French Pete Trail
| French Pete Trail | |
|---|---|
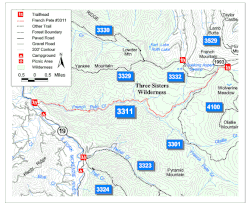 Map of French Pete area and surroundings | |
| Length | 9.9 mi (15.9 km) |
| Location | Cascade Range, Lane County, Oregon |
| Designation | Three Sisters Wilderness Willamette National Forest |
| Trailheads | French Pete Trailhead (west) Pat Saddle Trailhead (east) |
| Use | hikers, horses |
| Elevation change | about 1,000 feet (300 m) |
| Difficulty | easy to moderate |
| Season | late March to mid-December |
| Months | about 9 |
| Sights | French Pete Creek old-growth forest |
| Surface | natural |
The French Pete Trail is a 9.9-mile (15.9 km) hiking trail in the valley of French Pete Creek in the Three Sisters Wilderness of western Oregon.[1] The trail passes through low-elevation old-growth forest that was a nationwide political issue in the 1960s and 1970s because of conflicting plans for logging and for wilderness designation, respectively. In 1978, the U.S. Congress passed a bill adding the French Pete area to the Three Sisters Wilderness.
Description
The heavily used trail is in an old-growth forest in the western part of the Three Sisters Wilderness within the Willamette National Forest.[1][2] At the trailhead at the path's western end, the elevation is 1,850 feet (560 m). Open for hiking from spring through fall, the trail climbs about 1,000 feet (300 m) over 5 miles (8.0 km) and ends 9.9 miles (15.9 km) from the trailhead. French Pete Creek flows beside the trail for the trail's first five miles, approximately.[3] The forest is made up of "gargantuan Douglas firs and 1000-year-old cedars,"[3] with an understory that includes sword fern, Oregon grape, and twinflower.[3]
Area history

In 1938, the U.S. Forest Service added 55,620 acres (225.1 km2), including the French Pete area, to the Three Sisters Primitive Area, which had been established in 1937.[4] In 1957, the Forest Service reduced the size of the protected area, removing French Pete from protection, so that more land could be available for timber sales.[4][5] Conservation advocates sought to regain protection for French Pete. Their frustration with the Forest Service's level of authority over timber production and wilderness areas contributed to the inception and enactment of the Wilderness Act in Congress in 1964.[5] The law created new wilderness areas and controversy over the management for the new areas. It marked the establishment and growth of an activist environmental movement at a time when both logging and recreation were rapidly increasing.[4][6] The movement is best known for the controversy surrounding management of French Pete.[6]
The Forest Service announced a plan for logging in the valley in 1968. Conservation groups and most local citizens were opposed to the plan. U.S. Senator Bob Packwood, a Republican from Oregon, recommended that the Forest Service abandon it. Groups such as the Oregon Wilderness Coalition and the Save French Pete Committee campaigned for protection of French Pete.[4] The latter group appealed a logging proposal in court, but the appeal was rejected, and instead the logging was only delayed,[7][8] adding to political tensions.[7]

The Forest Service had a history of encouraging logging in the forests of western Oregon. It planned to log at least 3,000,000 board feet (7,100 m3) of timber if the area was not protected to ensure that the logging industry would be able "to survive the mounting demands from preservationists to stop logging scenic areas."[9][10] There was also concern that without logging, there would be a heightened risk of wildfire, because many of the area's trees were diseased or had been infested and killed by beetles. A forester from Springfield said, "It will be a very short time until the happenstance of lightning once again starts a fire that will wipe out the countryside."[11]
In 1972, former U.S. Senator Wayne Morse, a Democrat from Oregon, hiked into the area with conservation activists and encouraged Republican U.S. Senator Mark Hatfield to do the same. Morse expressed confidence that French Pete would be protected, while Hatfield still supported the plan for logging.[12] However, Hatfield later reversed his position and began to support wilderness designation in general.[13]
In 1978, after "14 years of ardent protest by hikers, students, and environmentalists,"[3] the Endangered Wilderness Act protected 45,400 acres (18,400 ha) of the French Pete forest as wilderness, effective February 28.[14][15] French Pete became one of the first low-elevation, old-growth valleys to be designated as wilderness in the United States.[3][4][5]
References
- ^ a b "French Pete Campground". Willamette National Forest. Retrieved 6 August 2010.
- ^ "French Pete Creek". Trails.com. Retrieved 7 August 2010.
- ^ a b c d e Sullivan, William L. (2014). 100 Hikes in the Central Oregon Cascades (Fourth ed.). Eugene, Oregon: Navillus Press. pp. 178, 186–187. ISBN 978-0981570174.
- ^ a b c d e Marsh, Kevin. "Three Sisters Wilderness". The Oregon Encyclopedia. Portland State University. Retrieved 27 May 2015.
- ^ a b c Hughes, J. Donald (2009). An Environmental History of the World (2nd ed.). New York, New York: Routledge. pp. 203–204. ISBN 978-0-415-48149-6.
- ^ a b "A brief history of the Willamette National Forest"". Willamette National Forest. 24 October 2003. Retrieved 12 September 2010. This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b Williams, Gerald W. (2007). The Forest Service: Fighting for Public Lands. Westport, Connecticut: Greenwood Press. p. 181. ISBN 978-0-313-33794-9.
- ^ Wuerthner, George (2002). Oregon's Wilderness Areas: the Complete Guide. Englewood, Colorado: Westcliffe Publishers. p. 20. ISBN 1-56579-434-6.
- ^ Smith, A. Robert (26 May 1972). "Hatfield to visit French Pete, then reveal stance". The Register-Guard. Eugene, Oregon. p. C1. Retrieved 5 March 2011.
- ^ Marsh, Kevin R. (2007). Drawing Lines in the Forest. Seattle, Washington: University of Washington Press. p. 133. ISBN 978-0-295-98702-6.
- ^ Paseman, Lloyd (18 November 1971). "French Pete Valley facing threat of fire, forester says". The Register-Guard. p. B1. Retrieved 17 October 2010.
- ^ Willis, Henny (15 August 1972). "Morse pledges to fight for bill to preserve French Pete area". The Register-Guard. p. 6B. Retrieved 8 August 2010.
- ^ Kerr, Andy (2004). Oregon Wild: Endangered Forest Wilderness. Portland, Oregon: Oregon Natural Resources Council. p. 57. ISBN 0-9624877-8-3.
- ^ "Wilderness dispute resolved". The Bulletin. Bend, Oregon. Associated Press. 24 January 1978. p. 11. Retrieved 19 October 2010.
- ^ McArthur, Lewis A.; McArthur, Lewis L. (2003) [1928]. Oregon Geographic Names (7th ed.). Portland, Oregon: Oregon Historical Society Press. p. 384. ISBN 978-0875952772.
External links
- Photo of French Pete Creek by Andrew Kumler
- French Pete Trail # 3311 from the Willamette National Forest
