Geomagnetic Field Monitoring Program of SUPARCO
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these template messages)
|
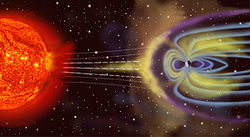
The Geomagnetic Field Monitoring Program,[1] is a scientific mission of the Space and Upper Atmosphere Research Commission of Pakistan (SUPARCO) to undertake research in geophysics, particularly geomagnetism.[1] The objective of the mission is to provide better understanding of the Earth's magnetic field, and of associated hazard mitigation. [1] The program monitors mathematical variation in the South Asian regional geomagnetic field.[1] Research is conducted in specially established geomagnetic observatories in Islamabad and Karachi. Data collected provides the basis for continuous studies of Earth's magnetic field, and is made available to various national and international institutions.[1]
The program was established in 1983 at the Sonmiani space facility. The second geomagnetic observatory was established in 2008.[2] Suparco regularly releases a public domain bulletin of geomagnetic data to national and international users, [1][3] containing research on the effects of solar flares and severe magnetic storms recorded by the observatories.[1]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g SUPARCO. "Geomagnetic Field Monitoring Program". Geomagnetic Field Monitoring Program. Geomagnetic Field Monitoring Program. Retrieved 30 September 2012.
- ^ "Workshop On Geomagnetic Observatories and their Applications". Geomagnetic Observatories and their Applications. Retrieved 30 September 2012.
- ^ SUPARCO. "Geomagnetic Field Monitoring". Retrieved 30 September 2012.
External links
- "Space Research in Pakistan 2006-2007" (PDF). Cospar-Suparco report. Cospar-Suparco report. pp. 17–20. Retrieved 30 September 2012.
- "2008-2009 Space Research in Pakistan" (PDF). SUPARCO. Cospar-Suparco 38h Paper report. pp. 10–11. Retrieved 30 September 2012.
