Hemiazygos vein
| Hemiazygos vein | |
|---|---|
 Diagram showing completion of development of the parietal veins. (Hemiazygos vein visible at center-left.) | |
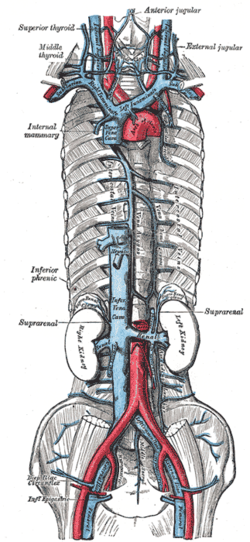 The venæ cavæ and azygos veins, with their tributaries. | |
| Details | |
| Precursor | Left supracardinal vein[1] |
| Drains to | Azygos vein |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vena hemiazygos |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The hemiazygos vein (vena azygos minor inferior) is a vein running superiorly in the lower thoracic region, just to the left side of the vertebral column.
Structure
[edit]The hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein, when taken together, essentially serve as the left-sided equivalent of the azygos vein.[2] That is, the azygos vein serves to drain most of the posterior intercostal veins on the right side of the body, and the hemiazygos vein and the accessory hemiazygos vein drain most of the posterior intercostal veins on the left side of the body.[2] Specifically, the hemiazygos vein mirrors the bottom part of the azygos vein.
The structure of the hemiazygos vein is often variable. It usually begins in the left ascending lumbar vein or renal vein, and passes upward through the left crus of the diaphragm to enter the thorax. It continues ascending on the left side of the vertebral column, and around the level of the ninth thoracic vertebra, it passes rightward across the column, behind the aorta, esophagus, and thoracic duct, to end in the azygos vein.[2][3]
It receives the 9th, 10th, and 11th posterior intercostal veins and the subcostal vein of the left side, and some esophageal and mediastinal veins.
Variations
[edit]The hemiazygos may or may not be continuous superiorly with the accessory hemiazygos vein.[4]
Clinical significance
[edit]The dilated hemiazygos system displayed by chest or abdominal X-ray films can be misdiagnosed as a mediastinal or retroperitoneal neoplasm, lymphadenopathy or aortic dissection (2, 5–7, 10). Venostasis which is the consequence of pathological conditions such as acquired obstruction of the IVC or SVC, the right heart failure, portal hypertension or due to pregnancy can have the same clinical presentation as hemiazygos continuation of the IVC (5, 6, 10, 13). In the case of hemiazygos continuation of the IVC, the hepatic veins can drain directly into the right atrium (3, 10). An incidental finding of this condition during venous cannulation for cardiopulmonary bypass complicates the procedure, since no solid IVC trunk for placing the cannula is present. Separate cannulation of the SVC and the right atrium should be used in this case.[5]
History
[edit]The name for this vein is derived from that of the azygos vein. Azygos means 'unpaired', and hemi means half. This vein mirrors the bottom half of the azygos vein.
References
[edit]![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 667 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 667 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Edward Lamperti; Michael Schuenke; Erik Schulte; Udo Schumacher; Ross, Lawrence J. (2006). General Anatomy and Musculoskeletal System (Thieme Atlas of Anatomy). Thieme Publishing Group. p. 13. ISBN 3-13-142081-2.
- ^ a b c Rakovich, George; Fréchette, Éric; Deslauriers, Jean (2010-01-01), Lewis, Michael I.; McKenna, Robert J.; Falk, Jeremy A.; Chaux, George E. (eds.), "8 - Thoracic Surgical Anatomy and Procedures", Medical Management of the Thoracic Surgery Patient, Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders, pp. 95–105, doi:10.1016/b978-1-4160-3993-8.00008-8, ISBN 978-1-4160-3993-8, retrieved 2020-11-12
- ^ Akoum, Nazem; Hermsen, Joshua (2018-01-01), Poole, Jeanne E.; Larson, Lyle W. (eds.), "9 - Considerations for Novel or Alternative Lead Placement", Surgical Implantation of Cardiac Rhythm Devices, Elsevier, pp. 173–180, doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-40126-5.00009-4, ISBN 978-0-323-40126-5, retrieved 2020-11-12
- ^ Satei, Alexander; Dhaliwal, Sampreet; Tsibulski, Alexander; Allen, Leslie (November 2022). "Two concurrently occurring rare anatomic variants of the accessory hemiazygos vein". Eurorad. doi:10.35100/eurorad/case.17915. Retrieved 2022-11-11.
- ^ TRUBAâ R1. & HRIBERNIK M2. PÁâ L1 (December 2002). "CONGENITAL INTERRUPTION OF THE INFERIOR VENA CAVA WITH HEMIAZYGOS CONTINUATION" (PDF). Med. Department of Anatomy, Faculty of Medicine, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic &Institute of Anatomy, Medical Faculty, University of Ljubljana, Ljubljana, Slovenia. Retrieved 2018-07-09.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link)
External links
[edit]- thoraxlesson5 at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (postmediastinumlevel5)
- Anatomy photo:21:12-0200 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center - "Mediastinum: The Azygos Vein and Posterior Intercostal Veins"
- figures/chapter_24/24-2.HTM: Basic Human Anatomy at Dartmouth Medical School
