Ammonium thiocyanate
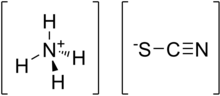
| |||
| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|||
| ChEBI | |||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.015.614 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
| RTECS number |
| ||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
| NH4SCN | |||
| Molar mass | 76.122 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | Colorless hygroscopic crystalline solid | ||
| Density | 1.305 g/cm3 | ||
| Melting point | 149.5 °C (301.1 °F; 422.6 K) | ||
| Boiling point | 170 °C (338 °F; 443 K) (decomposes) | ||
| 128 g/100 mL (0 °C) | |||
| Solubility | soluble in liquid ammonia, alcohol, acetone | ||
| -48.1·10−6 cm3/mol | |||
| Hazards | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | External MSDS | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |||
Ammonium thiocyanate is an inorganic compound with the formula NH4SCN. It is the salt of the ammonium cation and the thiocyanate anion.
Uses
Ammonium thiocyanate is used in the manufacture of herbicides, thiourea, and transparent artificial resins; in matches; as a stabilizing agent in photography; in various rustproofing compositions; as an adjuvant in textile dyeing and printing; as a tracer in oil fields; in the separation of hafnium from zirconium, and in titrimetric analyses.
Ammonium thiocyanate can also be used to determine the iron content in soft drinks by colorimetry.
Preparation
Ammonium thiocyanate is made by the reaction of carbon disulfide with aqueous ammonia. Ammonium dithiocarbamate is formed as an intermediate in this reaction, which upon heating, decomposes to ammonium thiocyanate and hydrogen sulfide:
- CS2 + 2 NH3(aq) → NH2C(=S)SNH4 → NH4SCN + H2S
Reactions
Ammonium thiocyanate is stable in air; however, upon heating it isomerizes to thiourea:
The equilibrium mixtures at 150 °C and 180 °C contain 30.3% and 25.3% (by weight) thiourea, respectively. When heated at 200 °C, the dry powder decomposes to ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, and carbon disulfide, leaving a residue of guanidinium thiocyanate.
NH4SCN is weakly acidic; reacts with caustic soda or caustic potash to form sodium thiocyanate or potassium thiocyanate. It reacts with ferric salts to form a deep-red ferric thiocyanate complex:
- 6 SCN− + Fe3+ → [Fe(SCN)6]3−
Ammonium thiocyanate reacts with several metal ions including copper, silver, zinc, lead, and mercury, forming their thiocyanate precipitates, which may be extracted into organic solvents.
References
- A. F. Wells, Structural Inorganic Chemistry, 5th ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford, UK, 1984. ISBN 978-0198553700




