Arytenoid muscle
| Arytenoid muscle | |
|---|---|
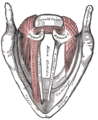
 Muscles of larynx. Posterior view. Oblique arytenoid: The "X" in the center. Transverse arytenoid: Bands underneath the "X". Aryepiglotticus: Wraps around back. | |
 | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Arytenoid cartilage on one side |
| Insertion | Arytenoid cartilage on opposite side |
| Artery | superior laryngeal artery |
| Nerve | recurrent laryngeal branch of the vagus |
| Actions | approximate the arytenoid cartilages (close rima glottis) |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus arytaenoideus |
| TA98 | A06.2.08.012 A06.2.08.010 |
| TA2 | 2203, 2205 |
| FMA | 46582 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The arytenoid /ær[invalid input: 'ɨ']ˈtiːnɔɪd/ is a single muscle, filling up the posterior concave surfaces of the arytenoid cartilages.
It arises from the posterior surface and lateral border of one arytenoid cartilage, and is inserted into the corresponding parts of the opposite cartilage.
It consists of oblique and transverse parts.
Action
The Arytœnoideus approximates the arytenoid cartilages, and thus closes the opening of the glottis, especially at its back part to eliminate the posterior commissure of the vocal folds.
Additional images
-
The cartilages of the larynx. Posterior view.
-
Muscles of larynx. Side view. Right lamina of thyroid cartilage removed.
-
Aryepiglotic muscle
-
Muscles of the larynx, seen from above.
-
Dissection of the muscles of the palate from behind.
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1082 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1082 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)