Abraham Bradley Jr.
Abraham Bradley Jr. | |
|---|---|
| Born | February 22, 1767 |
| Died | May 7, 1838 (aged 71) |
| Nationality | United States |
| Other names | Abraham Bradley IV |
| Alma mater | Litchfield Law School |
| Occupation | Assistant Postmaster General |
| Years active | 1793–1829 |
| Employer | Post Office Department |
| Spouse | Hannah Smith |
| Children | Joseph Habersham Bradley, son |
| Relatives | Phineas Bradley, brother |
| Signature | |
Abraham Bradley Jr. (February 22, 1767 – May 7, 1838) was an American lawyer, judge, and cartographer who was assistant postmaster general for 30 years during the earliest history of the United States Post Office Department. Bradley was responsible for moving the federal government's post office from Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, to the new capital at Washington, D.C., hosting the national post office in his own home for a period. The continuity brought by Bradley's long employment during the tenure of five different United States postmasters general helped establish the budding postal service as a reliable provider; Bradley drew detailed and innovative postal route maps which contributed significantly to the office's efficiency. Bradley's original work of 1796 was one of the first comprehensive maps of the United States as it existed, which "represented the first clear cartographic break in European-dominated map making and introduced a new, more distinctly American style of cartography to the United States."[1]
Early life
Born in Litchfield, Connecticut, Abraham Bradley was the fourth consecutive scion of the colonial family established by early Guilford, Connecticut, pioneer Stephen Bradley to bear the surname Abraham.[2] Abraham Bradley's father Abraham was himself a Yale College graduate who listed his various employments: "... a surveyor of land, master of a vessel, selectman, town treasurer, representative in the state legislature, justice of the peace, a zealous Whig, captain in the Revolutionary War, judge of the court, town clerk, and something of a scribbler in prose and verse."[3] The son Abraham Bradley showed promise as a student and graduated from the celebrated law school run by Litchfield attorney Tapping Reeve.[4]

Postal career
Bradley moved to the Wyoming Valley of frontier Pennsylvania in 1788 and established himself in private law practice. While briefly serving as a county judge in Wilkes-Barre, he made the acquaintance of local judge Timothy Pickering. Bradley accompanied him as a personal clerk when Pickering was appointed postmaster general by President George Washington and moved to Philadelphia in 1791.[5] Bradley was described by a contemporary as "an unassuming man, modest and retiring almost to diffidence, yet a lawyer of competent learning, with a clear and discriminating mind, and an industry that knew no relaxation when there was a duty to perform ..."[6]
Philadelphia
As one of his many responsibilities as clerk to the postmaster general, Bradley began to compile information for a complete postal service map, including routes, stations, and distances between each. Handicapped by his lack of training in the fields of topography and cartography, Bradley utilized cartographic knowledge imparted in earlier maps by Robert Erskine and Thomas Hutchins.[7] When Postmaster General Pickering was succeeded by Joseph Habersham in 1795, Bradley's postal route maps and voluminous knowledge of the department made him an irreplaceable figure.
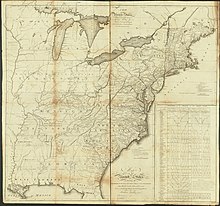
Map of 1796
In September 1796 Bradley published the first combined map of the post office stations, routes, and distances between. The map included a remarkable and innovative table that indicated times and days of the week to expect mail at various important postal coach stops along the primary eastern route. By this chart it could be determined that a letter posted in northernmost station at Brewer, Maine, could be expected to reach St. Marys, Georgia, in six weeks plus four days, 46 days of travel.[8] Bradley spent much of his career improving, expanding, and refining U.S. postal maps during the rapid westward expansion of America in the early 19th century. Appointed assistant postmaster general by Habersham in 1799, he would serve in the office until 1828.[7]
Washington, D.C.
