Tricolored heron
This article includes a list of general references, but it lacks sufficient corresponding inline citations. (November 2010) |
| Tricolored heron | |
|---|---|

| |
| Egretta tricolor on Marco Island, Florida | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Aves |
| Order: | Pelecaniformes |
| Family: | Ardeidae |
| Genus: | Egretta |
| Species: | E. tricolor
|
| Binomial name | |
| Egretta tricolor (Statius Muller, 1776)
| |
| |
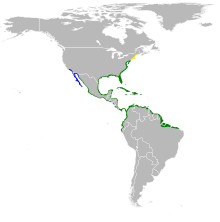
| Range of E. tricolor Breeding range Year-round range Wintering range
| |
The tricolored heron (Egretta tricolor), formerly known as the Louisiana heron, is a small species of heron native to coastal parts of the Americas; in the Atlantic region, it ranges from the northeastern United States, south along the coast, through the Gulf of Mexico and the Caribbean, to northern South America as far south as Brazil. In the Pacific region, it ranges from Peru to California, but it is only a nonbreeding visitor to the far north.
Habitat and breeding
Tricolored herons breed in swamps and other coastal habitats. They nest in colonies, often with other herons, usually on platforms of sticks in trees or shrubs. In each clutch, three to seven eggs are typically laid.
Description
This species measures from 56 to 76 cm (22 to 30 in) long and has a typical wingspan of 96 cm (38 in).[2] The slightly larger male heron weighs 415 g (14.6 oz) on average, while the female averages 334 g (11.8 oz).[3] It is a medium-large, long-legged, long-necked heron with a long, pointed, yellowish or greyish bill with a black tip. Its legs and feet are dark.
Adults have a blue-grey head, neck, back, and upper wings, with a white line along the neck. The belly is white. In breeding plumage, they have long, blue, filamentous plumes on their heads and necks, and buff ones on their backs.
Behavior and diet
The tricolored heron stalks its prey in shallow or deeper water, often running as it does so. It eats fish, crustaceans, reptiles, and insects.
Gallery
-
Flying
-
Juvenile
-
In full breeding colors in central Florida
References
- ^ BirdLife International (2012). "Egretta tricolor". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2012. Retrieved 26 November 2013.
{{cite journal}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help) - ^ "Tricolored Heron". All About Birds. Cornell Lab of Ornithology.
- ^ "Biological and Ecotoxicological Characteristics of Terrestrial Vertebrate Species Residing in Estuaries: Tricolored Heron". USGS.
Further reading
- Hilty, Steven L. (2003). Birds of Venezuela. Princeton University Press. ISBN 0-7136-6418-5.
- Field Guide to the Birds of North America. National Geographic. 1987. ISBN 0-7922-6877-6.
- Stiles, F. Gary; Skutch, Alexander F. (1989). A Guide to the Birds of Costa Rica. Comstock Publishing Associates. ISBN 0-8014-9600-4.
External links
- Tricolored Heron - Egretta tricolor - USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter
- Tricolored heron photos at Field Guide: Birds of the World on Flickr
- Tricolored heron Bird Sound at Florida Museum of Natural History
- "Tricolored heron media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Tricolored heron photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Tricolored Heron species account at Neotropical Birds (Cornell Lab of Ornithology)
- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Egretta
- Birds of the Americas
- Birds of the Caribbean
- Birds of the Guianas
- Birds of Mexico
- Birds of Panama
- Birds of Colombia
- Birds of Venezuela
- Birds of Ecuador
- Birds of Peru
- Birds of Brazil
- Native birds of the Southeastern United States
- Birds described in 1776
- Taxa named by Philipp Ludwig Statius Müller








