrahydrouridine | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.257.727 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C9H14N2O6 | |
| Molar mass | 246.217 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Dihydrouridine (abbreviated as D,[1] DHU, or UH2) is a pyrimidine nucleoside which is the result of adding two hydrogen atoms to a uridine, making it a fully saturated pyrimidine ring with no remaining double bonds. D is found in tRNA and rRNA molecules as a nucleoside; the corresponding nucleobase is 5,6-dihydrouracil.

Because it is non-planar, D disturbs the stacking interactions in helices and destabilizes the RNA structure. D also stabilizes the C2’-endo sugar conformation, which is more flexible than the C3’-endo conformation; this effect is propagated to the 5’-neighboring residue. Thus, while pseudouridine and 2’-O-methylations stabilize the local RNA structure, D does the opposite.[2]
The tRNAs of organisms that grow at low temperatures (psychrophiles) have high 5,6-dihydrouridine levels (40-70% more on average) which provides the necessary local flexibility of the tRNA at or below the freezing point.[3]
References
- ^ IUPAC-IUB Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature (1970). "Abbreviations and symbols for nucleic acids, polynucleotides, and their constituents". Biochemistry. 9 (20): 4022–4027. doi:10.1021/bi00822a023.
- ^
 Dalluge JJ; Hashizume T; Sopchik AE; McCloskey JA; Davis DR. (Mar 15, 1996). "Conformational flexibility in RNA: the role of dihydrouridine". Nucleic Acids Res. 24 (6): 1073–1079. doi:10.1093/nar/24.6.1073. PMC 145759. PMID 8604341.
Dalluge JJ; Hashizume T; Sopchik AE; McCloskey JA; Davis DR. (Mar 15, 1996). "Conformational flexibility in RNA: the role of dihydrouridine". Nucleic Acids Res. 24 (6): 1073–1079. doi:10.1093/nar/24.6.1073. PMC 145759. PMID 8604341.
- ^
 Dalluge JJ; Hamamoto T; Horikoshi K; Morita RY; Stetter KO; McCloskey JA (March 1, 1997). "Posttranscriptional modification of tRNA in psychrophilic bacteria". J Bacteriol. 179 (6): 1918–1923. PMC 178914. PMID 9068636.
Dalluge JJ; Hamamoto T; Horikoshi K; Morita RY; Stetter KO; McCloskey JA (March 1, 1997). "Posttranscriptional modification of tRNA in psychrophilic bacteria". J Bacteriol. 179 (6): 1918–1923. PMC 178914. PMID 9068636.