In 1800, the seat of U.S. government was transferred from urban Philadelphia to the newly surveyed, mostly rural District of Columbia. Under Habersham, Bradley was assigned the task of moving the General Post Office Department files and furniture to a location in the nation's new capital.[9] Bradley acquired a three-story house at the northeast corner of 9th and E streets NW, installed his family in the top floor, Habersham's and his own offices on the second story, and the clerks' offices on the ground level.[10]
We have not been able to open the office and to accommodate business until to-day. I left Philadelphia Wednesday the 27th of May and arrived here on the evening of the 29th. The President [Adams] left Philadelphia the 26th and arrived at Georgetown the first of June. The situation of the city is extremely pleasant and it will probably become the greatest city in America ...
Bradley to Joseph Habersham, June 11, 1800[10]
Bradley found property rents and prices in Washington, D.C., unnecessarily high, roughly 500 houses scattered over a ten square mile tract, but believed the scale of the enterprise guaranteed the new capital's success.[10] Bradley invited his brother, Wilkes-Barre physician Phineas Bradley, to join him in bringing his family to the budding village, soon to be a thriving seat of government; Phineas became one of Washington's first town councilmen. In 1802, Bradley and his wife Hannah had a son they would name Joseph Habersham Bradley after the Georgia postmaster and family friend.[9]

Map of 1804
As a Federalist, Bradley desired the re-election of John Adams in 1800;[11] the new president, Thomas Jefferson, appointed Gideon Granger to the office of postmaster general. Granger kept the sober and reliable Bradley as his assistant. By the time of the purchase of Louisiana in 1803, the old postal road map was vastly outdated, and with the assistance of British cartographer Aaron Arrowsmith, Bradley prepared a new map, published in 1804.[12] The 1804 map, produced in color, reflected the enormous changes the service and the country had undergone in the eight years between the two maps' creation. The Ohio Country and the Louisiana and Mississippi territories were well marked, and the postal routes of the new states of Kentucky and Tennessee fully developed. Like the original 1796 version, copies of this map were printed and distributed to be displayed in every large post office in the United States.[8]
Bradley continued to create maps during Postmaster General Granger's tenure, publishing a significant revision in 1810, but the War of 1812 made reliable mail delivery a much more hazardous enterprise. Return J. Meigs Jr., former governor of Ohio, was appointed to replace the retiring Granger in March 1814; again the incoming postmaster general kept the first assistant. As the wartime threat to Washington, D.C., grew, Bradley began looking for a farm away from the city where he and his wife could raise their children; in 1814 Bradley acquired a 218-acre (0.88 km2) farm in Montgomery County, Maryland near the tiny community of Chevy Chase. During the burning of Washington in 1814, many of the postal records and a few public officials were transferred for safety to the Bradley farmhouse, ten miles (16 km) north of the White House.[13]

Map of 1825
In 1823, Meigs was in ill health, and was replaced by John McLean, also from Ohio. McLean, who was later to become an associate justice of the United States Supreme Court, proved an industrious and creative postmaster general. McLean, like his predecessors, kept Bradley as his chief assistant. Bradley and his brother Dr. Phineas Bradley managed an office of thirty postal clerks and serviced several thousand local post offices.
By 1825, the map Bradley had assembled included postal routes in the newly acquired states of Arkansas, Illinois, and Missouri, while still providing accurate cartographic information on areas such as Michigan, Minnesota, and Wisconsin territories. The completed map measured roughly four feet high and five feet wide, and included an inset map depicting the known extent of the North American continent.
In the election of 1828, Bradley and his brother supported the incumbent president, John Quincy Adams, but when Andrew Jackson was elected instead, Jackson partisans called for the ouster of Bradley. Jackson seems to have viewed the Bradley brothers as being corrupted by their high government salaries and their unique positions to decide the winners of lucrative mail contracts.[14] First Abraham, then brother Phineas were removed from their positions in 1829, months after Jackson's inauguration.[15]
Legacy
After his removal, Bradley made no attempt to defend himself from partisan attack, but he did make several public communications pointing out what were in his view defective actions by the new administration in regards to postal service. Bradley became for a time secretary of the Franklin Insurance Company. When Abraham Bradley died in his home in Washington, D.C., May 7, 1838,[5] he left eight children, including lawyer Joseph H. Bradley, best known for his successful defense of John Surratt, accused of attempting to assassinate Abraham Lincoln. The younger Bradley inherited the Chevy Chase farm and himself had a namesake son, also a Washington, D.C., attorney who assisted the Surratt defense team.
