Diphosphine ligands

Diphosphines, sometimes called bisphosphanes, are organophosphorus compounds most commonly used as bidentate phosphine ligands in inorganic and organometallic chemistry. They are identified by the presence of two phosphino groups linked by a backbone, and are usually chelating.[1] A wide variety of diphosphines have been synthesized with different linkers and R-groups. Alteration of the linker and R-groups alters the electronic and steric properties of the ligands which can result in different coordination geometries and catalytic behavior in homogeneous catalysts.
Synthesis

From phosphide building blocks

Many widely used diphosphine ligands have the general formula Ar2P(CH2)nPAr2. These compounds can be prepared from the reaction of X(CH2)nX (X=halogen) and MPPh2 (M = alkali metal):[2]
- Cl(CH2)nCl + 2 NaPPh2 → Ph2P(CH2)nPPh2 + 2 NaCl
Diphosphine ligands can also be prepared from dilithiated reagents and chlorophosphines:[3]
- XLi2 + 2 ClPAr2 → X(PAr2)2 + 2 LiCl (X = hydrocarbon backbone)
This approach is suitable for installing two dialkylphosphino groups, using reagents such as chlorodiisopropylphosphine.
Another popular method, suitable for preparing unsymmetrical diphosphines, involves the addition of secondary phosphines to vinylphosphines:
- Ph2PH + 2 CH2=CHPAr2 → Ph2PCH2-CH2PAr2
(2-Lithiophenyl)diphenylphosphine can be used also to give unsymmetrical diphosphines. The lithiated reagent is available from (2-bromophenyl)diphenylphosphine:
- Ph2P(C6H4Br) + BuLi → Ph2P(C6H4Li) + BuBr
- Ph2P(C6H4Li) + R2PCli → Ph2P(C6H4PR2) + LiCl
From bis(dichlorophosphine) precursors
Many diphosphines are prepared from compounds of the type X(PCl2)2 where X = (CH2)n or C6H4. The key reagents are 1,2-bis(dichlorophosphino)ethane and 1,2-bis(dichlorophosphino)benzene.

Chain length and coordinating properties
The short-chain diphosphine dppm tends to promote metal-metal interactions as illustrated by A-frame complexes. When the two phosphine substituents are linked by two to four carbon centres, the resulting ligands often chelate rings with a single metal. A common diphosphine ligand is dppe, which forms a five-membered chelate ring with most metals.
Some diphosphines, such as the extraordinary case of tBu2P(CH2)10PtBu2, give macrocyclic complexes with as many as 72 atoms in a ring.[6]
To position phosphine donor groups trans on a coordination sphere, several atoms are required to link the donor centres and long-chain diphosphines are typically floppy and do not chelate well. This challenge has been resolved by the long but rigid diphosphine SPANphos.[7] The bite angle of the diphosphine influences the reactivity of the metal center.[8]
Some examples of non-chelating diphosphine also exist. Due to steric effect, these phosphorus atoms can not react with anything except a proton. [9] It can be changed from non-chelating to chelating diphosphine by tuning the length of the linking arm.[10]
Representative ligands
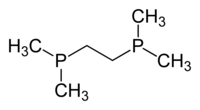
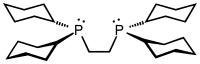
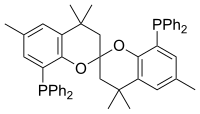
Particularly common diphosphine ligands are shown in the table below:[11]
See also
Dialkylbiaryl phosphine ligands
References
- ^ Hartwig, J. F. Organotransition Metal Chemistry, from Bonding to Catalysis; University Science Books: New York, 2010. ISBN 189138953X
- ^ Wilkinson, G.; Gillard, R.; McCleverty, J. Comprehensive Coordination Chemistry: The synthesis, reactions, properties & applications of coordination compounds, vol.2.; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1987; p. 993. ISBN 0-08-035945-0
- ^ Gareth J. Rowlands "Planar Chiral Phosphines Derived from [2.2]Paracyclophane" Israel Journal of Chemistry 2012, Volume 52, Issue 1-2, pages 60–75.doi:10.1002/ijch.201100098
- ^ Burt, Roger J.; Chatt, Joseph; Hussain, Wasif; Leigh, G.Jeffery (1979). "A convenient synthesis of 1,2-bis(dichlorophosphino)ethane, 1,2-bis(dimethylphosphino)ethane and 1,2-bis(diethylphosphino)ethane". Journal of Organometallic Chemistry. 182 (2): 203–206. doi:10.1016/S0022-328X(00)94383-3.
- ^ Moloy, Kenneth G.; Petersen, Jeffrey L. (1995). "N-Pyrrolyl Phosphines: An Unexploited Class of Phosphine Ligands with Exceptional .pi.-Acceptor Character". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 117 (29): 7696–7710. doi:10.1021/ja00134a014.
- ^ Cotton, F.A.; Wilkinson, G. Advanced Inorganic Chemistry: A Comprehensive Text, 4th ed.; Wiley-Interscience Publications: New York, NY, 1980; p.246. ISBN 0-471-02775-8
- ^ Z. Freixa, M. S. Beentjes, G. D. Batema, C. B. Dieleman, G. P. F. v. Strijdonck, J. N. H. Reek, P. C. J. Kamer, J. Fraanje, K. Goubitz and P. W. N. M. Van Leeuwen (2003). "SPANphos: A C2-Symmetric trans-Coordinating Diphosphane Ligand". Angewandte Chemie. 42 (11): 1322–1325. doi:10.1002/anie.200390330. PMID 12645065.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Birkholz, M.-N., Freixa, Z., van Leeuwen, P. W. N. M., "Bite angle effects of diphosphines in C-C and C-X bond forming cross coupling reactions", Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, vol. 38, 1099.
- ^ Zong, J., J. T. Mague, C. M. Kraml, and R. A. Pascal, Jr., A Congested in,in-Diphosphine, Org. Lett. 2013, 15, 2179-2181.
- ^ Zong, J., J. T. Mague, and R. A. Pascal, Jr., "Encapsulation of non-hydrogen atoms by in, in-bis (triarylelement)-containing cyclophanes." Tetrahedron, 2017, 73, 455-460.
- ^ http://old.iupac.org/reports/provisional/abstract04/RB-prs310804/TableVII-3.04.pdf [bare URL PDF]
















![General Josiphos ligand[3]](http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/commons/thumb/6/63/Josiphos.png/200px-Josiphos.png)
