Depth hoar
Appearance

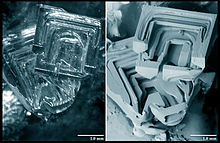

Depth hoar, also called sugar snow[1] or temperature gradient snow (or TG snow),[2] are large snow-crystals occurring at the base of a snowpack that form when uprising water vapor deposits, or desublimates, onto existing snow crystals. Depth hoar crystals are large, sparkly grains with facets that can be cup-shaped and that are up to 10 mm in diameter. Depth hoar crystals bond poorly to each other, increasing the risk for avalanches.
The formation of depth hoar in Arctic or Antarctic firn can cause isotopic changes in the accumulating ice. This can influence analysis of ice cores in scientific research.
References
- ^ "Be Aware of Depth Hoar". Powder Magazine. Retrieved April 15, 2014.
- ^ "Depth Hoar". Avalanche.org. American Avalanche Association. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- Pfeffer, W. T.; Mrugala, R. (2002). "Temperature gradient and initial snow density as controlling factors in the formation and structure of hard depth hoar". Journal of Glaciology. 48 (163): 485–494. doi:10.3189/S0022143000002008.
External links
- The Avalanche Encyclopedia, extensive summary with animation of formation process