Bradley's service to the country as assistant postmaster general is regarded as influential.[11] Bradley's postal routes and schedules, enforced rigidly over a thirty-year period, gave the Post Office Department a rapid and reliable engine for delivering information across vast distances, instilling in citizens the importance of the connectedness they shared with their distant neighbors. The numerous maps Bradley published, while later discarded and redrawn by the new Jackson administration, created in their time a sense of the immensity of American territory.[8]
References
- ^ Ristow, Walter W. (1985). American maps and mapmakers - Commercial Cartography in the nineteenth century quoted in Smith, Ben A.; Vining, James W. (2003). American Geographers, 1784-1812: a bio-bibliographical guide. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 23. ISBN 0-313-32336-4. Retrieved June 8, 2009.
- ^ Colonial Dames of America (1910). Ancestral records and portraits. Vol. 1. New York: Grafton Press. p. 256. Retrieved June 11, 2009.
- ^ Bradley, Charles S.; Columbia Historical Society (1903) [May 12, 1902]. "The Bradley Family and Times in Which They Lived". Records of the Columbia Historical Society, Washington, D.C. Vol. 6. Washington, D.C.: Columbia Historical Society. Retrieved June 8, 2009.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help), p. 124 - ^ Kulp, George Brubaker (1890). Families of the Wyoming Valley: Biographical, Genealogical and Historical. Sketches of the Bench and Bar of Luzerne County, Pennsylvania. Vol. 3. Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania: E.B. Yordy, Printer. p. 1053.
- ^ a b Pickering, Octavius; Upham, Charles Wentworth (1873). The Life of Timothy Pickering. Vol. 2. Boston, Massachusetts: Little, Brown, and Company. p. 507. Retrieved June 8, 2009.
- ^ Bradley, The Bradley Family ..., p. 130
- ^ a b Ernst, C.W. (January 1897). "A Postal Centenary". In Victory, John F. (ed.). The Postal Record. Vol. 10, no. 1. Washington, D.C.: National Association of Letter Carriers. p. 11. Retrieved June 8, 2009.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Pope, Nancy A. "Bradley Postal Map". National Postal Museum. Washington, D.C.: Smithsonian Institution. Retrieved October 16, 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Bradley, The Bradley Family ..., p. 131
- ^ a b c Bradley, The Bradley Family ..., p. 132
- ^ a b John, Richard R. (1998) [1995]. "3, Completing the Network". Spreading the News: The American Postal System from Franklin to Morse. Cambridge, Massachusetts: Harvard University Press. ISBN 0-674-83342-2. Retrieved June 17, 2009.
{{cite book}}: External link in|chapterurl=|chapterurl=ignored (|chapter-url=suggested) (help), p. 71 - ^ Ristow & Smith and Vining 1985, p. 24.
- ^ Bradley, The Bradley Family ..., p. 133
- ^ Jackson, Andrew (2007). Feller, Daniel; Moser, Harold D.; Moss, Laura-Eve; Coens, Thomas (eds.). The papers of Andrew Jackson. Vol. 7, 1829. University of Tennessee Press. p. 456. ISBN 1-57233-593-9. Retrieved June 8, 2009.
- ^ United States Congress (1834). Gales, Joseph; Seaton, William Winston (eds.). Register of Debates in Congress: Comprising the Leading Debates and Incidents of the Second Session of the Eighteenth Congress: Dec. 6, 1824, to the First Session of the Twenty-fifth Congress, Oct. 16, 1837. Vol. 10. Gales & Seaton. p. 232. Retrieved June 8, 2009.
