Bibenzyl
Appearance
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1,1'-(Ethane-1,2-diyl)dibenzene | |
| Other names
1,2-Diphenylethane
Dibenzil Dibenzyl Dihydrostilbene sym-Diphenylethane | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.816 |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C14H14 | |
| Molar mass | 182.266 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Crystalline solid[1] |
| Density | 0.9782 g/cm3[1] |
| Melting point | 52.0 to 52.5 °C (125.6 to 126.5 °F; 325.1 to 325.6 K)[1] |
| Boiling point | 284 °C (543 °F; 557 K)[1] |
| Insoluble | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
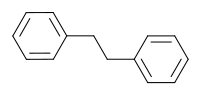
Bibenzyl (1,2-diphenylethane) is an aromatic chemical compound that can be considered a derivative of ethane in which one phenyl group is attached to each carbon atom.
Natural occurrences
Bibenzyl forms the central core of some natural products like dihydrostilbenoids[2] and isoquinoline alkaloids.
See also
References
- ^ a b c d The Merck Index, 11th Edition, 1219
- ^ John Gorham; Motoo Tori; Yoshinori Asakawa (1995). The biochemistry of the stilbenoids. Springer. ISBN 0-412-55070-9.
