Evening grosbeak
| Evening grosbeak | |
|---|---|

| |
| Male evening grosbeak in Cap Tourmente National Wildlife Area, Quebec | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Genus: | Bonaparte, 1850
|
| Species: | H. vespertina
|
| Binomial name | |
| Hesperiphona vespertina (W. Cooper, 1825)
| |
| |
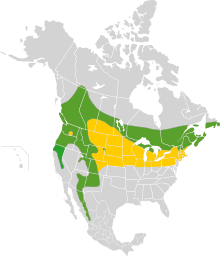
| Range of H. vespertina Year-round range Wintering range
| |
| Synonyms | |
|
Coccothraustes vespertinus | |
The evening grosbeak (Hesperiphona vespertina) is a passerine bird in the finch family Fringillidae found in North America.
Description
The evening grosbeak is similar in appearance to the Eurasian hawfinch, both being bulky, heavily built finches with large bills and short tails. The evening grosbeak ranges in length from 16 to 22 cm (6.3 to 8.7 in) and spans 30 to 36 cm (12 to 14 in) across the wings.[2][3] In a large sampling of grosbeaks in Pennsylvania during winter, males weighed from 38.7 to 86.1 g (1.37 to 3.04 oz), with an average of 60 g (2.1 oz), while females weighed from 43.2 to 73.5 g (1.52 to 2.59 oz), with an average of 58.7 g (2.07 oz).[4] Among standard measurements, the wing chord is 10.45 to 11.6 cm (4.11 to 4.57 in), the tail is 6 to 6.95 cm (2.36 to 2.74 in), the bill is 1.6 to 2 cm (0.63 to 0.79 in) and the tarsus is 1.95 to 2.2 cm (0.77 to 0.87 in).[5] The adult has a short black tail, black wings and a large pale bill. The adult male has a bright yellow forehead and body; its head is brown and there is a large white patch in the wing. The adult female is mainly olive-brown, greyer on the underparts and with white patches in the wings.
Breeding and ecology
The breeding habitat is coniferous and mixed forest across Canada and the western mountainous areas of the United States and Mexico. It is an extremely rare vagrant to the British Isles, with just two records so far. The nest is built on a horizontal branch or in a fork of a tree.
The migration of this bird is variable; in some winters, it may wander as far south as the southern U.S.
These birds forage in trees and bushes, sometimes on the ground. They mainly eat seeds, berries, and insects. Outside of the nesting season they often feed in flocks. Sometimes, they will swallow fine gravel.
The range of this bird has expanded far to the east in historical times, possibly due to plantings of Manitoba maples and other maples and shrubs around farms and the availability of bird feeders in winter.
Taxonomy
The International Ornithologists' Union places the evening grosbeak in the genus Hesperiphona.[6] The species together with the hooded grosbeak are sometimes placed together with the hawfinch in the genus Coccothraustes.[7] The name of the genus Hesperiphona was introduced by Charles Lucien Bonaparte in 1850.[8]
Gallery
-
Female evening grosbeak in Algonquin Provincial Park, Ontario, Canada
-
Male evening grosbeak in Truchas, New Mexico
-
Female in winter, Gatineau Park, Quebec, Canada
-
Feeding on sunflower seeds
References
- ^ Template:IUCN
- ^ "Evening grosbeak". All About Birds. Cornell Lab of Ornithology.
- ^ "Evening grosbeak". Guide to North American Birds. National Audubon Society.
- ^ Dunning, John B., Jr., ed. (1992). CRC Handbook of Avian Body Masses. CRC Press. ISBN 978-0-8493-4258-5.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: editors list (link) - ^ Clement, Peter (1999). Finches and Sparrows. Princeton University Press. ISBN 978-0691048789.
- ^ Gill, Frank; Donsker, David (eds.). "Finches, euphonias". World Bird List Version 5.2. International Ornithologists' Union. doi:10.14344/IOC.ML.5.2. Retrieved 5 June 2015.
- ^ Clements, J.F.; Schulenberg, T.S.; Iliff, M.J.; Roberson, D.; Fredericks, T.A.; Sullivan, B.L.; Wood, C.L. (2014). "eBird/Clements checklist of birds of the world: Version 6.9". The Cornell Lab of Ornithology. Retrieved 23 June 2015.
- ^ Bonaparte, Charles Lucien. "Sur plusieurs genres nouveaux de Passereaux". Comptes rendus hebdomadaires des séances de l'Académie des sciences (in French). 31: 424.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|trans_title=ignored (|trans-title=suggested) (help)
External links
- Evening Grosbeak - Coccothraustes vespertinus - USGS Patuxent Bird Identification InfoCenter
- BirdLife species factsheet for Coccothraustes vespertinus
- "Hesperiphona vespertina". Avibase.
- "Evening grosbeak media". Internet Bird Collection.
- Evening grosbeak photo gallery at VIREO (Drexel University)
- Evening grosbeak species account at Neotropical Birds (Cornell Lab of Ornithology)
- Interactive range map of Coccothraustes vespertinus at IUCN Red List maps
- Audio recordings of Evening grosbeak on Xeno-canto.
- Hesperiphona vespertina in Field Guide: Birds of the World on Flickr
- Evening grosbeak media from ARKive




