Brazil-nut poison frog
| Brazil-nut poison frog | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Amphibia |
| Order: | Anura |
| Family: | Dendrobatidae |
| Genus: | Adelphobates |
| Species: | A. castaneoticus
|
| Binomial name | |
| Adelphobates castaneoticus | |
| |
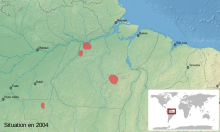
| Distribution of the Brazil-nut poison frog | |
| Synonyms[3] | |
|
Dendrobates castaneoticus Caldwell and Myers, 1990[2] | |
The Brazil-nut poison frog (Adelphobates castaneoticus) is a species of frog in the family Dendrobatidae. It is endemic to the state of Pará in Brazil.[3] The frog is believed to have received its common name from the fact that its tadpoles sometimes develop in the hard capsules of the Brazil nut tree, which are common in its range. The nuts fall to the forest floor where they are broken open by agoutis and other animals seeking the seeds, and empty husks fill with water.[4]
Description
The Brazil-nut poison frog is a very small frog with a snout-to-vent length of 18 to 23 mm (0.7 to 0.9 in); females are usually larger than males. The dorsal surface is of a shiny black colour with spots and markings of white or various shades of yellow.[5] There is a bright yellow or orange spot where the foreleg joins the body and two more similarly coloured spots on either side of the knee joint on the hind leg, which combine to make a single large spot when the animal is stationary. A further spot on the underside of the calf is only visible from below.[4]
Distribution
The Brazil-nut poison frog is endemic to the rainforest of central Brazil. It is known from several localities in the state of Pará; from Cachoeira Juruá, Xingu River, the type locality; from Taperinha some 300 km (186 mi) to the north west;[5] and from Flona Tapajos, Santarém. These locations are some distance apart and it is likely that this frog has a more widespread distribution than is known but has passed undetected in other parts of its range.[1] It lives among the leaf litter on the forest floor and sometimes climbs into low vegetation.[4]
Biology
The Brazil-nut poison frog is diurnal and feeds on ants, termites and other small invertebrates.[6] The eggs are laid on the ground where they are guarded by the male. When they hatch, it carries the tadpoles to temporary pools such as water holes in trees and stumps, and water-filled empty nut cases on the forest floor.[4] Here the tadpoles develop rapidly, devouring mosquito larvae, smaller tadpoles, and other creatures that share these ephemeral pools, as well as suitably-sized plant material. This frog may become sexually mature in five to seven months.[4]
Status
The Brazil-nut poison frog is common within its range and the population trend seems stable, although data on its conservation status is somehow insufficient.[5] As a result, the IUCN lists its conservation status as being of "least concern".[6] The main threats it faces are logging, habitat destruction, wildfire and collection of animals to be sold as pets on an international market. There are some conservation areas within its range.[1][4]
References
- ^ a b c Rodrigues, Miguel Trefaut; Azevedo-Ramos, Claudia (2004). "Adelphobates castaneoticus". The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2004. IUCN: e.T55179A11252315. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2004.RLTS.T55179A11252315.en. Retrieved 3 January 2018.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Caldwell, Janalee P.; Myers, Charles W. (1990). "A new poison frog from Amazonian Brazil, with further revision of the quinquevittatus group of Dendrobates". American Museum Novitates. 2988: 1–21.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Frost, Darrel R. (2018). "Adelphobates castaneoticus (Caldwell and Myers, 1990)". Amphibian Species of the World: an Online Reference. Version 6.0. American Museum of Natural History. Retrieved 2 October 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f KU Herpetology Class (2005-01-13). "Adelphobates castaneoticus". AmphibiaWeb. Retrieved 2014-06-29.
- ^ a b c Lima, Amanda; Gallati, Ulisses (24 February 2011). "Amphibia, Anura, Dendrobatidae, Adelphobates castaneoticus (Caldwell and Myers 1990): distribution extension and geographic distribution map" (PDF). Herpetology Notes. 4: 93–94. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Dendrobatidae - Poison Frogs". NHPT. New Hampshire Public Television. Archived from the original on 14 July 2014. Retrieved 6 July 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
External links
![]() Data related to Adelphobates castaneoticus at Wikispecies
Data related to Adelphobates castaneoticus at Wikispecies

