Cystohepatic triangle
| Cystohepatic triangle | |
|---|---|
 The cystic artery branches from the right hepatic artery. | |
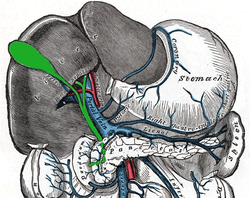 Relationship to other vessels. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | trigonum cystohepaticum |
| TA98 | A10.1.02.428 |
| TA2 | 3756 |
| FMA | 24230 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The hepatobiliary triangle (or cystohepatic triangle) is an anatomic space bordered by the common hepatic duct medially, the cystic duct laterally and inferior border of liver /cystic artery superiorly.[1]
Eponym
Another name used to refer to this region is Calot's Triangle. It is named for Jean-François Calot.[2][3] Of note, Calot's original description of the triangle in 1891 included the cystic duct, the common hepatic duct, and the cystic artery (not the inferior border of the liver as is commonly believed).[4] The Hepatocystic triangle is the area bound by the cystic duct, common hepatic duct, and the liver margin.[5]
Clinical significance
General surgeons frequently quiz medical students on this term and the name for the lymph node located within the triangle, Mascagni's lymph node or Lund's node, however many often erroneously refer to it as "Calot's node." The latter is frequently enlarged due to inflammation of the gallbladder (e.g. cholecystitis) or the biliary tract (e.g. cholangitis) and may be removed along with the gallbladder during surgical treatment (cholecystectomy).
Calot's triangle, containing the cystic artery, may also contain an accessory right hepatic artery or anomalous sectoral bile ducts. As a result dissection in the triangle of Calot is ill-advised until the lateral-most structures have been cleared and identification of the cystic duct is definitive. According to SESAP 12 (produced and distributed by the American College of Surgeons) dissection in the triangle of Calot is the most common cause of common bile duct injuries.
References
- ^ Haubrich, W (November 2002). "Calot of the triangle of Calot". Gastroenterology. 123 (5): 1440. doi:10.1053/gast.2002.1231440. PMID 12404217.
- ^ synd/4023 at Who Named It?
- ^ J. F. Calot. De la cholécystectomie. Doctoral thesis, Paris, 1891.
- ^ Haubrich WS (2002). "Calot of the triangle of Calot". Gastroenterology. 123 (5): 1440. doi:10.1053/gast.2002.1231440. PMID 12404217.
- ^ Schwartz's Manual of Surgery BRUNICARDI C.F 10th edition
6. Bailey & Love's Short Practice of Surgery 26th edition (see page 1098).
